Abstract
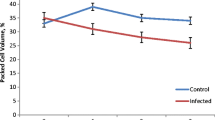
Feline myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) has been diagnosed in many cats infected with feline leukemia virus, although the pathogenesis of this hematopoietic deficiency has been unclear. In this study, we assayed the bone marrow erythroid colony-forming units (CFU-E) and granulocyte-machrophage CFUs (CFU-GM) to investigate the pathogenesis of feline MDS. The number of CFU-E colonies was decreased in 4 of 7 cats with MDS, and the number of CFU-GM colonies was also decreased in 4 cats. Furthermore, small colonies of CFU-GM were found in all 7 cases. These findings indicated that refractory cytopenia of feline MDS could be caused by abnormal maturation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow, as it is in human MDS. The pathogenesis of feline MDS might be similar to that of human MDS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jain N. Classification of myelodysplastic disorders in cats using criteria proposed by the animal leukemia study group: a retrospective study of 181 cases (1969-1992).Com Haematol Int. 1993;3:125–134.
Hisasue M, Nishigaki K, Katae H, et al. Clonality analysis of various hematopoietic disorders in cats naturally infected with feline leukemia virus.J Vet Med Sci. 2000;62:1059–1065.
Hisasue M, Okayama Y, Okayama T, et al. Hematological abnormalities and outcomes in 16 cats with myelodysplastic syndromes.J Vet Int Med. In press.
Jain N, Blue C, Grindem J, et al. Proposed criteria for classification of acute myeloid leukemia in dogs and cats.Vet Clin Pathol. 1991;20:63–80.
Bennett J, Catovsky D, Daniel M, et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes.Brit J Haematol. 1982;51:189–199.
Bennett J. World Health Organization classification of acute leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome.Int J Hematol. 2000;72:131–133.
Simoda T, Shiranaga N, Mashita T, Yuji K, Hasegawa A. A hematological study on thirteen cats with myelodysplastic syndrome.J Vet Med Sci. 2000;62:59–64.
Iscove NN, Sieber F. Erythroid progenitors in mouse bone marrow detected by macroscopic colony formation in culture.Exp Hematol. 1975;3:32–43.
Ruutu T, Partanen S, Lintula R, Teerenhovi L, Knuutila S. Erythroid and granulocyte-macrophage colony formation in myelodysplastic syndromes.Scand J Haematol. 1984;32:395–402.
Lepelley P, Campergue L, Grardel N, Preudhomme C, Cosson A, Fenaux P. Is apoptosis a massive process in myelodysplastic syndromes?Brit J Haematol. 1996;95:368–371.
Yoshida, Y, Kawabata, H, Anzai, N, Tohyama, K. Apoptosis as a cell biological abnormality in myelodysplasia.Pathol Biol (Paris). 1997;45:573–578.
Travaras T, Stewart M, McDougall A, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a defective recombinant feline leukaemia virus associated with myeloid leukemia.J Gene Virol. 1990;71:343–354.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nagashima, N., Hisasue, M., Higashi, K. et al. Bone Marrow Colony-Forming Unit Assay in Cats With Naturally Occurring Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Int J Hematol 73, 453–456 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02994006
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02994006