Abstract
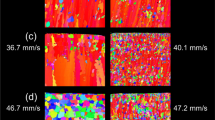
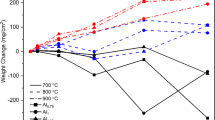
The mechanical properties of tungsten heavy alloys are sensitive to the processing cycle and are adversely affected by residual porosity. Sintering times greater than 2 hours usually result in pore growth with degraded properties. The development of an optimized sintering atmosphere has allowed exploration of long sintering times without significant property degradation due to pore growth. The optimal cycle was used to sinter two heavy alloy compositions (88 and 95 wt pct W) for times up to 600 minutes at 1480 °C. The 88 pct W samples slumped, but the 95 pct W samples were fully densified and suitable for tensile testing. At long sintering times, the tungsten grains flattened and the tungsten contiguity decreased, indicating a transition to low-energy configurations for the solid-liquid interfaces. The cube of the mean grain size varied linearly with the isothermal sintering time. This allowed determination of grain size effects on mechanical properties, showing a decreasing yield strength with increasing time in agreement with the Hall-Petch behavior. The tensile strength and elongation were highest for sintering times from 30 to 90 minutes, reflecting a minimum in the residual porosity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Srikanth and G.S. Upadhyaya:Int. J. Refract. Hard Met., 1986, vol. 5, pp. 49–54.
W.E. Gurwell:Prog. Powder Metall., 1986, vol. 42, pp. 569–90.
R.M. German, J.E. Hanafee, and S.L. DiGiallonardo:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 121–28.
R.M. German and K.S. Churn:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 747–54.
H. Danninger, W. Pisan, G. Jangg, and B. Lux:Z. Metallkd., 1983, vol. 74, pp. 151–55.
C.C. Ge, X.I. Xia, and E.T. Henig:Proc. P/M-82, Int. Powder Metallurgy Conf., Florence, Italy, June 1982, Associazione Italiana di Metallurgia, Milan, Italy, pp. 709–14.
T.K. Kang, E.T. Henig, W.A. Kaysser, and G. Petzow: inMod- ern Developments in Powder Metallurgy, H.H. Hausner, H.W. Antes and G.D. Smith, eds., Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, 1981, vol. 14, pp. 189–203.
K.S. Churn and D.N. Yoon:Powder Metall., 1979, vol. 22, pp. 175–78.
H. Fischmeister, A. Kannappan, L. Ho-Yi, and E. Navara:Phys. Sintering, 1969, vol. 1, pp. G1-G13.
A. Bose and R.M. German:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 2467–76.
S. Farooq, P.B. Kemp, R.M. German, and A. Bose:Int. J. Refract. Hard Mat., 1989, vol. 8, pp. 236–43.
C.M. Kipphut, A. Bose, S. Farooq, and R.M. German:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 1905–13.
C.M. Kipphut, R.M. German, A. Bose, and T. Kishi: inAdvances in Powder Metallurgy, T.B. Gasbarre and W.F. Jandeska, eds., Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, 1989, vol. 2, pp. 415-29.
V. Srikanth and G.S. Upadhyaya:Metallog. 1986, vol. 19, pp. 437–45.
S.C. Yang, S. Mani, and R.M. German:J. Met., 1990, vol. 42 (5), pp. 16–19.
R.M. German:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 1247–52.
K.P. Wieters, I.J. Boiko, and W. Schart:Cryst. Res. Technol., 1984, vol. 19, pp. 1195–1200.
I. Hansson and A. Tholen:Phil. Mag. A, 1978, vol. 37A, pp. 535–59.
G. Petzow and H.E. Exner:Z. Metallkd., 1976, vol. 67, pp. 611–18.
W.J. Muster and H. Willerscheid:Metallog., 1979, vol. 12, pp. 287–94.
T.H. Courtney:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 679–84.
S. Takajo, M. Kawano, M. Nitta, W.A. Kaysser, and G. Petzow:Sintering ’87, S. Somiya, M. Shimada, M. Yoshimura, and R. Watanabe, eds., Elsevier, London, 1988, vol. 1, pp. 465-70.
