Abstract
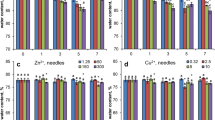
During long-term exposure of pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) seedlings to trichloro- and monochloroacetic acids via root uptake or acid mist treatments, both substances were removed from the plant tissues by metabolic activity. None of the treated plants exhibited visible stress symptoms at the concentrations used. In addition, the exposure to both substances led to dramatic changes in the activity of xenobiotic detoxification enzymes (peroxidase and gluthatione S-transferase) in the needles of the plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton, F.M.;A.S. Crafts (1973): Mode of action of herbicides. Wiley-Interscience Publ. Chichester, New York
Bradford, M.M. (1976): A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye-binding. Anal. Biochem.72:248–254
Castillo, F.J. (1986): Extracellular peroxidases as markers of stress? In:Greppin, H., Penel, C. andGaspar, T. (Eds.) Molecules and physiological aspects of plant peroxidases. Centr. Botan. Genéve, 420–426
Castillo, F.J.;P.R. Miller;H. Greppin (1987): Extracellular biochemical markers of photochemical oxidant air pollution damage to Norway spruce. Experientia43:111–115
Dean, J.V.;J.W. Gronwald;C.V. Eberlein (1990): Induction of glutathione S-transferase isoenzymes in sorghum by herbicide antidotes. Plant Physiol.92:467–473
Debus, R.; B. Dittrich; J. Vollmer; P. Schröder (1989): Biomonitoring organischer Luftschadstoffe — Aufnahme und Wirkung in Pflanzen (Literaturstudie). Landsberg, München, Zürich, ecomed Verlagsgesellschaft AG & Co. KG
Dekant, W.; S. Vamvakas; K. Bertold; S. Schmidt; D. Wild; D. Henschler (1986): Bacterial-Lyase mediated cleavage and mutagenicity of cysteine conjugates derived from the nephrocarcinogenic alkenes trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene and hexachlorobutadiene. Chem.-Biol. Int.: 31–45
Figge, K. (1990): Luftgetragene, organische Schadstoffe in Blattorganen. UWSF — Z. Umweltchem. Ökotox.2(4): 200–207
Fjellstedt, T.A.;R.H. Allen;B.K. Duncan;W.B. Jakoby (1973): Enzymatic conjugation of epoxides with glutathione. J. Biol. Chem.248 (10): 3702–3707
Frank, H.;W. Frank (1985): Chlorophyll-bleaching by atmospheric pollutants and sunlight. Naturwiss.72:139–141
Frank, H.;A. Vincon;J. Reiss;H. Scholl (1990): Trichloroacetic acid in the foliage of forest trees. J. High Resol. Chromatogr.13:733–736
Frank, H.;H. Scholl;S. Sutinen;Y. Norokorpi (1992): Trichloroacetic acid in conifer needles in Finland. Ann. Bot. Fennici29:263–267
Frank, H.;H. Scholl;D. Renschen;B. Rether;A. Laouedj;Y. Norokorpi (1994): Haloacetic acids, phytotoxic secondary air pollutants. ESPR — Environ. Sci. and Pollut. Res.1:4–11
Gürtel, R.;U. Möller;S. Sommer;H. Muller;K. Kleinermanns (1994): Photooxidation of exhaust pollutants. III. Photooxidation of chloroethenes: Degradation efficiencies, quantum yields and products. Chemosphere29:1671–1682
Habig, W.H.;M.J. Pabst;W.B. Jakoby (1974): Glutathione S-transferase. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem.249:7130–7139
Hoekstra, E.J.; E.W.B. De Leer (1993): Natural production of chlorinated compounds in soil. In:Arendt, F., Annokkee, G.J., Bosman, R. and van den Brink, W.J. (Eds.) Contaminated soil’93. Kluwer Acad. Publ., pp. 215–224
Hoekstra, E.J.;E.W.B. De Leer (1995): Organohalogens: the natural alternatives. Chem Brit31:127–131
Hunaiti, A.A.;B.R. Ali (1990): Glutathione S-transferase from oxidiazon treated chickpea. Phytochemistry29:2431–2435
Itoh, N.;S. Kutsuna;T. Ibusuki (1994): A product study of the OH radical initated oxidation of perchloroethylene and trichloroethylene. Chemosphere11:2029–2040
Juun, S.;Y. Norokorpi;J. Ruuskanen (1995): Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) in pine needles caused by atmospheric emissions of kraft pulp mills. Chemosphere30:439–448
Juuti, S.;Y. Norokorpi;T. Helle;J. Ruuskanen (1996): Trichloroacetic acid in conifer needles and arboreal lichens in forest environments. Sci. Tot. Environ.180:117–124
Lamoureux, G.L.; D.S. Frear (1979): Pesticide metabolism in higher plants: in vitro enzyme studies. In:Paulson, D.G., Frear, D.S. and Marks, E.P. (Eds.) Xenobiotic metabolism: In vitro methods. ACS Symposium Series, Washington, D.C. pp. 77–128
Lamoureux, G.L.;D.G. Rusness (1989): The role of glutathione and glutathione S-transferases in pesticide metabolism; selectivity and mode of action in plants and insects. In:Dolphin, D., Poulson, R., Avramovic, O. (Eds.) Glutathione: Chemical biochemical and medical aspects, Vol IIIB, Series: Enzyme and Cofactors. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 153–196
