Abstract
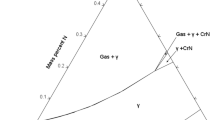
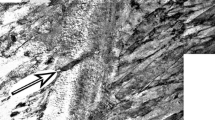
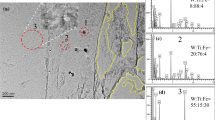
Carbide precipitation during the eutectoid decomposition of austenite has been studied in an Fe-0.12 pct C-3.28 pct Ni alloy by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) supplemented by optical microscopy. Nodular bainite which forms during the latter stages of austenite decomposition at 550 °C exhibits two types of carbide arrangement: (a) banded interphase boundary carbides with particle diameters of about 20 to 90 nm and mean band spacings between 180 and 390 nm and (b) more randomly distributed (“nonbanded”) elongated particles exhibiting a wide range of lengths between 33 and 2500 nm, thicknesses of approximately 11 to 50 nm, and mean intercarbide spacings of approximately 140 to 275 nm. Electron diffraction analysis indicated that in both cases, the carbides are cementite, obeying the Pitsch orientation relationship with respect to the bainitic ferrite. The intercarbide spacings of both morphologies are significantly larger than those previously reported for similar microstructures in steels containing alloy carbides other than cementite (e.g., VC, TiC). Both curved and straight cementite bands were observed; in the latter case, the average plane of the interphase boundary precipitate sheets was near {110}α//{011}c consistent with cementite precipitation on low-energy {110}α//{111}γ ledge terrace planes (where α,β, andc refer to ferrite, austenite, and cementite, respectively). The results also suggest that the first stage in the formation of the nonbanded form of nodular bainite is often the precipitation of cementite rods, or laths, in austenite at the α:γ interfaces of proeutectoid ferrite secondary sideplates formed earlier. Although these cementite rods frequently resemble the “fibrous” microstructures observed by previous investigators in carbide-forming alloy steels, they are typically much shorter than fibrous alloy carbides. The bainitic microstructures observed here are analyzed in terms of a previously developed model centered about the roles of the relative nucleation and growth rates of the product phases in controlling the evolution of eutectoid microstructures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Mannerkoski:Acta Polytech. Scand., 1964, ch. 26.
K. Relander:Acta Polytech. Scand., 1964, ch. 34.
A.T. Davenport, F.G. Berry, and R.W.K. Honeycombe:Met. Sci., 1968, vol. 2, p. 104.
F.G. Berry, A.T. Davenport, and R.W.K. Honeycombe:The Mechanism of Phase Transformations in Crystalline Solids, Institute of Metals, London, Monograph 33, 1969, pp. 228–92.
F.G. Berry and R.W.K. Honeycombe:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 3279–86.
A.T. Davenport and R.W.K. Honeycombe:Proc. R. Soc. A, 1971, vol. 322, pp. 191–205.
R.K.W. Honeycombe:Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 915–36.
R.K.W. Honeycombe:Phase Transformations in Ferrous Alloys, TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 259-80.
J. McCann and J.A. Ridai:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1964, vol. 202, pp. 441–47.
K. Campbell and R.W.K. Honeycombe:Met. Sci., 1974, vol. 8, pp. 197–203.
R.G. Baker and J. Nutting:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1959, vol. 192, pp. 257–68.
A.D. Batte and R.W.K. Honeycombe:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1973, vol. 211, pp. 284–89.
D.V. Edmonds and R.W.K. Honeycombe:Met. Sci., 1978, vol. 12, pp. 399–405.
Y. Ohmori, A.T. Davenport, and R.W.K. Honeycombe:Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1972, vol. 12, pp. 129–37.
N.K. Balliger: Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1977.
A.T. Davenport and P.C. Becker:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2962–64.
G.J. Shiflet, H.I. Aaronson, and J.R. Bradley:Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1743–50.
W.T. Reynolds, Jr., F.Z. Li, S.K. Liu, S. Hartfield, and H.I. Aaronson:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1479–91.
H.I. Aaronson: inThe Decomposition of Austenite by Diffusional Processes, V.F. Zackay and H.I. Aaronson, eds., Interscience, New York, NY, 1962, pp. 387–546.
H.J. Lee, G. Spanos, G.J. Shiflet, and H.I. Aaronson:Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 1129–40.
G. Spanos, H.S. Fang, D.S. Sarma, and H.I. Aaronson:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1391–1411.
W.T. Reynolds, Jr., F.Z. Li, C.K. Shui, G.J. Shiflet, and H.I. Aaronson: inPhase Transformations ’87, G.W. Lorimer, ed., Institute of Metals, London, 1988, pp. 330–33.
H.I. Aaronson:The Mechanism of Phase Transformations in Crystalline Solids, Institute of Metals, London, Monograph 33, 1969, pp. 270–81.
H.I. Aaronson and H.J. Lee:Scripta Metall., 1987, vol. 21, pp. 1011–16.
H.J. Lee, G. Spanos, G.J. Shiflet, and H.I. Aaronson:Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 1129–40.
H.I. Aaronson, W.T. Reynolds, Jr., G.J. Shiflet, and G. Spanos:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1343–80.
M. Hillert: inThe Decomposition of Austenite by Diffusional Processes, V.F. Zackay and H.I. Aaronson, eds., Interscience, New York, NY, 1962, pp. 197–237.
W. Pitsch:Acta Metall., 1962, vol. 10, pp. 79–80.
P.D. Southwick: Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1978.
J.M. Rigsbee and H.I. Aaronson:Acta Metall., 1979, vol. 27, pp. 365–76.
J.M. Rigsbee and H.I. Aaronson:Acta Metall., 1979, vol. 27, pp. 351–63.
T. Furuhara and H.I. Aaronson:Scripta Metall., 1988, vol. 22, pp. 1635–37.
R.A. Ricks and P.R. Howell:Acta Metall., 1983, vol. 31, pp. 853–61.
H.I. Aaronson, G. Spanos, E.S.K. Menon, M.G. Hall, W.F. Lange III, and K. Chattopadhyay: inStructure and Energy of Interphase Boundaries, K.N. Subramanian and M.I. Imam, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1986, pp. 3–20.
P.D. Southwick and R.W.K. Honeycombe:Met. Sci., 1980, vol. 14, pp. 253–61.
T. Obara, G.J. Shiflet, and H.I. Aaronson:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 1159–67.
H.J. Lee and H.I. Aaronson:J. Mater. Sci., 1988, vol. 23, pp. 150–60.
B. Uhrenius: inHardenability Concepts with Applications to Steel, D.V. Doane and J.S. Kirkaldy, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1978, pp. 28–81.
K.C. Russell: inPhase Transformations, H.I. Aaronson, ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1970, pp. 219–312.
W.F. Lange, III, M. Enomoto, and H.I. Aaronson:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 427–40.
H.I. Aaronson, T. Furuhara, J.M. Rigsbee, W.T. Reynolds, Jr., and J.M. Howe:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 2369–2409.
H.I. Aaronson:Metall. Trans. A, in press.
G. Spanos, W.T. Reynolds, Jr., and R.A. Vandermeer:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1367–80.
P.G. Shewmon:Diffusion in Solids, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1963.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spanos, G. The morphology, crystallography, and mechanism of carbide precipitation in an Fe-0.12 Pct C-3.28 Pct Ni alloy. Metall Trans A 23, 171–181 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02660863
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02660863