A.N. Niemi and T.H. Courtney:J. Mater. Sci., 1981, vol. 16, pp. 226–36.
S. Takajo, W.A. Kaysser, and G. Petzow:Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 107–13.
T.H. Courtney:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 685–89.
T.H. Courtney and J.K. Lee:Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 943–47.
R.V. Makarova, O.K. Teodorovich, and I.N. Frantsevich:Sov. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 1965, vol. 4, pp. 554–59.
E.G. Zukas, P.S.Z. Rogers, and R.S. Rogers:Int. J. Powder Metall. Powder Technol., 1977, vol. 13, pp. 27–38.
E.G. Zukas and H. Sheinberg:Powder Technol., 1976, vol. 13, pp. 85–96.
L. Kozma, W.J. Huppmann, L. Bartha, and P. Mezei:Powder Metall., 1981, vol. 24, pp. 7–11.
W.J. Huppmann, H. Riegger, and G. Petzow: in Sintering—NewDevelopments, M.M. Ristic, ed., Elsevier, New York, NY, 1979, pp. 272–78.
B.H. Rabin and R.M. German:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 1523–32.
O.J. Kwon and D.N. Yoon:Int. J. Powder Metall. Powder Technol., 1981, vol. 17, pp. 127–33.
O.J. Kwon and D.N. Yoon: inSintering Processes, G.C. Kuczynski, ed., Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1980, pp. 203–18.
A. Bose, B.H. Rabin, and R.M. German:Prog. Powder Metall., 1986, vol. 42, pp. 557–67.
T. Kishi and R.M. German:Int. J. Refract. Hard Mat., 1990, vol. 9, pp. 40–45.
C.M. Kipphut: M.S. Thesis, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, 1988.
A. Bose, D.M. Sims, and R.M. German:Prog. Powder Metall., 1987, vol. 43, pp. 79–92.
A. Bose, G. Jerman, and R.M. German:Powder Metall. Int., 1989, vol. 21 (3), pp. 9–13.
R.M. German, A. Bose, P.B. Kemp, and H. Zhang: inAdvances in Powder Metallurgy, T.B. Gasbarre and W.F. Jandeska, eds., Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, 1989, vol.2, pp. 401–13.
L.L. Bourguignon and R.M. German:Inter. J. Powder Metall., 1988, vol. 24, pp. 115–21.
S. Yang, S.S. Mani, and R.M. German: inAdvances in Powder Metallurgy, E.R. Andreotti and P.J. McGeehan, eds., Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, 1990, vol. 1, pp. 469-82.
R.M. German:Liquid Phase Sintering, Plenum Press, New York, NY, 1985.
C. Zubillaga, F. Hernandez, J.J. Urcola, and M. Fugntes:Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 1865–72.
V. Srikanth and G.S. Upadhyaya:Trans. Powder Metall. Assoc. India, 1987, vol. 14, pp. 83–92.
A. Kannappan:Particle Growth in Liquid Phase Sintering of W-Fe-Ni Alloys, Report ITS-31, International Team for Sintering, Ljubljana, Yugoslavia.
N.C. Kothari:J. Less-Common Met., 1967, vol. 13, pp. 457–68.
R.M. German and S. Farooq:Sintering ’87, S. Somiya, M. Shimada, M. Yoshimura and R. Watanabe, eds., Elsevier, London, 1988, vol. 1, pp. 459-64.
H. Hofmann and G. Petzow:Modern Developments in Powder Metallurgy, H.H. Hausner, E. Aqua, and C. Whitman, eds., Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, 1985, vol. 17, pp. 7-31.
G.D. White and W.E. Gurwell: inAdvances in Powder Metallurgy, T.B. Gasbarre and W.F. Jandeska, eds., Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ, 1989, vol. 2, pp. 355-69.
R.M. German, L.L. Bourguignon, and B.H. Rabin:J. Met., 1985, vol. 37 (8), pp. 36–39.
A. Bose and R.M. German:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1325–27. $
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
German, R.M., Bose, A. & Mani, S.S. Sintering time and atmosphere influences on the microstructure and mechanical properties of tungsten heavy alloys. Metall Trans A 23, 211–219 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02660866
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02660866