Lamoureux, G.L.;D.G. Rusness (1993): Glutathione in the metabolism and detoxification of the xenobiotics in plants. In:De Kok, L.J., Stulen, I., Rennenberg, H., Brunold, C., Rauser, W. (Eds). Sulfur nutrition and assimilation in higher plants. SPB Academic Press, The Hague
Levine, A.;R. Tenhaken;R. Dixon;C. Lamb (1994): H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell79: 583–593
Markkola, A.M.;R. Ohtonen;O. Tarvainen (1990): Peroxidase activity as an indicator of pollution stress in the fine roots of Pinus sylvestris. Water; Air; Soil Poll.52:149–156
Ostlund-Farrants, A.K.;D.J. Meyer;B. Coles;C. Southan;A. Aitken;P.J. Johnson;B. Ketterer (1989): The separation of glutathione S-transferase subunits by using reverse-phase highpressure liquid chromatography. Biochem. J.245: 423–428
Pflugmacher, S.;P. Schröder (1994): Glutathione S-transferases in trees: Inducibility by various organic xenobiotics. Z. Pflanzenernährung und Bodenkunde158: 71–73
Ploemen, J.H.;A. Van Schanke;B. Van Ommen;P.J. Van Bladeren (1994): Reversible conjugation of ethacrynic acid with glutathione and human glutathione S-transferase P1-1. Cancer Res54: 915–919
Plumacher, J.;P. Schröder (1994): Accumulation and fate of C1/ C2-chlorocarbons and trichloroacetic acid in spruce needles from an Austrian mountain site. Chemosphere29:2467–2476
Reimann, S.;K. Grob;H. Frank (1996): Chloroacetic acids in rain water. ES&T30: 2340–2344
Roy, S.;O. Häninen (1994): Pentachlorophenol: Uptake/elimination kinetics and metabolism in an aquatic plant,Eichhornia crassipes. Env. Toxicol. Chem.13(5): 736–773
Sandermann, H. (1992): Plant metabolism of xenobiotics. Trends Biochem. Sci.17:82–84
Sandermann, H. ( 1994): Higher plant metabolism of xenobiotics: the “green liver” concept. Pharmacogenetics4: 225–241
Schröder, P.;E.J. Belford (1996): Untersuchungen zur Aktivität von Glutathion S-Transferasen in Nadeln von Fichten im Schulterberg- und Christlumprofil. FBVA-Berichte94: 75–82
Schröder, P.;C. Berkau (1993): Characterization of cytosolic glutathione S-transferase in spruce needles. Bot. Acta106:301–306
Schröder, P.;R. Debus (1991): Responses of spruce trees (Picea abies L. Karst) to fumigation with Halon 1211 — first results of a pilot study. In: Plants for toxicity assessment.Gorsuch, J.W., Lower, W.R., Lewis, M.A., Wang, W. (Eds.) ASTM, Philadelphia, pp. 259–266
Schröder, P.;C. Götzberger (1997): Partial purification and characterization of glutathione S-transferase isozymes from the leaves ofJuniperus communis, Larix decidua andTaxus baccata. Appl. Botany71: 31–37
Schröder, P.;C. Götzberger;S. Pflugmacher (1994): On the presence and the isozyme pattern of glutathione S-transferase in leaves of aspen (Populus tremula L.) and beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) — results of a pilot study. Plant Physiol. (Life Sci. Adv.)13: 205–211
Schröder, P.;S. Pflugmacher;H. Rennenberg (1992): Biomarker für organische Schadstoffe in Fichten: Dynamik des Entgiftungsenzyms Glutathion S-Transferase. Angew. Botanik66 (2/1): 174–179
Schröder, P.;H. Rennenberg (1992) Characterization of glutathione S-transferase from dwarf pine needles (Pinus mugo TURR). Tree Physiol.11(2): 151–160
Schröder, P.;D.G Rusness;G.L. Lamoureux;H. Rennenberg (1990): Glutathione-S-Transferase activity in spruce needles. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol.37: 211–218
Schröder, P.; A. Weiss (1991): Uptake and detoxification of chlorinated hydrocarbons by spruce trees. In:Schwartz, S.E. and Slinn, G.W.N. (Eds.) Precipitation Scavenging and Atmosphere Surface Exchange. Hemisphere Publ., 1011–1021
Schröder, P.;A. Wolf (1996): Characterization of glutathione S-transferase from needles of spruce trees from a forest decline stand. Tree Physiol.16 (5): 503–508
Sutinen, S.;S. Juun;L. Korvisto;M. Turunen;J. Ruuskanen (1995): The uptake of and structural changes induced by trichloroacetic acid in the needles of Scots pine seedlings. J. Exp. Bot.46:1223–1231
Sutinen, S.; S. Juun; A. Ryyppö (1997): Long term exposure of scots pine seedlings to monochloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid: Effects on the needles and growth. Ann. Bot. Fennici, accepted
Tuazon, E.C.;R. Atkinson;S.M. Aschmann;M.A. Goodman;A.M. Winer (1988): Atmospheric reactions of chloroethenes with the OH radical. Int. J. Chem. Kinet.20:241–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schröder, P., Juuti, S., Roy, S. et al. Exposure to chlorinated acetic acids: Responses of peroxidase and glutathione S-transferase activity in pine needles. Environ. Sci. & Pollut. Res. 4, 163–171 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02986326
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02986326