Abstract
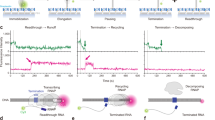
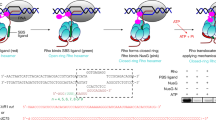
Escherichia coli transcription termination factor Rho catalyzes the unwinding of RNA/DNA duplex in reactions that are coupled to ATP binding and hydrolysis. Fluorescence stopped-flow methods using ATP and the fluorescent 2’(3’)-O-(N-methylanthraniloyl) derivatives (mant-derivatives) of ATP and ADP were used to probe the kinetics of nucleotide binding to and dissociation from the Rho-RNA complex. Presteady state nucleotide binding kinetics provides evidence for the presence of negative cooperativity in nucleotide binding among the multiple nucleotide binding sites on Rho hexamer. The binding of the first nucleotide to the Rho-RNA complex occurs at a bimolecular rate of 3.6×106 M−1sec−1, whereas the second nucleotide binds at a slower rate of 4.7×105 M−1 sec−1 at 18°C. RNA complexed with Rho affects the kinetics of nucleotide interaction with the active sites through conformational changes to the Rho hexamer, allowing the incoming nucleotide to be more accessible to the sites. Adenine nucleotide binding and dissociation is more favorable when RNA is bound to Rho, whereas ATP binding and dissociation step in the absence of RNA occurs significantly slower, at a rate ∼70- and ∼40-fold slower than those observed with the Rho-RNA complex, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brennan, C. A., A. J. Dombroski, and T. Platt (1987) Transcription termination factor rho is an RNA-DNA helicase.Cell 48: 945–952.
Geiselmann, J., Y. Wang, S. E. von Seifried, and P. H. Hippel (1993) A physical model for the translocation and helicase activities ofEscherichia coli transcription termination protein Rho.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 7754–7758.
Richardson, J. P. (1996) Structural organization of transcription termination factor Rho.J. Biol. Chem. 271: 1251–1254.
Stitt, B. L. (1988)Escherichia coli transcription termination protein rho has three hydrolytic sites for ATP.J. Biol. Chem. 263: 11130–11137.
Geiselmann, J. and P. H. von Hippel (1992). Functional interactions of ligand cofactorswithEscherichia coli transcription termination factor rho: I. Binding of ATP.Protein Sci. 1: 850–860.
Kim, D. E., K. Shigesada, and S. S. Patel (1999) Transcription termination factor Rhocontains three noncatalytic nucleotide binding sites.J. Biol. Chem. 274: 11623–11628.
Geiselmann, J., T. D. Yager, and P. H. von Hippel (1992) Functional interactions of ligand cofactors withEscherichia coli transcription termination factor rho: II. Binding of RNA.Protein Sci. 1: 861–873.
Wang, Y. and P. H. von Hippel (1993)Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho: II. Binding of oligonucleotide cofactors.J. Biol. Chem. 268: 13947–13955.
McSwiggen, J. A., D. G. Bear, and P. H. von Hippel (1988) Interactions ofEscherichia coli transcription termination factor rho with RNA: I. Binding stoichiometries and free energies.J. Mol. Biol. 199: 609–622.
Yu, X., T. Horiguchi, K. Shigesada, and E. H. Egelman (2000) Three-dimensional reconstruction of transcription termination factor rho: Orientation of theN-terminal domain and visualization of an RNA-binding site.J. Mol. Biol. 299: 1279–1287.
Richardson, J. P. (1982) Activation of rho protein ATPase requires simultaneous interaction at two kinds of nucleic acid-binding sites.J. Biol. Chem. 257: 5760–5766.
Wang, Y. and P. H. von Hippel (1993)Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho: I. ATPase activation by oligonucleotide cofactors.J. Biol. Chem. 268: 13940–13946.
Miwa, Y., T. Horiguchi, and K. Shigesada (1995) Structural and functional dissections of transcription termination factor rho by random mutagenesis.J. Mol. Biol. 254: 815–837.
