Abstract
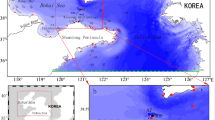
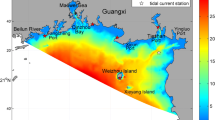
This study is based on a series of numerical modeling experiments to understand the tidal circulation in the Kangjin Bay (KB). The tidal circulation in the KB is mostly controlled by the inflow from two channels, Noryang and Daebang which introduce the open ocean water into the northern part of the KB with relatively strong tidal current, while in the southern part of the KB, shallowest region of the entire study area, weak tidal current prevails. The model prediction of the sea level agrees with observed records at skill scores exceeding 90 % in terms of the four major tidal constituents (M2, S2, K1, O1). However, the skill scores for the tidal current show relatively lower values of 87, 99, 59, 23 for the semi-major axes of the constituents, respectively. The tidal ellipse parameters in the KB are such that the semi-major axes of the ellipse for M2 range from 1.7 to 38.5 cm/s and those for S2 range from 0.5 to 14.4 cm/s. The orientations of the major-axes show parallel with the local isobath. The eccentricity values at various grid points of ellipses for M2 and S2 are very low with 0.2 and 0.06 on the average, respectively illustrating that the tidal current in the KB is strongly recti-linear. The magnitude of the tidal residual current speed in the KB is on the order of a few cm/s and its distribution pattern is very complex. One of the most prominent features is found to be the counter-clockwise eddy recirculation cell at the mouth of the Daebang Channel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blumberg, A. F. and G. L. Mellor. 1987. A description of a three-dimensional coastal ocean circulation model. p. 1–16. In:Three-Dimensional Coastal Ocean Models, Coastal Estuarine Sci., vol. 4, ed. by N. S. Heaps, AGU, Washington, D. C.
Blumberg, A.F., L.A. Khan, and J.P. John. 1999. Three-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Model of New York Harbor Region.J. Hydr. Eng.,125 (8), 799–816.
Cai S., Q. Huang, and X. Long. 2003. Three-dimensional numerical model study of the residual current in the South China Sea.Oceanologica Acta,26 (5), 597–607.
Fong, D. A. 1998. Dynamics of freshwater plumes: Observations and numerical modeling of the wind forced response and along-shore freshwater transport. Ph.D. thesis, MIT/WHOI Joint Program in Oceanography, Woods Hole.
Foreman, M.G.G. 1978. Manual for Tidal Current Analysis and Prediction. Pacific Marine Science Report 78-6, Institute of Ocean Sciences, Patricia Bay, Victoria, B.C. 39 p.
Gomez-Valdes, J., J.A. Delgado, and J.A. Dworak. 2003. Overtides, compound tides and tidal-residual current in Ensenada de la Paz Lagoon, Baja California Sur, Mexico.Geophysica Int.,42, 623–634.
Horrevoetsa, A.C., H.H.G. Savenijea, J.N. Schuurmana, and S. Graasa. 2004. The influence of river discharge on tidal damping in alluvial estuaries.J. Hydrol.,294, 213–228.
Ji, Z. G., G. Hu, J. Shen, and Y. Wan. 2007. Three-dimensional modeling of hydrodynamic processes in the St. Lucie Estuary.Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci.,73, 188–200.
Jung, K.Y. 2007. Three-Dimensional Numerical Modeling of Tidal, Wind-Driven and Density Currents in the Kangjin bay, South Sea, Korea. M.S. thesis, Chungnam National University. 130 p.
Kourafalou, V.H., L. Oey, J. Wang, and T.N. Lee. 1996a. The fate of river discharge on the continental shelf, 1, Modeling the river plume and inner shelf coastal current.J. Geophys. Res.,101, 3415–3434.
Kourafalou, V.H., T.N. Lee, L. Oey, and J. Wang. 1996b. The fate of river discharge on the continental shelf, 2, Transport of coastal low-salinity waters under realistic wind and tidal forcing.J. Geophys. Res.,101, 3435–3456.
