Abstract
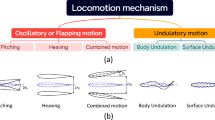
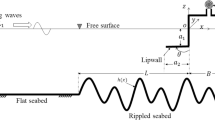
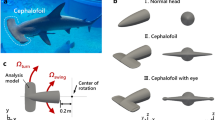
The hydrodynamic performance of fish undulatory swimming has been studied by means of the linear three-dimensional and the non-linear two-dimensional waving-plate theories developed recently by the present authors. The morphological adaptation of the anguilliform mode, carangiform mode, and lunate-tail swimming propulsion in the biological evolution process of fishes has been understood tentatively from the point of view of hydrodynamic analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi A R, Widnall S E 1986 Energetics and optimum motion of oscillating lifting surfaces of finite span.J. Fluid Mech. 162: 261–282
Cheng H K, Murillo L E 1984 Lunate-tail propulsion as a problem of curved lifting line in unsteady flow. Part 1. Asymptotic theory.J. Fluid Mech. 143: 327–350
Cheng J Y 1988Hydrodynamic study on aquatic animals’ swimming, Ph D dissertation, University of Science and Technology of China (in Chinese)
Cheng J Y, Zhuang L X, Tong B G 1989 Swimming performance analysis for anguilliform propulsion.J. Hydrodyn. (Engl. Ed.) 4: 89–102
Cheng J Y, Zhuang L X, Tong B G 1991a Numerical calculation of propulsive characteristics of fish’s swimming.Acta Aerodyn. Sin. 9: 94–103 (in Chinese)
Cheng J Y, Zhuang L X, Tong B G 1991b Analysis of three dimensional waving plate swimming.J. Fluid Mech. 232: 341–356
Cheng J Y, Zhuang L X, Tong B G 1991c The effects of spanwise deformation and closeness to the ground on the swimming of waving plates.J. China Univ. Sci. Technol. 21: 423–427 (in Chinese)
Chopra M G, Kambe T 1977 Hydromechanics of lunate-tail swimming propulsion.J. Fluid Mech 79: 49–60
Karpouzian G, Spedding G, Cheng H K 1990 Lunate-tail propulsion. Part 2. Performance analysis.J. Fluid Mech. 210: 329–351
Lan C E 1979 The unsteady quasi-vortex-lattice method with application to animal propulsion.J. Fluid Mech. 93: 747–765
Lighthill M J 1975Mathematical biofluiddynamics (Philadelphia:SIAM)
Tong B G, Wang A P 1991 A numerical study on the acceleration of a three-dimensional waving plate.Acta Aerodyn. Sin. 9: 285–293 (in Chinese)
Webb P W 1971 The swimming energetics of trout.J. Exp. Biol. 55: 484–520
Wu T Y 1961 Swimming of a waving plate.J. Fluid Mech. 10: 321–344
Wu T Y 1971 Hydromechanics of swimming propulsion.J. Fluid Mech. 46: 521–568
Yates G T 1983 Hydromechanics of body and caudal fin propulsion. InFish biomechanics (eds) P W Webb, D Weihs (New York: Prager)
Zhuang L X, Shida Y, Takami H 1990 Two-dimensional unsteady flow around a waving plate in wall effects.Fluid Dyn. Res. 5: 321–336
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, BG., Zhuang, LX. & Cheng, JY. The hydrodynamic analysis of fish propulsion performance and its morphological adaptation. Sadhana 18, 719–728 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02744375
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02744375