Abstract
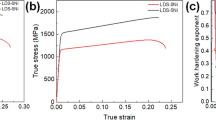
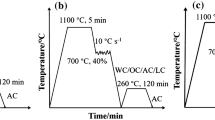
The purpose of this study is to clarify the correlation between microstructural factors and mechanical properties of ultrafine steels processed by thermomechanical controlled treatments. Three steels deformed at high strain rates in a pilot plant rolling mill showed very fine ferritic microstructure, whose grains became more equiaxed and finer with increasing fraction of alloying elements, and had good tensile and fracture properties, although they contained only about 0.01 pct carbon. Especially in the Ni-added steel, tensile properties were greatly improved because of the high dislocation density and the fineness of the ferritic substructure, readily satisfying the requirements for commercial-grade high-strength, high-toughness steels. The formation of ultrafine equiaxed grains in the steels might be explained by a possible strain-induced dynamic transformation mechanism associated with the austenite → ferrite transformation caused by heavy deformation in the austenite range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.M. Sellars:Hot Working and Forming Processes, Metals Society, London, 1980, p. 3.
W. Roberts, A. Sandberg, T. Siwecki, and T. Weriefers:HSLA Steels Technology and Applications, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1983, p. 67.
S. Dionne, M.R. Krishnadev, L.E. Collins, and J.D. Boyd: inAccelerated Cooling of Rolled Steel, P.D. Southwick, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1986, pp. 71–84.
S. Lee, B.C. Kim, and D. Kwon:Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 2803–16.
H. Yada, Y. Matsumura, and T. Senuma:Proc. Int. Conf. on Martensite Transformation, Japan Institute of Metals, Nara, 1986, pp. 515–20.
Y. Matsumura and H. Yada:Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1987, vol. 27, pp. 492–98.
H. Yada, Y. Matsumura, and T. Senuma: inInt. Conf. on Physical Metallurgy of Thermomechanical Processing of Steels and Other Metals, I. Tamura, ed., JISI, Tokyo, 1988, pp. 200–07.
Y.K. Lee and O. Kwon:3rd Symp. on Phase Transformation, Korea Institute of Metals, Seoul, 1991, pp. 9–19.
Y.E. Smith, A.P. Coldren, and R.L. Cryderman:Toward Improved Ductility and Toughness, Climax Molybdenum Company, Ann Arbor, MI, 1971, pp. 119–42.
S.W. Thompson, D.J. Colvin, and G. Krauss:Scripta Metall., 1988, vol. 22, pp. 1069–74.
S.W. Thompson, D.J. Colvin, and G. Krauss:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1493–507.
B.L. Bramfitt and J.G. Speer:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 817–29.
W.C. Leslie:The Physical Metallurgy of Steels, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1982, ch. 5.
F.B. Pickering:Physical Metallurgy and the Design of Steels, Applied Science Publishers, London, 1978, ch. 4.
Sarawak Shell Berhad:Standard Engineering Specifications (SES), No. 1, p. 17.
International Marine Organization (1MO), 1983, vol. 3, ch. 6.
G. Spanos, H.S. Fang, D.S. Sarma, and H.I. Aaronson:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1391–411.
G. Spanos, H.S. Fang, and H.I. Aaronson:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1381–90.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and J.W. Christian:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 767–97.
Y. Ohmori, H. Ohtani, and T. Kunitake:Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1972, vol. 12, pp. 146–54.
H. Ohtani, S. Okaguchi, Y. Fujishiro, and Y. Ohmori:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 877–88.
V. Biss and R.L. Cryderman:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2267–76.
P.L. Mangonon:Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 1389–1400.
J.H. Eom: RIST Technical Report No. 1-227-A, 1992.
Military Specification MIL-S-16216K(SH), 1987.
Military Specification MIL-S-24645A(SH), 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Research Engineer with the Steel Products Division, Research Institute of Industrial Science and Technology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Kwon, D., Lee, Y.K. et al. Transformation strengthening by thermomechanical treatments in C-Mn-Ni-Nb steels. Metall Mater Trans A 26, 1093–1100 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670605
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670605