Levasseur, A., L. Shi, N.C. Wells, D.A. Purdie, and B.A. Kelly-Gerreyn. 2007. A three-dimensional hydrodynamic model of estuarine circulation with an application to Southampton Water, UK.Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci.,73, 753–767.
Matsumoto, K., T. Takanezawa, and M. Ooe. 2000. Ocean Tide Models Developed by Assimilating TOPEX/POSEIDON Altimeter Data into Hydrodynamical Model: A Global Model and a Regional Model Around Japan.J. Oceanogr.,56, 567–581.
McLaughlin, J.W., A. Bilgili, and D.R. Lynch. 2003. Numerical modeling of tides in the Great Bay Estuarine System: Dynamical balance and spring-neap residual modulation.Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci.,57, 283–296.
Marinone, S.G. and M.F. Lavýn. 2005. Tidal current ellipses in a three-dimensional baroclinic numerical model of the Gulf of California.Estuar. Coast.Shelf Sci.,64, 519–530.
Mellor, G.L. and T. Yamada. 1982. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problem.Rev. Geophys. Space Physics,20, 851–875.
Odamaki, M. 1989. Tides and Tidal Current in the Tusima Strait.J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,45, 65–82.
Orlanski, I. 1976. A simple boundary condition for unbounded hyperbolic flows.J. Comput. Phys.,21, 251–269.
Park, K., H.S. Jung, H.S. Kim, and S.M. Ahn. 2005. Three-dimensional hydrodynamic-eutrophication model (HEM-3D): Application to Kwang-Yang Bay, Korea.Mar. Environ. Res.,60 (2), 171–193.
Pawlowicz, R., B. Beardsley, and S. Lentz. 2002. Classical tidal harmonic analysis including error estimates in MATLAB using T_TIDE.Comput. Geosci.,28, 929–937.
Ro, Y.J. 2006. Internet-based Realtime Monitoring of the Environm ental Parameters in the Marine Large-Arc Shell Culture Bed and Its Productivity Assessment Model, Final Report, Ministry of Maritime Affairs and Fisheries. 155 p.
Ro, Y.J. 2007. Tidal and Sub-tidal Current Characteristics in the Kangjin Bay, South Sea, Korea.Ocean Sci. J.,42 (1), 19–30.
Ro, Y. J., K.H. Na, and C. K. Kim. 2004. 1st year Interim report for the Internet based Realtime Monitoring of the Oceanic Condition in the Kangjin Bay for Aqua-culture and its Productivity Estimation submitted to KMI, MOMAF. 95 p.
Ro, Y.J. and K.Y. Jung. 2007. 3-D Baroclinic Numerical Modeling of River Plume and Density Current due to Dam Water Discharge. To be submitted toOcean Science Journal.
Ro, Y.J. and Y.H. Choi. 2004. Application of the Realtime Monitoring of Oceanic Conditions in the Coastal water for Environmental Management.J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr.,39 (2), 148–154.
Ro, Y.J., W.S. Jun, K.Y. Jung, and B.H. Kim. 2005. Numerical Modeling of River Plume in the Kangjin Bay and Its Implication for the Ecosystem. Proc. of Autumn Meeting, 2005 of the Korean Society of Oceanography, Nov. 3–4, 2005, Ansan, Korea, 218–220.
Smagorinsky, J. 1963. General circulation experiments with the primitive equations, I. The basic experiments.Mon. Weather Rev.,91, 99–164.
Valle-Levinson, A. and T. Matsuno. 2003. Tidal and subtidal Flow along a Cross-shelf Transect on the East China Sea.J. Oceanogr.,59, 573–584.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ro, Y.J., Jung, K.Y., Jun, W.S. et al. Numerical modeling of tide and tidal current in the kangjin bay, south sea, Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 42, 153–163 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03020919
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03020919