Abstract
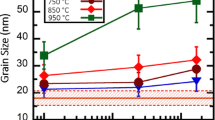
The elevated temperature stability of the fibrous copper-chromium eutectic was studied and found to depend strongly upon the extent of structural defects in the as-grown eutectic. Both highly branched and nearly “ideal,” or regular, fibrous structures were obtained by controlling the crystal growing conditions. The branched structure coarsens at a much faster rate than the regular structure. In the regular structure, the initial stage of coarsening is described by a simple two-dimensional Ostwald ripening mechanism modified to take into account the effects of fiber geometry and volume fraction. The coarsening rate is limited by volume diffusion of the chromium solute in the copper matrix. The activation energy for coarsening is approximately 298 kJ/mol. After long time annealing, the chromium-rich fibers begin to pinch off and three dimensional coarsening is initiated which leads to a rapid increase in the coarsening rate. Application of theoretical analyses to the observed coarsening rate yields the productDΣ as 1.3 × 10−13 J/s at 1000°C, whereD is the diffusivity of Cr in solid Cu and Σ the Cu-Cr interfacial energy. Using reported values ofD, Σ is bracketed between 0.27 and 2.5 J/m2. The latter is quite high for a solid-solid interfacial energy, but is consistent with the rapid coarsening observed in this system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. E. Cline:Acta Met., 1971, vol. 19, p. 481.
H. B. Smartt and T. H. Courtney:Met. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, p. 222.
Y. G. Nakagawa and G. C. Weatherly:Acta Met., 1972, vol. 20, p. 345.
L. Y. Lin and T. H. Courtney:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 513.
R. Kossowsky and W. C. Johnston:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1969, vol. 245, p. 1826.
M. Salkind, F. George, and W. Tice:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1969, vol. 245, p. 2339.
L. D. Graham and R. W. Kraft:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 236, p. 94.
Y. G. Nakagawa and G. C. Weatherly:Met. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, p. 3223.
G. Garmong and C. G. Rhodes:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, p. 2507.
A. R. T. deSilva and G. A. Chadwick:Metal. Sci. J., 1972, vol. 6, p. 157.
F. D. Lemkey and R. W. Kraft:Rev. Sci. Inst., 1962, vol. 33, p. 846.
R. W. Hertzberg and R. W. Kraft:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1963, vol. 227, p. 530.
H. B. Smartt and T. H. Courtney:Met. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, p. 2000.
H. E. Cline, J. L. Walter, E. Lifshin, and R. R. Russell:Met. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, p. 189.
G. A. Chadwick:J. Inst. Metals, 1963, vol. 91, p. 169.
M. J. Salkind, F. D. Lemkey, and F. D. George:Whisker Technology, A. P. Levitt, ed., p. 343, J. Wiley Interscience, New York, N. Y., 1970.
S. Marich:Met. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, p. 2953.
C. Wagner:Z. Elektrochem., 1961, vol. 65, p. 581.
I. M. Lifshitz and V. V. Slyozov:J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1961, vol. 19, p. 35.
G. E. Greenwood:Acta Met., 1956, vol. 4, p. 243.
G. R. Speich and R. A. Oriani:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1965, vol. 232, p. 623.
A. J. Ardell:Met. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, p. 1395.
H. B. Smartt, L. K. Tu, and T. H. Courtney:Met. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, p. 2717.
H. B. Smartt and T. H. Courtney:Met. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, p. 123.
R. P. Elliott:Constitution of Binary Alloys, First Supplement, p. 344, McGraw Hill Book Co., New York, N. Y., 1965.
G. Barreau, G. Brunei, and G. Cizeron:Compt. Rendu. Sci., Ser. C, 1971, vol. 272, p. 618.
C. Zener:Trans. AIME, 1946, vol. 167, p. 550.
W. A. Tiller:Liquid Metals and Solidification, A. S. M., Cleveland, Ohio, 1958.
G. A. Chadwick:Progr. Mater. Sci., vol. 12, p. 97, Pergamon Press, New York, N. Y., 1958.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L.Y., Courtney, T.H., Stark, J.P. et al. The thermal stability of the fibrous copper-chromium eutectic. Metall Trans A 7, 1435–1441 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658830
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658830