Abstract
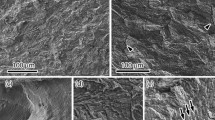
Internal hydrogen effects on stage II crack growth rates in AISI 4340 steel have been studied as a function of test temperature. A model is developed that is physically based in that classical thermodynamics relates to solubility and trapping and Fick’s second law controls hydrogen transport. Both of these are microstructurally related to how trapping affects both the crack initiation site and diffusion to it. For two tempered conditions of 4340 steel, it is shown that there is a test temperature,T 0, for stage II crack growth, above which the crack does not grow. The fractography associated with test temperatures approachingT 0 tends toward 100 pct intergranular for both 1340 MPa and 1620 MPa strength levels. At lower test temperatures, there is as much as 50 pct microvoid coalescence or 30 pct quasi-cleavage. In the lower strength condition, hydrogen traps at oxysulfide particles with a binding energy near 75 kJ/mol. Where these intersect the prior austenite grain boundaries, this promotes fingers of intergranular fracture which later triggers tearing of 100 μm size ligaments by microvoid coalescence. For the higher strength material, it is proposed that hydrogen traps along martensite lath intersections with prior austenite grain boundaries, the binding energy being near 27 kJ/mol. This promotes 1 μm size striations along intergranular facets. In both cases the fractography is consistent with a proposed model of stress field concentration of hydrogen, further concentration along trap sites, fracture nucleation at trap sites, and local, discontinuous fracture instabilities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. H. Johnson, J.G. Morlet, and A.R. Troiano:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1958, vol. 212, p. 528.
A. R. Troiano:Trans. ASM, 1960, vol. 52, p. 54.
A. S. Tetelman:Fundamental Aspects of Stress Corrosion Cracking, The Ohio State University, 1967, NACE, Houston, TX, 1969, pp. 446–64.
D.P. Williams and H. G. Nelson:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, p. 63.
R.A. Oriani:Bunsen-Gesellshaft Phys. Chem., 1972, vol. 76, p. 848.
H. P. van Leeuwen:Corrosion, 1973, vol. 29, p. 197.
C. St. John and W. W. Gerberich:Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, p. 589.
W. W. Gerberich:Hydrogen in Metals, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1974, pp. 115–47.
C. J. McMahon, Jr., C. L. Briant, and S. K. Banerji:Fracture 1977, Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 19.7, p. 363.
R.P. Gangloff and R.P. Wei:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, p. 1043.
S. P. Lynch and N. F. Ryan:Proc. of 2nd Inter. Congress on Hydro- gen in Metals, Paris, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1977.
G.W. Simmons, P.S. Pao, and R.P. Wei:Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, p. 1147.
A. W. Thompson:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, p. 727.
J. K. Tien:Effect of Hydrogen on the Behavior of Materials, A. W. Thompson and I.M. Bernstein, eds., TMS-AIME, New York, NY, 1976, p. 309.
H. Vehoff and P. Neumann:Hydrogen Degradation of Ferrous Alloys, R. A. Oriani, J. P. Hirth, and M. Smialowska, eds., Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985, pp. 686–711.
S.V. Nair and J. K. Tien:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, p. 2333.
C.D. Beachem:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, p. 437.
R. W. Pasco, K. Sieradzki, and P. J. Ficalora:Scripta Metall., 1982, vol. 16, p. 881.
H. W. Liu:Trans. ASME, J. Basic Engng., 1970, vol. 92, p. 633.
P. Doig and G.T. Jones:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, p. 1993.
H. P. van Leeuwen:Reviews on Coatings and Corrosion, The Tech- nion, Haifa, Israel, 1979, vol. V, no. 1, pp. 5–93.
H. G. Nelson and D. P. Williams:Stress Corrosion Cracking and Hydrogen Embrittlement of Iron Base Alloys, Unieux-Firminy, France, NACE, Houston, TX, 1973, pp. 390–404.
R.P. Wei:Hydrogen Effects in Metals, A. W. Thompson and I.M. Bernstein, eds., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1981, p. 677.
