Abstract
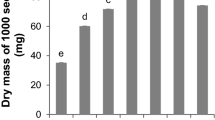
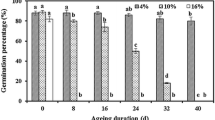
Changes in the percentage of seed germination, the growth and respiration rate of the seedlings were observed at 15-day intervals from the stage of the full germination capacity of rice (Oryza saliva L.) seeds till they became non-viable. At the beginning, the respiration rate changed but little, but afterwards, with the approach of non-viability, the rate declined sharply. A positive correlation of respiration with a decrease in the germination percentage and the length of seedlings and a negative correlation with days of storage were also established. A strong correlation existed between catalase and peroxidase activity with respiration, indicating that the activity of these enzymes can be used as an indicator of metabolism, and therefore can be considered as part of the respiratory mechanism of rice seedlings.
Abstract
Byly zjišfovány zmíny v klíčivosti semen a v růstu a v intensitě dích ání klíðních rostlin ríže v 15-denních intervalech pŕi skladodání od plné klíčivosti až do doby ztráty klíčivosti. Aktivita katalázy a peroxidázy zíetehiě korelovaly s intensitou díchání.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla, F. H., Roberts, E. H.: The effects of temperature and moisture on the induction of genetic changes in seeds of barley, broad beans and peas during storage. — Ann. Bot.33: 153–167, 1969a.
Abdalla, F. H., Roberts, E. H.: The effects of seed storage conditions on the growth and yield of barley, broad beans and peas. — Ann. Bot.33: 169–184, 1969b.
Chance, B., Maehly, A. C: Assay of catalases and peroxidases. — In: Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 2. Pp. 764–775. Academic Press, New York 1955.
Crocker, W., Barton, L. V.: Physiology of Seeds. — Pp. 184–203. Chronica Botanica Co., Waltham, Mass. 1957.
Dey, B., Sircar, S. M.: The presence of abscisic acid like factor in non-viable rice seeds. — Physiol. Plant.21: 1054–1059, 1968.
Dey, B., Sircar, P. K., Sircar, S. M.: Phenolics in relation to non-viability of rice seeds. — In: Proc. int. Symp. Plant Growth Substances. Pp. 57–64. Univ. Calcutta, Calcutta 1968.
Gasper, T., Lacoppe, J.: The effect of CCC and Amo-1618 on growth, catalase, peroxidase and IAA oxidase activity of young barley seedlings. — Physiol. Plant.21: 1104–1109, 1968.
GustaFsson, A.: Death of a nuclear process. — Hereditas23: 1–37, 1937.
Koller, D., Mayer, A. M., Poljakoff-Mayber, A., Klein, S.: Seed germination. — Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.13: 437–464, 1962.
Mayer, A.M., Poljakoff-Mayber, A.: The Germination of Seeds. Pp. 101–156. Pergamon Press, New York 1963.
Mikkelson, D. S.: Germination inhibitors as a possible factor in rice dormancy. — Int. Rice Comm. Newsletter (Spec. Issue). Pp. 132–145, 1967.
Paul, A. K., Mukherji, S., Sircar, S. M.: Metabolic changes in rice seeds during storage. — Ind. J. agr. Sci.40: 1031–1036, 1970a.
Paul, A. K., Mukherji, S., Sircar, S. M.: Enzyme activities in germinating mungbean(Phaseolus aureus) seeds and their relation with promoter and inhibitors of protein synthesis. — ðsterr. bot. Z.118: 311–320, 1970b.
Roberts, E. H.: Dormancy of rice seed. I. The distribution of dormancy periods. — J. exp. Bot.12: 319–329, 1961.
Sircar, S. M.: Physiology of the rice plant. - Pres. Address, Bot. Sect. Proe. 50th Ind. Sci. Congr., Part II, 1963.
Sircar, S. M.: Biochemical changes in rice seed germination and its control mechanism. — Trans. Bose Res. Inst.30: 189–198, 1967.
Umbreit, W. W., Burris, R. H., Stauffer, J. F.: Manometric Techniques and Tissue Metabolism. — Burgess Publ. Co., Minneapolis 1957.
Woodstock, L. W.: Initial respiration rates and subsequent growth of corn seedlings. — BioScience15: 783–784, 1965.
Woodstock, L. W., Combs, M. F.: Effects of gamma-irradiation of corn seed on the respiration and growth of the seedling. — Amer. J. Bot.52: 568–569, 1965.
Woodstock, L. W., Feeley, J.: Early seedling growth and initial respiration rates as potential indicators of seedling vigour in corn. — Proc. Assoc. Of fic. Seed Analysts55: 131–138, 1965.
Woodstock, L. W., Grabe, D. F.: Relationship between seed respiration during imbibition and subsequent growth inZea mays L. — Plant Physiol.42: 1071–1076, 1967.
Woodstock, L. W., Pollock, B. M.: Physiological predetermination: imbibition, respiration and growth of lima bean seeds. — Science150: 1031–1032, 1965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, A.K., Mukherji, S. Change in respiration rate of rice seedlings as affected by storage and viability, and its possible relation with catalase and peroxidase activities during germination. Biol Plant 14, 414–419 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932982
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932982