Abstract
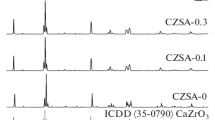
Up to the present, fully or partially stabilized zirconia has been used as a solid electrolyte material in probes for the determination of oxygen in metallic melts. In the present study, the ionic conduction behavior of HfO2 (CaO) solid solutions and the compound calcium zirconate CaZrO2 have been investigated. Both polarization experiments and EMF measurements on oxygen concentration cells point out that these two highly refractory oxide materials are also most suitable solid electrolytes. Their use is particularly recommended for oxygen probe measurements in deoxidized steel melts where extremely high chemical stability and low partial electronic conductivity of the solid electrolyte is required. In the paper, properties such as crystal structure, free energy of formation, thermal expansivity, ionic and total electrical conductivity are summarized and compared for fully and partially stabilized ZrO2, calcium zirconate CaZrO3, HfO2 (CaO), and ThO2 (Y2O3) solid solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. R. Richards, D. A. J. Swinkels, and J. Henderson:Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Japan, 1971,vol. 11, Suppl. I, pp. 371–76.
T. H. Etsell and S. N. Flengas:J. Electrochem. Soc., 1972, vol. 119, pp. 1–7.
A. V.R. Rao and V.B. Tare:Scripta Metallurg., 1972, vol. 6, pp. 141–48.
D. Janke and W. A. Fischer:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1975, vol. 46, pp. 477–82 and p. 683.
W. Pluschkell:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1975, vol. 46, pp. 11–18.
P. J. Kreyger, B. Slangen, and H. W. den Hartog:Stahl und Eisen, 1975, vol. 95, pp. 393–98.
W. Pluschkell:Stahl und Eisen, 1979, vol. 99, pp. 398–404.
D. Janke and H. Richter:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1979, vol. 50, pp. 93–100.
T. H. Etsell:Z. Naturforsch., Reihe A, 1972, vol. 27, pp. 1138–49.
D. Janke and W. A. Fischer:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1976, vol. 47, pp. 147–51.
D. Janke:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1978, vol. 49, pp. 217–24 and p. 413.
H. Schmalzried:Z. Elektrochem., Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem., 1962, vol. 66, pp. 572–76.
H. Schmalzried:Z. Phys. Chem. N.F., 1963, vol. 38, pp. 87–102.
O. Kubaschewski, E. Ll. Evans, and C.B. Alcock:Metallurgical Thermochemistry, 4th ed., New York, NY, Toronto, Oxford, 1967, pp. 421–29.
Refractory Materials: High temperature oxides, E. M. Alper, ed., New York, NY, London, 1970, vol. 5–II, pp. 99–166, 193–216.
I. Barin and O. Knacke: Thermochemical properties of inorganic substances, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, NY, and Düsseldorf, 1973, pp. 333, 337, 742, 746, 888, 916.
The Oxide Handbook, G.V. Samsonov, ed., New York, NY, Washington, DC, London, 1973, pp. 23–25, 105–114.
D. Janke and W. A. Fischer:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1977, vol. 48, pp. 255–60, 311–18, and 467–74.
M.G. Wolten:J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1963, vol. 46, pp. 418–22.
B. Ohnysty and F. K. Rose:J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1964, vol. 47, p. 398.
W.L. Bann:Science, 1963, vol. 140, p. 1330.
R. Ruh, H.J. Garrett, N.M. Talland, and R.F. Domagala:J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1968, vol. 51, p. 23.
D.K. Smith and C.F. Cline:J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 1962, vol. 45, pp. 249–50.
E. Viechnicki and V. Stubican:J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1965, vol. 48, pp. 292–97.
A. G. Boganov, V. S. Rudenko, and L. P. Marakov:Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1965, vol. 160, p. 1065.
C. Delamarre:Rev. Int. Hautes Temper, et Refract., 1972, vol. 9, pp. 209–24.
N. A. Godina and E. K. Keler:Russ. J. Inorg. Chem., 1959, vol. 4, p. 401.
F. M. Spirodonov, L. N. Komissarova, A. G. Kocharov, and V. I. Spitsyn:Russ. J. Inorg. Chem., 1969, vol. 14, p. 1332.
E.N Isupova, V.B. Glushkova, and E. K. Keler:Inorg. Mat. (USSR), 1968, vol. 4, p. 337.
Z. S. Volchenkova and S.F. Palguev:Tr. Inst. Elektrochim., Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ural Filial, 1964, vol. 5, p. 113;Chem. Abstr., 1965, vol. 62, p. 8472.
J. Besson, C. Deportes, and G. Robert:C.R. Acad. Sci., Paris, 1966, vol. 262, p. 527.
J. P. Traverse and M. Foëx:High Temperatures, High Pressures, 1969, pp. 409–27.
W. A. Fischer, D. Janke, and M. Schulenburg:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1976, vol. 47, pp. 51–56.
W. A. Fischer, D. Janke, and M. Schulenburg:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1976, vol. 47, pp. 525–30.
German Patent 2600103, January 2, 1976.
D. Janke, K. Schwerdtfeger, J. Mach, and G. Bamberg:Stahl und Eisen, 1979, vol. 99, pp. 1211–15.
D. Janke and W. A. Fischer:Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1975, vol. 46, pp. 755–60.
D. Janke:Advances in Ceramics. The American Ceramic Society, Columbus, OH, pp. 419–36.
T.H Etsell and S.N. Flengas:Chemical Reviews, 1970, vol. 70, pp. 339–76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janke, D. Oxygen probes based on calcia-doped hafnia or calcium zirconate for use in metallic melts. Metall Trans B 13, 227–235 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02664579
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02664579