Abstract
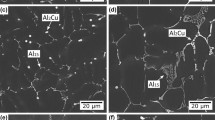
Conventional heat treatment techniques in Al-Si alloys to achieve optimum mechanical properties are limited to precipitation strengthening processes due to the presence of second-phase particles and spheroidization of silicon particles. The iron intermetallic compounds present in the microstructure of these alloys are reported to be stable, and they do not dissolve during conventional (equilibrium) heat treatments. The dissolution behavior of iron intermetallics on nonequilibrium heat treatment has been investigated by means of microstructure and mechanical property studies. The dissolution of iron intermetallics improves with increasing solution temperature. The addition of manganese to the alloy hinders the dissolution of iron intermetallics. Nonequilibrium heat treatment increases the strength properties of high iron alloys until a critical solution temperature is exceeded. Above this temperature, a large amount of liquid phase is formed as a result of interdendritic and grain boundary melting. The optimum solution treatment temperature for Al-6Si-3.5Cu-0.3Mg-lFe alloys is found to be between 515 °C and 520 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Couture:AFS Int. Cast Met. J., 1981, vol. 6, (4), pp. 9–17.
P. Jonason:AFS Trans., 1992, vol. 100, pp. 601–07.
A. Griger, V. Stefaniay, A. Lendval, and T. Turmezey:Aluminum, 1989, vol. 10, pp. 1049–56.
G. Gustafsson, T. Thorvaldsson, and G.L. Dunlop:Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 45–52.
Aluminum 319.0, “Data on world wide Metals and Alloys,”Alloy Digest, 1985, May, Filing Code: Al-266.
Y. Shimizu, Y. Awano, and M. Nakamura: Paper presented at 96th Casting Congress, Milwaukee, WI, 1992, AFS no. 92–135.
L. Anantha Narayanan: Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, 1994.
L. Anantha Narayanan, F.H. Samuel, and J.E. Gruzleski:AFS Trans., 1992, vol. 100, pp. 383–91.
S. Shivkumar, S. Ricci, B. Steenhoff, and G. Sigworth:AFS Trans., 1989, vol. 97, pp. 791–810.
F. Paray: Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, 1992.
Y. Osame, K. Toyoda, Y. Tsumura, M. Suzuki, S. Furuya, and K. Nagayama:J. Inst. Light Met. (Japanese), 1986, vol.36(12), pp. 813–18.
L. Backerud, G. Chai, and J. Tamminen:AFS/Skan Aluminium, 1990, vol. 2, pp. 95–102.
P.Y. Zhu and Q.Y. Liu:Mater. Sci. Technol., 1986, vol. 2, pp. 500–07.
L. Anantha Narayanan, F.H. Samuel, and J.E. Gruzleski:Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 1761–73.
J. Gauthier, F.H. Samuel, and H. Liu:Proc. Int. Symp. Light Metals Processing and Applications, ed. C. Bickert, M. Bouchard, G. Davies, E. Ghali, E. Jiran, The Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum, 1993, pp. 283–291.
U. Bischofberger, G. Neite, and H.E. Exner:Key Engineering Materials, 1990, vols. 44, 45, pp. 333–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narayanan, L.A., Samuel, F.H. & Gruzleski, J.E. Dissolution of iron intermetallics in Al-Si Alloys through nonequilibrium heat treatment. Metall Mater Trans A 26, 2161–2174 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670687
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670687