Abstract
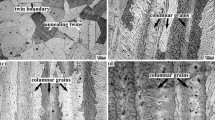
The influence of tungsten content, swaging, and grain size on the dynamic behavior of commercially available tungsten-nickel-iron (W-Ni-Fe) alloys has been examined using the compression Kolsky bar. The observed flow stresses increase with increasing tungsten content and with degree of swaging but are essentially independent of grain size for these compressive deformations. Further, the flow stresses sustained by these materials have a distinct dependence on strain rate, in that the flow stress increases by at least 20 pct over a range from 10-4 s-1 to 7 × 103 s-1. The rate sensitivity itself increases with increasing tungsten content. The rate sensitivity of the alloy with the highest tungsten content (97 pct W) appears to be essentially the same as that of pure polycrystalline tungsten. In addition to showing greater strain hardening, the unswaged alloy also shows a much higher rate dependence than the swaged alloys, with the flow stress almost doubling when the rate of deformation increases from quasistatic to 5 X 103 s-1. The rate-hardening mechanism within the composite appears to be essentially that as- sociated with the tungsten grains; however, the matrix contribution is significant in the case of an unswaged alloy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.H. Krock and L.A. Shepard:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1963, vol. 227, pp. 1127–34.
L. Ekbom: inModem Developments in Powder Metallurgy, H.H. Hausner, H.-W. Antes, and G.D. Smith, eds., Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, 1981, vol. 14, pp. 177–88.
B.H. Rabin and R.M. German:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 1523–32.
R.G. O'Donnell and R.L. Woodward:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 744–48.
V. Srikanth and G.S. Upadhyaya:J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1988, vol. 7, pp. 195–97.
R.S. Coates and K.T. Ramesh:Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1991, vol. 145, pp. 159–66.
R.L. Woodward, I.G. McDonald, and A. Gunner:J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1986, vol. 5, pp. 413–14.
L.L. Bourguignon and R.M. German:Int. J. Powder Metall., 1988, vol. 24 (2), pp. 115–21.
L.W. Meyer, H.D. Kunze, and E. Staskewitsch:Proc. 7th Int. Symp. on Ballistics, KIVI, The Hague, The Netherlands, 1983, pp. 289–93.
T. Nicholas: AFWAL-TR-80-4053, 1980.
G.R. Johnson, J.M. Hoegfeldt, U.S. Lindholm, and A. Nagy:J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 1983, vol. 105, pp. 48–53.
J. Lankford, C.E. Anderson, and S.R. Bodner:J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1988, vol. 7, pp. 1355–58.
J. Lankford, H. Couque, A. Bose, and C.E. Anderson:Shock Waves and High Strain Rate Phenomena in Materials, Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, 1992.
H. Kolsky:Proc. Phys. Soc., London, 1949, vol. 62B, pp. 676–700.
U.S. Lindholm:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1964, vol. 12, pp. 317–35.
P.S. Follansbee, G. Regazzoni, and U.F. Kocks:Mechanical Properties at High Rates of Strain, Institute of Physics Conf. Ser. No. 70, 1984, pp. 71–80.
H. Davies and S.C. Hunter:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1963, vol. 11, p. 155.
A.K. Zurek, P.S. Follansbee, and D. Kapoor:High Strain Rate Behavior of Refractory Metals and Alloys, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 179–92.
L.W. Meyer and C.-Y. Chiem:Mechanical Properties at High Rates of Strain, Institute of Physics Conf. Ser. No. 102, 1989, pp. 227–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly with The Johns Hopkins
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, K.T., Coates, R.S. Microstructural influences on the Dynamic Response of Tungsten Heavy Alloys. Metall Trans A 23, 2625–2630 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658066
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658066