Abstract
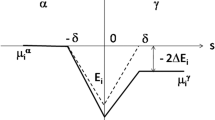
An earlier theory for the nonequilibrium transformation of austenite in Fe-C alloys to partially supersaturated plates of ferrite is extended to include a recent solute trapping model by Aziz. The previous model yielded a relationship between interface velocity and supersaturation for a specified transformation temperature. However, a unique growth velocity was determined from a velocity maximization criterion that could not be justified. By including the Aziz solute trapping function as a third interface response function (in addition to functions describing the diffusion field velocity and interface mobility), it has been possible to obtain a more physically based unique solution to the growth velocity for a specified temperature. The new calculations on an Fe-C alloy indicate a smoothly increasing supersaturation during both nucleation and growth, as the transformation temperature is reduced. Both the nucleation and growth processes tend to become completely diffusionless only below the martensite start temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D :
-
diffusivity of carbon in austenite
- −D :
-
weighted average diffusivity of carbon in austenite
- ΔG :
-
magnitude of Gibbs free energy change per unit volume
- Qo :
-
activation free energy necessary to overcome the resistance to interfacial motion in the absence of an interfacial driving force
- Q* :
-
activation free energy for interfacial motion
- Gdd :
-
Gibbs free energy per unit volume, dissipated in the diffusion of solute ahead of the transformation interface
- Gid :
-
Gibbs free energy per unit volume, dissipated in the process of interfacial motior
- Gel :
-
stored free energy per unit volume due to elastic strains
- G surf :
-
stored free energy per unit volume, due to interface
- k:
-
Boltzmann constant
- ke :
-
equilibrium partition coefficient
- kp :
-
actual partition coefficient
- p :
-
Peclet number
- p :
-
plate tip radius
- T :
-
absolute temperature
- V :
-
velocity for the continuous motion of a planar interface
- Vd :
-
velocity as calculated using the diffusion field velocity law
- Vk :
-
velocity as calculated using the Aziz solute trapping law
- Vi :
-
velocity as calculated using the interfacial mobility law
- Vo :
-
preexponential velocity factor for thermally activated interface motion
- x :
-
carbon concentration, mole fraction
- −x :
-
average carbon concentration in alloy, mole fraction
- xl :
-
carbon concentration in γ at the α/γ interface
- xα :
-
carbon concentration in α at the α/γ interface
- x αγ :
-
equilibrium carbon concentration in ferrite
- x γα :
-
equilibrium carbon concentration in austenite
- α :
-
ferrite
- γ :
-
austenite
- μ :
-
shear modulus of austenite
- Gid′ :
-
maximum glide resistance presented by obstacles to dislocation motion
- Ω:
-
volume per atom
References
J.W. Christian: Iron and Steel Institute Special Report 93, Iron and Steel Institute, London, 1965, p. 1.
J.W. Christian and D.V. Edmonds: inPhase Transformations in Ferrous Alloys, A.R. Marder and J.I. Goldstein, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1983, p. 293.
G.B. Olson, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, and M. Cohen:Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 381–90.
M. Grujicic, G.B. Olson, and W.S. Owen:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, p. 1713.
M. Grujicic, G.B. Olson, and W.S. Owen:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, p. 1723.
M. Grujicic, G.B. Olson, and W.S. Owen:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, p. 1735.
G.P. Ivantsov:Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR, 1947, vol. 58, p. 567.
M.J. Aziz:J. Appl. Phys., 1982, vol. 53, pp. 1158–68.
M.J. Aziz:Appl. Phys. Lett., 1983, vol. 43, pp. 552–54.
L.M. Goldman and M.J. Aziz:J. Mater. Res., 1987, vol. 2, pp. 524–27.
U.F. Kocks, A.S. Argon, and M.F. Ashby:Proc. Mater. Sei., 1975, vol. 19, p. 1.
F.R.N. Nabarro:Proc. Roy. Soc, 1982, vol. A381, p. 285.
G.B. Olson: Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, unpublished research, 1984.
R. Trivedi and G.M. Pound:J. Appl. Phys., 1967, vol. 38, p. 3569.
R.H. Siller and R.B. McLellan:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, p. 985.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia:Met. Sci., 1981, vol. 15, p. 477.
A. Hultgren:Jernkontorets Ann., 1951, vol. 135, p. 403.
J.C. Baker and J.W. Cahn:Solidification, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1971, p. 23.
J.W. Christian:Theory of Transformations in Metals and Alloys, 2nd ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1975, part I, pp. 77–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is based on a presentation made in the symposium “International Conference on Bainite” presented at the 1988 World Materials Congress in Chicago, IL, on September 26 and 27, 1988, under the auspices of the ASM INTERNATIONAL Phase Transformations Committee and the TMS Ferrous Metallurgy Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olson, G.B., Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. & Cohen, M. Coupled diffusional/displacive transformations: Part II. Solute trapping. Metall Trans A 21, 805–809 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02656563
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02656563