Abstract
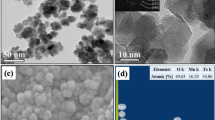
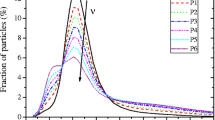
In order to improve the stability of magnetorheological (MR) fluids, viscoelastic medium having 2.2 Pa yield stress has been used as a continuous phase and nanosized CrO2 particles are added too. The rheological properties as well as the dispersion stability of MR fluids have been studied by using a stress-controlled rheometer and sedimentation test. The steady-shear MR response was independent of the continuous and nano additives and the fieldinduced yield stress increased subquadratically with the flux density. Since the constant stress is generated within the limit of zero shear rate, the plateau in the flow curve corresponds to the Bingham yield stress. Under an external field, the yield stress varied as B3/2. The yield stress has an approximately linear relation with the particle volume fraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chhabra, R. P., “Bubbles, Drops, and Particles in Non-Newtonian Fluids,” CRC Press Boca Raton (1993).
Chin, B. D., Lee, Y. S. and Park, O. O., “Effect of Conductivity and Dielectric Behaviors on the Electrorheological Response of Semiconductive Poly(p-phenylene) Suspension,”J. Collid Int Sci.,201(2), 172 (1998).
Chin, B. D. and Park, O. O., “Rheology and Microstructures of Electrorheological Fluids Containing both Dispersed Particles and Liquid Drops in a Continuous Phase,”J Rheo.,44(2), 397 (2000).
Chin, B. D. and Park, O. O., “Electrorheological Responses of Particulate Suspensions and Emulsions in a Small-Strain Dynamic Shear Flow; Viscoelasticity and Yielding Phenomena,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 54 (2001).
Chin, B. D., Park, J. H. and Park, O. O., “Rheological Properties and Stability of Magnetorheological (MR) Suspensions,”Rheo Acta,40 (3), 211 (2001).
Ginder, J. M., in Encyclopedia of Applied Physics, vol. 16, edited by E. Immergut, VCH, New York, 487 (1996).
Ginder, J. M., Davis, L. C. and Elie, L. D., “Rheology of Magnetorheological Fluids: Models and Measurements,”Int J Mod Phys B,10 (23–24), 3293 (1996).
Jordan, T. C., Shaw, M. T. and Mcleish, T. C. B., “Viscoelastic Response of Electrorheological Fluids. II. Field Strength and Strain Dependence,”J. Rheo.,36(3), 441 (1992).
Kim, Y D. and Klingenbery, D. J., “The Nonlinear Behavior of Surfactant-Activated Electrorheological Suspensions,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,14, 23 (1997).
Kormann, C., Laun, H. M. and Richter, H. J., “MR Fluids with Nano-Sized Magnetic Particles,”Int J Mod Phys B,10(23–24), 3167 (1996).
Lee, H. J., Chin, B. D., Yang, S. M. and Park, O. O., “Surfactant Effect on the Stability and Electrorheological Properties of Polyaniline Particle Suspension,”J Colloid Int Sci.,206, 424 (1998).
Margida, A. J., Weiss, K. D. and Carlson, J. D., “Magnetorheological Materials Based on Iron Alloy Particles,”Int J Mod Phys B,10(23–24), 3335 (1996).
Nakano, M., Yamamoto, H. and Jolly, M. R., Proc of 6th International Conference on ERF, Magneto-rheological Suspensions and Their Applications, World Scientific, Singapore, 551 (1998).
Phule, P. P., “Synthesis of Novel Magnetorheological Fluids,”MRS Bull.,23, 23 (1998).
Phule, P. P. and Ginder, J. M., “Synthesis and Properties of Novel Magnetorheological Fluids Having Improved Stability and Redispersibility,”Int. J. Mod. Phys. B,13, 2019 (1999).
Rankin, P. J., Horvath, A. T. and Klingenberg, D. J., “Magnetorheology in Viscoplastic Media,”Rheo Acta,38, 471 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.H., Kwon, M.H. & Park, O.O. Rheological properties and stability of magnetorheological fluids using viscoelastic medium and nanoadditives. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 18, 580–585 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706371
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02706371