Abstract
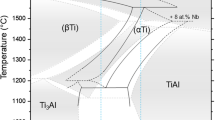
Solidification microstructures of arc-melted, near-equiatomic TiAl alloys containing boron additions are analyzed and compared with those of binary Ti-Al and Ti-B alloys processed in a similar fashion. With the exception of the boride phase, the matrix of the ternary alloy consists of the same α2 (DO19) and γ (Ll0) intermetallic phases found in the binary Ti-50 at. pct Al alloy. On the other hand, the boride phase, which is TiB (B27) in the binary Ti-B alloys, changes to TiB2 (C32) with the addition of Al. The solidification path of the ternary alloys starts with the formation of primary α (A3) for an alloy lean in boron (∼1 at. pct) and with primary TiB2 for a higher boron concentration (∼5 at. pct). In both cases, the system follows the liquidus surface down to a monovariant line, where both α and TiB2 are solidified concurrently. In the final stage, the α phase gives way to γ, presumably by a peritectic-type reaction similar to the one in the binary Ti-Al system. Upon cooling, the α dendrites order to α2 and later decompose to a lath structure consisting of alternating layers of γ and α2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.A. Lipsitt: inHigh Temperature Ordered Intermetallic Alloys MRS Symposia Proc, C.C. Koch, C.T. Liu, and N.S Stoloff eds., MRS, Pittsburgh, PA, 1985, vol. 39, pp. 351–64
M.J. Blackburn: Pratt & Whitney Aircraft, unpublished research, 1986.
J.L. Murray: inBinary Alloy Phase Diagrams, T.B. Massalski ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1986, p. 173.
L.A. Willey and H. Margolin: inMetals Handbook, 8th ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1973, vol. 8, p. 264.
R.E. Schafrik:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1003–06.
Harry A. Lipsitt, D. Shechtman, and Robert E. Schafrik:Metall Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 1991–96.
S.M.L. Sastry and H.A. Lipsitt: inTitanium '80: Science and Technology, H. Kimura and O. Izumi, eds., TMS-AIME Warrendale, PA, 1980, vol. 2, pp. 1231–43.
D.B. Marshall, B.N. Cox, and A.G. Evans:Acta Metall 1985 vol. 33(11), pp. 2013–21.
CK. Elliot, G.R. Odette, G.E. Lucas, and J.W. Sheckherd: inHigh Temperature/High Performance Composites, MRS Sym- posia Proc, F.D. Lemkey, A.G. Evans, S.G. Fishman, and J.R. Strife, eds., MRS, Pittsburgh, PA, 1988, vol. 120, pp. 95–102
S.M.L. Sastry, T.C. Peng, and L.P. Beckerman:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 1465–74.
R.G. Rowe and F.H. Froes: inProcessing of Structural Metals by Rapid Solidification, F.H. Froes and S.J. Savage, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1987, pp. 163–74.
J.M. Duva:J. Eng. Mater. Tech., 1984, vol. 106, pp. 317–21.
J.L. Murray, P.K. Liao, and K.E. Spear: inBinary Alloy Phase Diagrams, T.B. Massalski, ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1986, pp. 387–92.
H.B. Bomberger and F.H. Froes: inTitanium Rapid Solidifica- tion Technology, F.H. Froes and D. Eylon, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1986, pp. 21–43.
S.H. Whang:J. Mater. Sci., 1986, vol. 21, pp. 2224–38.
T. Lündstrom: inBoron and Refractory Borides, V.l. Matkovich, ed., Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 1977, pp. 351–76.
B.F. Decker and R. Kasper:Acta Crystalloer., 1954, vol 7 pp. 77–80.
C. McCullough, J.J. Valencia, H. Mateos, C. G. Levi, R. Mehrabian, and K.A. Rhyne:Scripta Metall., 1988, vol 22 pp. 1131–36.
M.J. Blackburn: inThe Science, Technology and Application of Titanium, R.I. Jaffee and N.E. Promisel, eds., Pergamon Press, London, 1970, pp. 633–43.
J.J. Valencia, C. McCullough, C. G. Levi, and R. Mehrabian:Scripta Metall., 1987, vol. 21, pp. 1341–46.
I. Maxwell and A. Hellawell:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1487–93.
L.F. Mondolfo:Aluminum Alloys, Structure and Properties, Butterworth's, London, 1976, pp. 437–39.
J.A. Marcantonio and L.F. Mondolfo:Metall.Trans.,1971,vol. 2, pp. 465–71.
L. Arnberg, L. BÄckerud, and H. Klang: inSolidification Tech- nology in the Foundry and the Cast House, Bartholomew Press, Surrey, United Kingdom, 1983, pp. 89–92.
G.P. Jones and J. Pearson:Metall. Trans. B, 1976, vol 7B pp. 223–34.
R.G. Fenish: Report No. NRM-138, Union Carbide Corp., Parma Research Center, Parma, OH, 1964.
F.W. Crossman and A.S. Yue:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol 2, pp. 1545–55.
G.J. Davies: inHigh Temperature Materials, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1965, pp. 603–50.
K.A. Jackson and J.D. Hunt:Trans. AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 1129–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyman, M.E., McCullough, C., Valencia, J.J. et al. Microstructure evolution in tial alloys with b additions: Conventional solidification. Metall Trans A 20, 1847–1859 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663215
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663215