M. Gao, M. Lu, and R.P. Wei:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, p. 735.
M. Gao, M. Lu, and R.P. Wei:Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, p. 2039.
W. W. Gerberich and K. A. Peterson: NBS/NRL Workshop on Stress Corrosion of Brittle Materials, Washington, DC, June 1981.
K. A. Peterson: Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, 1981.
W. W. Gerberich:Symposium on Hydrogen in Metals, Materials Research Society, Boston, MA, Nov. 1984.
W. W. Gerberich, T. Livne, and X. Chen: Symposium onModeling Environmental Effects on Crack Growth Processes, R. H. Jones and W.W. Gerberich, eds., TMS-AIME, 1986, p. 243.
W.W. Gerberich and Y.T. Chen:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, p. 271.
J.R. Rice:Corrosion, 1976, vol. 32, no. 1, p. 22.
P. Kedzierzawski:Hydrogen Degradation of Ferrous Alloys, R. A. Oriani, J.P. Hirth, and M. Smialowska, eds., Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985, pp. 251–70; pp. 271-88.
I.M. Bernstein and G.M. Pressouyre:Hydrogen Degradation of Ferrous Alloys, R. A. Oriani, J. P. Hirth, and M. Smialowska, eds., Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1985, pp. 641–85.
W. W. Gerberich and A. G. Wright:Environmental Degradation of Engineering Materials in Hydrogen, Virginia Tech Printing Depart- ment, Blacksburg, VA, 1981, pp. 183–205.
P. G. Shewmon:Diffusion in Solids, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1963.
H. H. Johnson:Stress Corrosion Cracking and Hydrogen Embrittle- ment of Iron Base Alloys, Unieux-Firminy, France, NACE, Houston, TX, 1973, pp. 382–89.
M. Ancouturier:Proc. First. Intern. Conf. on Current Solutions to Hydrogen Problems in Steels, C.G. Interrante and G.M. Pressouyre, eds., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1982.
H. Y. Yu and J. C. M. Li:J. Nucl. Mat’ ls., 1976, vol. 20, p. 872.
K. A. Esaklul, A. G. Wright, and W. W. Gerberich:Scripta Metall., 1983, vol. 17, p. 1073 ; K.A. Esaklul, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, 1984.
R. A. Page and W.W. Gerberich:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, p. 305.
D.L. Dull and L. Raymond:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, p. 2943.
D. D. Macdonald and H. H. Chung:Corrosion, 1985, vol. 41, no. 3, p. 151.
J.Y. Lee, J. L. Lee, and W. Y. Chou:Corrosion, 1985, vol. 41, no. 3, p. 423.
M.L. Jokl, J. Kameda, C.J. McMahon , Jr., and V. Vitek:Metal Science, 1980, p. 375.
C. L. Briant, H. C. Feng, and C. J. McMahon, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, p. 625.
T. Asaoka, C. Dagbert, M. Ancouturier, and P. Lacombe:Corro- sion, 1980, vol. 36, p. 53.
G.M. Pressouyre:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, p. 1571.
R. Gibala:Trans. TMS AIME, 1967, vol. 239, p. 1574.
R. A. Oriani:Acta Metall., 1970, vol. 18, p. 147.
T. Asaoka:Proc. JIMIS-2, Hydrogen in Metals, Minikami, Japan Inst. Met., 1980, p. 161.
Y. Sakamoto and T. Mantani:Trans. Japan Inst. Metals, 1976, vol. 17, p. 743.
J. F. Knott:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1966, vol. 204, p. 104.
H. G. Ellerbrock, G. Vibrans, and H. P. Stüwe:Acta Metall., 1972, vol. 20, p. 53.
G. M. Evans and E. C. Rollason:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1969, vol. 207, p. 1484.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerberich, W.W., L1vne, T., Chen, X.F. et al. Crack growth from internal hydrogen—temperature and microstructural effects in 4340 steel. Metall Trans A 19, 1319–1334 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02662593
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02662593