Burgess, B. R. and J. P. Richardson (2001) RNA passes through the hole of the protein hexamer in the complex with theEscherichia coli Rho factor.J. Biol. Chem. 276: 4182–4189.
Kim, D. E. and S. S. Patel (2001) The kinetic pathway of RNA binding to theEscherichia coli transcription termination factor Rho.J. Biol. Chem. 276: 13902–13910.
Lowery, C. and J. P. Richardson (1977) Characterization of the nucleoside triphosphatephosphohydrolase (ATPase) activity of RNA synthesis termination factor----: II. Influence of synthetic RNA homopolymers and random copolymers on the reaction.J. Biol. Chem. 252: 1381–1385.
Stitt, B. L. and Y. Xu (1998) Sequential hydrolysis of ATP molecules bound in interacting catalytic sites ofEscherichia coli transcription termination protein Rho.J. Biol. Chem. 273: 26477–26486.
Mori, H., M. Imai, and K. Shigesada (1989) Mutant rho factors with increased transcription termination activities: II. Identification and functional dissection of amino acid changes.J. Mol. Biol. 210: 39–49.
Finger, L. R. and J. P. Richardson (1981) Procedure for purification ofEscherichia coliribonucleic acid synthesis termination protein rho.Biochemistry 20: 1640–1645.
Geiselmann, J., T. D. Yager, S. C. Gill, P. Calmettes, and P. H. von Hippel (1992) Physical properties of theEscherichia coli transcription termination factor rho: 1. Association states and geometry of the rho hexamer.Biochemistry 31: 111–121.
Hiratsuka, T. (1983) New ribose-modified fluorescent analogs of adenine and guanine nucleotides available as substrates for various enzymes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 742: 496–508.
Jameson, D. M. and J. F. Eccleston (1997) Fluorescent nucleotide analogs: synthesis and applications.Methods Enzymol. 278: 363–390.
Moore, K. J. and T. M. Lohman (1994) Kinetic mechanism of adenine nucleotide binding toand hydrolysis by theEscherichia coli Rep monomer: 1. Use of fluorescent nucleotide analogues.Biochemistry 33: 14550–14564.
Piper, J. M. and S. J. Lovell (1981) One-step molybdate method for rapid determination of inorganic phosphate in the presence of protein.Anal. Biochem. 117: 70–75.
Cremo, C. R., J. M. Neuron, and R. G. Yount (1990) Interaction of myosin subfragment 1 with fluorescent ribosemodified nucleotides: A comparison of vanadate trapping and SH1-SH2 cross-linking.Biochemistry 29: 3309–3319.
Woodward, S. K., J. F. Eccleston, and M. A. Geeves (1991) Kinetics of the interaction of 2′(3′)-O-(N-methylanthraniloyl)-ATP with myosin subfragment 1 and actomyosin subfragment: 1. Characterization of two acto-S1-ADP complexes.Biochemistry 30: 422–430.
Bogden, C. E., D. Fass, N. Bergman, M. D. Nichols, and J. M. Berger (1999). The structural basis for terminator recognition by the Rho transcription termination factor.Molecular Cell 3: 487–493.
Martin, M. C. S., N. P. Stamford, N. Dammerova, N. E. Dixon, and J. M. Carazo (1995). A structural model for theEscherichia coli DnaB helicase based on electron microscopy data.J. Struct. Biol. 114: 167–176.
Yu, X., M. J. Jezewska, W. Bujalowski, and E. H. Egelman (1996). The hexamericE. coli DnaB helicase can exist in different quaternary states.J. Mol. Biol. 259: 7–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DE. Kinetic mechanism of nucleotide binding toEscherichia coli transcription termination factor Rho: Stopped-flow kinetic studies using ATP and fluorescent ATP analogues. Biotechnol Bioproc E 9, 23–34 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02949318
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02949318