Abstract
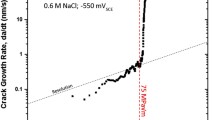
A new test specimen configuration, designated the T-notch double cantilever beam (TNDCB), was developed, calibrated and employed for a fracture mechanics study of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of cold worked Type-316 austenitic stainless steel exposed to hot aqueous solutions of 44.7 wt pct MgCl2. The effects of stress intensity (K I ), temperature (T) and electrochemical potential (E) upon the crack velocity (v) and fractography were investigated. The stress intensity (K ISCC ) below whichv became immeasurably small was ∼12 MN·m−3/2. Above this value, three regions of behavior were observed. Region I exhibitedK I dependent cracking followed by Region II which exhibitedK I independent cracking and an apparent activation energy of 63 to 67 kJ/mol, followed by Region III where cracking again became dependent uponK I . The relative proportions of intergranular and transgranular crack paths were markedly dependent upon bothK I andE, and less sensitive toT. Crack velocity was insensitive to small changes inE with respect to the free corrosion potentials (E corr), but could be terminated by an applied active potential of ∼−0.35 VSCE. The pH within the propagating crack was estimated to be <1.0 atE corr, rising to ∼4.5 at −0.35 VSCE. The mechanism of SCC was discussed with respect to film rupture events caused by crack tip plastic deformation, adsorption controlled processes on the metal surface, and hydrogen diffusion in the metal lattice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. O. Speidel:Met. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, pp. 631–51.
M. J. Blackburn, J. A. Feeney, and T. R. Beck,Advances in Corrosion Science and Technology, vol. 3, pp. 67–292, Plenum Press, NY, 1973.
L. P. Lee and D. Tromans:Environment Sensitive Fracture of Engineering Materials, Z. A. Foroulis, ed., AIME, 1979.
B. F. Brown:The Theory of Stress Corrosion Cracking in Alloys, J. C. Scully, ed., pp. 186–203, NATO, Brussels, 1971.
Stress Corrosion—New Approaches, H. L. Craig, ed., ASTM STP 610, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1976.
M. J. Robinson and J. C. Scully:Proceedings of 1973 Firminy Conference—Stress Corrosion Cracking and Hydrogen Embrittlement of Iron Base Alloys, R. W. Staehle, J. Hochman, R. D. McCright, and J. E. Slater, eds., pp. 1095–1103, NACE, Houston, 1977.
H. Lefakis and W. Rostoker:Corrosion, 1977, vol. 33, pp. 178–81.
M. O. Speidel:Corrosion, 1977, vol. 33, pp. 199–203.
M. O. Speidel:Corrosion, 1976, vol. 32, pp. 187–90.
A. Bursle: Ph.D Thesis, Univ. of New South Wales, 1977.
R. M. Latanision and R. W. Staehle.Proceedings of Conference—Fundamental Aspects of Stress Corrosion Cracking, R. W. Staehle, A. J. Forty, and D. van Rooyen, eds., pp. 214–96, NACE, Houston, 1969.
R. W. Staehle,The Theory of Stress Corrosion Cracking in Alloys, J. C. Scully, ed., pp. 223–86, NATO, Brussels, 1971.
S. W. Dean, Jr.,Stress Corrosion—New Approaches, H. L. Craig, ed., pp. 308–37, ASTM STP 610, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1976.
M. A. Streicher and I. B. Casale.Proceedings of Conference—Fundamental Aspects of Stress Corrosion Cracking, R. W. Staehle, A. J. Forty, and D. van Rooyen, eds., pp. 305–07, NACE, Houston, 1969.
A. J. Sedriks:Corrosion, 1975, vol. 31, p. 339.
H. Tada, P. C. Paris, and G. R. Irwin:The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook, Del Research Corp, Hellertown, PA, 1973.
W. F. Brown and J. E. Srawley: ASTM STP 410, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1966.
G. R. Irwin and J. A. Kies:Weld. J. Res. Suppl., 1954, vol. 33, pp. 193–98.
J. F. Knott:Fundamentals of Fracture Mechanics, Butterworths, London, 1973.
Metals Handbook—Properties and Selection of Metals, vol. 1, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1961.
