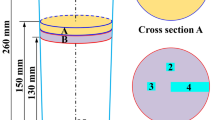
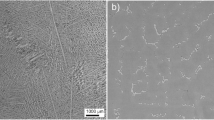
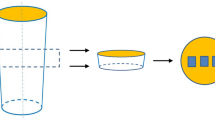
Abstract
A study was carried out to determine the effect of cerium addition on HAZ cracking susceptibility in cast alloy 718 welds. The cause of HAZ cracking was also investigated using commercial cast alloy 718 varying in grain size at three levels. The hot cracking test results for commercial cast alloy 718 indicated that the fine-grained alloy was less sensitive to HAZ cracking. Furthermore, cerium addition of up to 0.3 wt.% was found to have a beneficial effect in reducing HAZ cracking susceptibility. When cerium addition exceeds 0.3 wt%, HAZ cracking susceptibility increased further. The mechanism of HAZ cracking was found to be related to intergranular liquation caused by the eutectic melting of sulfur containing a laves cluster at the grain boundaries. The degree of grain boundary liquation in the fine-grained specimen was less than that of the coarse-grained specimen due to a decrease in the amount of laves cluster and sulfur segregation in it at the grain boundaries, which seems to be responsible for a reduction in hot cracking susceptibility in the fine-grained specimen. Microscopic observation suggested that the improved HAZ cracking susceptibility in cerium containing alloy could be attributed to a reduction in the amount of laves cluster and sulfur segregation in it at grain boundaries due to the grain size reduction and sulfur-scavenging effects of cerium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. L. Eiselstein,Advances in the Technology of Stainless Steels and Related Alloys, p. 62, ASTM STP 369, Philadelphia, PA (1965).
I. Woo, K. Nishimoto, K. Tanaka and M. Shirai,Welding Int. 14, 514 (2000).
R. G. Thompson and S. Genculu,Welding J. 62, 337 s (1967).
P. J. Valdez and J. B. Steinman,Effect of Minor Elements on the Weldability of High-Nickel Alloys, p. 93, Welding Research Council, New York, NY (1969).
R. G. Thompson,J. of Metals, 44s (1988).
K. Nishimoto, I. Woo and M. Shirai,ISIJ Int. 40, S39 (2000).
W. A. Baeslack and D. E. Nelson,Metallography 19, 371 (1986).
X. Hung, M. C. Chaturvedi and N. L. Richards,Metall. Trans. A 27, 785 (1996).
R. G. Thompson, D. E. Mayo and B. Radhakrishnan,Metall. Trans. A 22, 557 (1991).
F. Matsuda, H. Nakagawa, S. Katayama and Y. Arata,Trans. JWRI 11, 79 (1982).
C. H. Lee,Metals and Materials 2, 81 (1996).
K. Nishimoto, I. Woo and M. Shirai,IIW Doc. IX-1965-00 (2000).
I. Woo, K. Nishimoto, K. Tanaka and M. Shirai,Welding Int. 14, 365 (2000).
Y. Zhu, S. Zhang, T. Zhang, L. Lou, Y. Tong, X. Ning, Z. Hu and X. Xie,Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, p. 89, TMS, USA (1994).
H. Li, Mclean, J. W. Rutter and I. D. Sommerville,Metall. Trans. B 19, 383 (1988).
M. Guo and H. Suito,ISIJ Int. 39, 722 (1999).
T. Ohashi, T. Hiromoto, H. Fuji, Y. Nuri and K. Asano,Tetsu-to-Hagane 6, 614 (1976).
G. A. Knorovsky, M. J. Cieslak, T. J. Headley, A. D. Romig and W. F. Hammetter,Metall. Trans. A 20, 887 (1991).
K. Nishimoto and I. Woo,Report on Research of Welding Technologies for Space Crafts, p. 1, Jpn. Welding Eng. Soc, Japan (1999).
ASM Handbook, vol. 3, p. 203, ASM Int, USA (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, I., Nishimoto, K. Metallurgical factors contributing to HAZ cracking susceptibility in cast alloy 718 welds and its improvement by cerium addition. Met. Mater. Int. 7, 241–249 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03026982
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03026982