Abstract
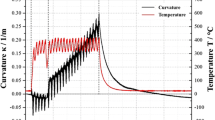
In this article, molybdenum particles were plasma sprayed on copper, zirconia, and glass substrates. The impact of the molten particles was monitored using a fast two-color optical fiber pyrometer focused on a small spot on the substrate surface. The apparent duration of the flattening process and the cooling speed, both determined from the pyrometer signals, were found to depend on the substrate conditions and to vary with coating thickness. The substrate material and its roughness were also found to influence the texture in the sprayed coatings. Furthermore, a transient thermal flow numerical model was used to compute reliable thermal histories of the impinging particles and the underlying lamellae, the interfacial thermal resistance being determined by comparison of experimental thermograms with computed ones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Moreau, M. Lamontagne, and P. Cielo, Influence of the Coating Thickness on the Cooling Rate of Plasma-Sprayed Particles Impinging on a Substrate,Surf. Coat. Technol., Vol 53, 1992, p 107–114; andThermal Spray Coatings: Properties, Processes and Applications, T.F. Bernecki, Ed., ASM International, 1992, p 237–243.
J. Madejski, Solidification of Droplets on a Cold Substrate,Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, Vol 19,1976, p 1009–1013.
J. Madejski, Droplets on Impact with a Solid Surface,Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, Vol 26 (No. 7), 1983, p 1095–1098.
A.I. Fedorchenko and O.P. Solonenko, Dynamics of Crystallization Processes of Molten Particles at Their Interaction with Surface,Plasma Jets,O.P. Solonenko and A.I. Fedorchenko, Ed., VSP, 1990, p 283-297.
C. Moreau, P. Cielo, M. Lamontagne, S. Dallaire, and M. Vardelle, Impacting Particle Temperature Monitoring During Plasma Spray Deposition,Meas. Sci. Technol., Vol 1,1990, p 807–814.
M. Vardelle, A. Vardelle, P. Fauchais, and M.I. Boulos, Plasma-Particle Momentum and Heat Transfer: Modelling and Measurements,AlChEJ., Vol 29 (No. 2), 1983, p 236–243.
J.R. Fincke and W.D. Swank, Simultaneous Measurement of Ni-Al Particle Size, Velocity, and Temperature in Atmospheric Thermal Plasmas,Thermal Spray Research and Applications, T.F. Bernecki, Ed., ASM International, 1991, p 39-43.
C.S. Barrett and T.B. Massalski,Structure of Metals, 3rd ed., Pergamon Press, 1980, p 536.
S. Sampath and H. Herman, Microstructural Development of Plasma Sprayed Coatings,Proc. 12th Int. Conf. Thermal Spraying, I.A. Bucklow, Ed., The Welding Institute, London, 1989, p 53–1 to 53-10.
R. McPherson, A Model for the Thermal Conductivity of Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic Coatings,Thin Solid Films, Vol 112, 1984, p 89–95.
R. McPherson, A Review of Microstructure and Properties of Plasma Sprayed Ceramic Coatings,Surf. Coat. Technol., Vol 39/40, 1989, p 173–181.
R. McPherson, The Relationship between the Mechanism of Formation, Microstructure and Properties of Plasma-Sprayed Coatings,Thin Solid Films, Vol 83,1981, p 297–310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreau, C., Cielo, P. & Lamontagne, M. Flattening and solidification of thermally sprayed particles. JTST 1, 317–323 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647159
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02647159