Abstract
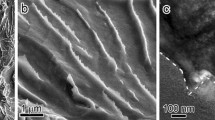
Underaged, peak strength (T6), and overaged (T73) microstructures were studied in 7075 plate material. Hydrogen charged and uncharged tensile specimens of longitudinal orientation were tested between −196°C and room temperature. The results confirm a hydrogen embrittlement effect, manifested mainly in the temperature dependence of the reduction of area loss; a classical behavior of hydrogen embrittlement. The maximum embrittlement shifted to lower temperatures with further aging. The effect of hydrogen was largest for the underaged condition and smallest for the overaged, thus following the pattern found for the sensitivity to stress-corrosion cracking in high strength aluminum alloys. The fracture path was predominantly transgranular, with minor amounts of intergranular fracture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Kelly and R. B. Nicholson:Progr. Mater Sci., 1963, vol. 10, pp. 151–391.
M. O. Speidel and M. V. Hyatt:Advances in Corrosion Science and Technology, vol. 2, pp. 115–335, Plenum, NY, 1972.
M. W. Hyatt and M. O. Speidel:Stress Corrosion Cracking in High Strength Steels and in Titanium and Aluminum Alloys, pp. 147–244, Naval Res. Lab., Washington 1972.
R. H. Brown, D. O. Sprowls, and M. B. Shumaker:Stress Corrosion Cracking of Metals—A State of the Art, pp. 87–118, STP 518, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1972.
G. M. Ugiansky, L. P. Skolnick, and S. W. Stiefel:Corrosion, 1969, vol. 25, pp. 77–86.
A. W. Thompson and I. M. Bernstein:Rev. Coat. Corros., 1975, vol. 2, pp. 3–44.
A. W. Thompson and I. M. Bernstein:Advances in Corrosion Science and Technology, vol. 7, pp. 53–175, Plenum, NY, 1979.
M. O. Speidel:The Theory of Stress Corrosion Cracking in Alloys, pp. 289–341, NATO, Brussels, 1971.
P. N. T. Unwin and R. B. Nicholson:Acta Met., 1969, vol. 17, pp. 1379–93.
J. K. Tien, A. W. Thompson, I. M. Bernstein, and R. J. Richards:Met. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 821–29.
M. O. Speidel:Hydrogen in Metals, pp. 249–73, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1974.
J. A. S. Green, H. W. Hayden, and W. G. Montague:Effect of Hydrogen on Behavior of Materials, pp. 200–15, TMS-AIME, NY, 1976.
J. R. Low:Progr. Mater. Sci., 1963, vol. 12, pp. 1–96.
W. E. Wood and W. W. Gerberich:Met. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 1285–94.
A. W. Thompson:Environmental Degradation of Engineering Materials, pp. 3–17, VPI Press, Blacksburg, VA, 1977.
J. Albrecht, B. J. McTiernan, I. M. Bernstein, and A. W. Thompson:Scr. Met., 1977, vol. 11, pp. 893–97.
R. J. Gest and A. R. Troiano:L’Hydrogene dans les Metaux, pp. 427–32, Editions Science et Industrie, Paris, 1972.
R. J. Gest and A. R. Troiano:Corrosion, 1974, vol. 30, pp. 374–79.
A. W. Thompson:Met. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 2819–25.
M. R. Louthan, G. R. Caskey, J. A. Donovan, and D. E. Rawl:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1972, vol. 10, pp. 357–68.
A. W. Thompson:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1974, vol. 14, pp. 253–64.
H. Y. Hunsicker:Aluminum, vol. 1, pp. 109–62 (esp. p. 154), ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1967.
Metals Handbook, vol. 8, 8th Ed., p. 31, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1973.
A. R. Troiano:Trans. ASM, 1960, vol. 62, pp. 54–80.
J. Albrecht and G. Lütjering:Influence of Microstructure on Fatigue Crack Propagation Rate of Aluminum Alloys, Report ESA-TT-418, European Space Agency, Access No. N78-18203, DFVLR, Cologne, W. Germany, 1974.
L. M. Foster, T. H. Jack, and W. W. Hill:Met. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 3117–24.
J. A. Donovan:Met. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 1677–83.
M. R. Louthan, G. R. Caskey, and A. H. Dexter:Radiation Effects and Tritium Technology for Fusion Reactors, vol. IV, pp. 117–32, Oak Ridge Nat’l. Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 1976.
H. W. Liu:J. Basic Eng. (Trans. ASME, Series D), 1970, vol. 92D, pp. 633–38.
L. Montgrain and P. R. Swann:Hydrogen in Metals, pp. 575–84, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1974.
G. M. Scamans, R. Alani, and P. R. Swann:Corros. Sci., 1976, vol. 16, pp. 443–59.
G. M. Scamans:J. Mater. Sci., 1978, vol. 13, pp. 27–36.
A. W. Thompson:Effect of Hydrogen on Behavior of Materials, pp. 467–77. TMS-AIME, NY, 1976.
A. W. Thompson:Met. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 727–31.
G. S. Ansell, H. S. Kim, and H. C. Rogers:Trans. ASM, 1966, vol. 59, pp. 630–43.
A. W. Thompson and I. M. Bernstein:Fracture 1977, vol. 2, pp. 249–54, Univ. of Waterloo Press, Waterloo, Ontario, 1977.
R. J. Jacko and D. J. Duquette:Met. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1821–27.
P. Doig, P. E. J. Flewitt, and J. W. Edington:Corrosion, 1977, vol. 33, pp. 217–21.
J. M. Chen, T. S. Sun, R. K. Viswanadham, and J. A. S. Green:Met. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1935–40.
U. R. Evans:Stress Corrosion Cracking and Embrittlement, pp. 158–62, Wiley, NY, 1956.
J. C. Scully:Effect of Hydrogen on Behavior of Materials, pp. 129–47, TMS-AIME, NY, 1976.
R. M. Latanision, O. H. Gastine, and C. R. Compeau:Environment-Sensitive Fracture of Engineering Materials, pp. 48–70, TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1979.
A.J. Bursle and E. N. Pugh:, pp. 18–47.
A. W. Thompson:, pp. 379–410.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
J. ALBRECHT, formerly with the Department of Metallurgy and Materials Science, Carnegie-Mellon University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albrecht, J., Thompson, A.W. & Bernstein, I.M. The role of microstructure in hydrogen-assisted fracture of 7075 aluminum. Metall Trans A 10, 1759–1766 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811712
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811712