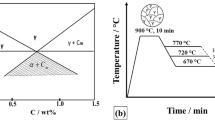
Abstract
As-cast ductile cast iron with an as-machined shiny metal surface was remelted with a high-power (1 kW) pulsed Nd:YAG laser using both single- and multipass overlap melt tracks. Changes in the microstructure of the underlying laser melted track caused by the transient overlap heating during multipass overlap remelting process were studied. The rapidly solidified metastable ledeburite structure of the underlying laser melted track was found to be rapidly graphitized during overlap remelting. The graphitized zone consists of a fully graphitized zone containing extremely fine graphite nodules and a partially graphitized zone containing extremely fine graphite nodules and undissolved cementite. The overlap ratios of the melt tracks were shown to have no noticeable influence on either the graphitized microstructure and the size of the graphitization zones. This newly observed rapid graphitization phenomenon is preliminarily discussed in terms of the microstructural characteristics of the rapidly solidified ductile iron and the unique heating behavior of pulsed laser beam to material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.L. Mordike:Laser Treatment of Materials, B.L. Mordike, ed., DGM Informationsgesellschaft-Verlag, Berlin, 1992, pp. 171–80.
S.L. Ream:Surface Engineering—Surface Modification of Materials, R. Kossowsky and S.C. Singhal, eds., Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Boston, 1984, pp. 285–99.
C. Banas and R. Nuss:ECLAT’90, Proc. 3rd Eur. Conf. on Laser Treatment of Materials, H.W. Bergmann and R. Kupfer, eds., Sprechsall Publishing Group, Coburg, Germany, 1990, pp. 103–10.
H.W. Bergmann:Surf. Eng., 1985, vol. 1, pp. 137–55.
C.H. Chen, C.J. Altestetter, and J.M. Rigsbee:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 719–28.
Z.D. Chen, D.R.F. West, and W.M. Steen:The Changing Frontiers of Laser Materials Processing, C.M. Banas and G.L. Whitney, eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1986, pp. 27–35.
H.W. Bergmann, B.L. Mordike, and T. Bell:Optoelectronics in Engineering, W. Waidellich, ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1984, pp. 335–49.
A. Zwick, A. Gasser, E.W. Kreutz, and K. Wissenbach:ECLAT90, Proc. 3rd Eur. Conf. on Laser Treatment of Materials, H.W. Bergmann and R. Kupfer, eds., Sprechsaal Publishing Group, Coburg, Germany, 1990, pp. 389–98.
H.W. Bergmann, T. Endres, R. Anders, and D. Müller:Laser Treatment of Materials, B.L. Mordike, ed., DMG Informationsgesellschaft-Verlag, Berlin, 1992, pp. 363–68.
B.L. Mordike:Processing of Metals and Alloys, R.W. Cahn, ed., VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Weinheim, 1992, pp. 112–35.
D. Petring, P. Abels, and E. Beyer:Proc. ICALEO, Santa Clara, CA, 1988, pp. 293–302.
I. Hawkes, L. Lundberg, A.M. Walker, W.M. Steen, and D.R.F. West:The Physical Metallurgy of Cast Iron, H. Fredriksson and M. Hillert, eds., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1984, pp. 447–56.
R. Jaschek, R. Taube, K. Schutte, A. Lang, and H.W. Bergmann:Laser Treatment of Materials, B.L. Mordike, ed., DMG Informationsgesellschaft-Verlag, Berlin, 1992, pp. 673–78.
C.H. Chen, C.P. Ju, and J.M. Rigsbee:Mater. Sci. Technol., 1988, vol. 4, pp. 161–66.
J.M. Rigsbee:Surface Engineering—Surface Modification of Materials, R. Kossowsky and S. Singhal, eds., Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Boston, MA, 1984, pp. 300–17.
D.N.H. Trafford, T. Bell, J.H.P.C. Megaw, and A.S. Bransden:Met. Technol., 1983, vol. 10, pp. 69–77.
M. Bamberger, M. Bass, and O. Akin:Z. Metellkd., 1988, vol. 79, pp. 806–12.
M. Bass:Laser Materials Processing, North-Holland Publishing Company, New York, NY, 1983, pp. 1–20.
R. IfflÄnder:Festköperlaser zur Materialbearbeitung, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1990, pp. 1–3.
H.S. Carslaw and J.C. Jaeger:Conduction of Heat in Solid, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1992, ch. XIV.
H.M. Wang, H. Stiele, A. Lang, C. Körner, and H.W. Bergmann:SPIE Proc., Proc. Int. Symp. on High Power Lasers and Applications V, Apr. 5–8, 1994, Vienna, Austria, vol. 2207, in press.
P.L. Roy, A.K. Chakrabarti, and P. Banerjee:The Physical Metallurgy of Cast Iron, H. Fredriksson and M. Hillert, eds., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1984, pp. 287–96.
E. Elliott:Materials Science and Technology—A Comprehensive Treatment, R.W. Cahn, P. Haasen, and E.J. Kramer, eds., vol. 7,Constitution and Properties of Steels, F.B. Pickering, ed., VCH, Weinheim, 1992, pp. 724–29.
Metals Handbook, 8th ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1961, vol. 1, pp. 366–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
H.M. WANG, formerly Research Fellow, Alexander von Humboldt Foundation of Germany, Institut für Werkstoffwissenschaften 2 (Metalle), UniversitÄt Erlangen-Nürnberg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H.M., Bergmann, H.W. Rapid graphitization of a pulsed laser remelted ductile cast iron during multipass overlap melting. Metall Mater Trans A 26, 793–800 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649077
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649077