H. H. Lee and H. H. Uhlig:J. Electrochem. Soc., 1970, vol. 117, pp. 18–22.
J. A. Davis and B. E. Wilde:J. E. Electrochem. Soc., 1970, vol. 117, pp. 1348–51.
Digby D. Macdonald:Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry, B. E. Conway and J. O'M Bockris, eds., no. 11, pp. 141–97, Plenum Press, NY, 1975.
R. J. Biernat and R. G. Robins:Electrochem. Acta, 1972, vol. 17, pp. 1261–83.
H. H. Uhlig and E. W. Cook, Jr.:J. Electrochem. Soc., 1969, vol. 116, pp. 173–77.
P. Doig and P. E. J. Flewitt:Met. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, pp. 357–62.
Chemical Engineers Handbook, J. H. Perry, ed., McGraw Hill, NY, 1941.
T. P. Nikiforuk: M.A. Sc. Thesis, Univ. of British Columbia, 1976.
M. Marek and R. F. Hochman:Corrosion, 1970, vol. 26, pp. 5–6.
J. D. Harston and J. C. Scully:Corrosion, 1970, vol. 26, pp. 387–95.
B. G. Ateya and H. W. Pickering:Hydrogen in Metals, I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson, eds., pp. 207–22, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1974.
B. E. Wilde:J. Electrochem. Soc., 1971, vol. 118, pp. 1717–25.
W. F. Linke and A. Seidell:Solubilities Inorganic and Metal-Organic Compounds, vol. II, 517, Chem. Soc., Washington, D.C., 1965.
J. W. Cobble:J. Am Chem. Soc., 1964, vol. 86, pp. 5394–5401.
M. G. Fontana and N. D. Greene:Corrosion Engineering, McGraw-Hill, NY, 1978.
J. C. Scully:The Theory of Stress Corrosion Cracking in Alloys, J. C. Scully, ed., pp. 1–16, NATO, Brussels, 1971.
D. A. Vermilyea:Proceedings of 1973 Firminy Conference—Stress Corrosion Cracking and Hydrogen Embrittlement of Iron Base Alloys, R. W. Staehle, J. Hochmann, R. D. McCright, and J. E. Slater, eds., pp. 208–17, NACE, Houston, 1977.
D. S. Dugdale:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1960, vol. 8, p. 100.
F. A. McClintock and G. R. Irwin:Fracture Toughness Testing and Its Applications, pp. 84–113, ASTM STP 381, ATM Philadelphia, 1964.
S. Glasstone, K. Laidler, and H. Eyring:Theory of Rate Processes, McGraw-Hill, NY, 1941.
M. R. Louthan, Jr. and R. G. Derrick:Corros. Sci. 1975, vol. 15, pp. 565–77.
J. C. Scully:Met. Sci., 1978, vol. 12, pp. 290–300.
Passivity and Its Breakdown on Iron and Iron Base Alloys, R. W. Staehle and H. Okada, eds., NACE, Houston, 1976.
H. H. Uhlig:Proceedings of Conference—Fundamental Aspects of Stress Corrosion Cracking, R. W. Staehle, A. J. Forty, and D. van Rooyen, eds., pp. 86–91, NACE, Houston, 1969.
H. H. Uhlig:Passivity and Its Breakdown on Iron and Iron Base Alloys, R. W. Staehle and H. Okada, eds., pp. 110–11, NACE, Houston, 1976.
M. R. Louthan Jr.:Hydrogen in Metals, I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson, eds., pp. 53–75, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1974.
A. W. Thompson:Hydrogen in Metals, I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson, eds., pp. 91–102, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1974.
H. Okada, S. Abe and T. Murata:Passivity and Its Breakdown on Iron and Iron Base Alloys, R. W. Staehle and H. Okada, eds., pp. 147–54, NACE, Houston, 1976.
J. M. West:Electrodeposition and Corrosion Processes, D. Van Nostrand, ed., London, 1965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Alan J. RUSSELL, formerly Research Student, University of British Columbia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russell, A.J., Tromans, D. A fracture mechanics study of stress corrosion cracking of type-316 austenitic steel. Metall Trans A 10, 1229–1238 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811978
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811978