Abstract
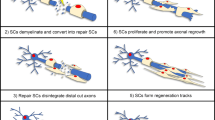
The mechanisms determining the fate of Schwann cells during disease and injury of the adult mammalian peripheral nervous system (PNS) are becoming defined by current advances in molecular neurobiology. It is now apparent that the molecular pathways which regulate the production of the mature myelinating Schwann cell during development may also apply to degenerative and regenerative mechanisms following PNS disease. This review outlines neurobiological responses of Schwann cells during development, injury and disease in order to define the molecular pathways which regulate these crucial events. These mechanisms have implications for our attempts to intervene pharmacologically during pathologies of the PNS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton ES, G Weskamp, LG Reichardt and WD Matthew (1994) Nerve growth factor and its low-affinity receptor promote Schwann cell migration.Proc. Natl. Acad. Set USA 91, 2795–2799.
Araki T, R Nagarajan and J Milbrandt (2001) Identification of genes induced in peripheral nerve after injury. Expression profiling and novel gene discovery.J. Biol. Chem. 276, 34131–34141.
Atanasoski S, S Shumas, C Dickson, SS Scherer and U Suter (2001) Differential cyclin-D1 requirements of proliferating Schwann cells during development and after injury.Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 18, 581–592.
Atanasoski S, SS Scherer, KA Nave and U Suter (2002) Proliferation of Schwann cells and regulation of Cyclin-D1 expression in an animal model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A.J. Neurosci. Res. 67, 443–449.
Baldwin ASJr(1996) The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins, new discoveries and insights.Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 649–683.
Bao L, JU Lindgren, Pvan der Meide, S Zhu, HG Ljunggren and J Zhu (2002) The critical role of IL-12p40 in initiating, enhancing, and perpetuating pathogenic events in murine experimental autoimmune neuritis.Brain Pathol. 12, 420–429.
Barnes PJ and M Karin (1997) Nuclear factor-kappaB, a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases.NEJM 336, 1066–1071.
Bellone E, E Di Maria, S Soriani, A Varese, LL Doria, F Ajmar and P Mandich (1999) A novel mutation (D305V) in the early growth response 2 gene is associated with severe Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1 disease.Hum. Mutat. 14, 353–354.
Bentley CA and KF Lee (2000) p75 is important for axon growth and Schwann cell migration during development.J. Neurosci. 20, 7706–7715.
Bhakar AL, PP Roux, C Lachance, D Kryl, C Zeindler and PA Barker (1999) The p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) alters tumour necrosis factor-mediated NF-κB activation under physiological conditions, but direct p75NTR-mediated NF-κB activation requires cell stress.J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21443–21449.
Bonetti B, P Valdo, C Stegagno, R Tanel, G Zanusso, D Ramarli, E Fiorini, S Turazzi, M Carner and G Moretto (2000) Tumour necrosis factor alpha and human Schwann cells: signalling and phenotype modulation without cell death.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 59, 74–84.
Brown MC, VH Perry, ER Lunn, S Gordon and R Heumann (1991) Macrophage dependence of peripheral sensory nerve regeneration, possible involvement of nerve growth factor.Neuron 6, 359–370.
Bui NT, HG Konig, C Culmsee, E Bauerbach, M Poppe, J Krieglstein and JH Prehn (2002) p75 neurotrophin receptor is required for constitutive and NGF-induced survival signalling in PC12 cells and rat hippocampal neurones.J. Neurochem. 81, 594–605.
Busuttil V, V Bottero, C Frelin, B Imbert, JE Ricci, P Auberger and JF Peyron (2002) Blocking NF-kappaB activation in Jurkat leukemic T cells converts the survival agent and tumor promoter PMA into an apoptotic effector.Oncogene 21, 3213–3224.
Chan JR, JM Cosgaya, YJ Wu and EM Shooter (2001) Neurotrophins are key mediators of the myelination program in the peripheral nervous system.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 14661–14668.
Chan JR, TA Watkins, JM Cosgaya, C Zhang, L Chen, LF Reichardt, EM Shooter and BA Barres (2004) NGF controls axonal receptivity to myelination by Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes.Neuron 43, 183–191.
Chandler S, KM Miller, JM Clements, J Lury, DJ Corkill, DCC Anthony, SE Adams and AJ Gearing (1997) Matrix metalloproteinases, tumour necrosis factor and multiple sclerosis, an overview.J. Neuroimmunol. 72, 155–161.
Chandross KJ, DC Spray, RI Cohen, NM Kumar, M Kremer, R Dermietzel and JA Kessler (1996) TNF-α inhibits Schwann cell proliferation, connexin46 expression, and Gap junctional communication.Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 7, 479–500.
Chang A, WW Tourtellotte, R Rudick and BD Trapp (2002) Premyelinating oligodendrocytes in chronic lesions of multiple sclerosis.NEJM 346, 165–173.
Cheung RT and DF Cechetto (2000) Neuropeptide Y-Y1 receptor antisense oligodeoxynucleotide increases the infarct volume after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.Neuroscience 98, 771–777.
Clements JM, JA Cossins, GM Wells, DJ Corkill, K Helfrich and ML Wood (1997) Matrix metalloproteinase expression during experimental autoimmune encephalitis and effects of a combined matrix metalloproteinase and tumour necrosis factor-α inhibitor.J. Neuroimmunol. 74, 85–94.
Cosgaya JM, JR Chan and EM Shooter (2002) The neurotrophin receptor p75NTR as a positive modulator of myelination.Science 298, 1245–1248.
Coulson EJ, K Reid, GL Barrett and PF Bartlett (1999) p75 neurotrophin receptor-mediated neuronal death is promoted by Bcl-2 and prevented by Bcl-xL.J. Biol. Chem. 274, 16387–16391.
Coulson EJ, K Reid, KM Shipham, S Morley, TJ Kilpatrick and PF Bartlett (2004) The role of neurotransmission and the Chopper domain in p75 neurotrophin receptor death signaling.Prog. Brain Res. 146, 41–62.
DiStefano PS, DM Chelsea, CM Schick and JF McKelvy (1993) Involvement of a metalloprotease in low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor truncation, inhibition of truncationin vitro andin vivo.J. Neurosci. 13, 2405–2414.
Dowsing BJ, WA Morrison, NA Nicola, GP Starky, T Bucci and TJ Kilpatrick (1999) Leukaemia inhibitory factor is an autocrine survival factor for Schwann cells.J. Neurochem. 13, 96–104.
Frade JM and YA Barde (1998) Microglia-derived nerve growth factor causes cell death in the developing retina.Neuron 20, 35–41.
Frade JM and YA Barde (1999) Genetic evidence for cell death mediated by nerve growth factor and the neurotrophin receptor p75 in the developing mouse retina and spinal cord.Development 126, 683–690.
Funakoshi H, J Frisen and G Barbany (1993) Differential expression of mRNAs for neurotrophins and their receptors after axotomy of the sciatic nerve.J. Cell. Biol. 123, 455–465.
Garratt AN, S Critsch and C Birchmeier (2000a) β-neuregulin-1, a factor with many functions in the life of a Schwann cell.Bioessays 22, 987–996.
Garratt AN, O Voiculescu, P Topilko, P Charnay and C Birchmeier (2000b) A dual role oferbB2 in myelination and in expansion of the schwann cell precursor pool.J. Cell. Biol. 148, 1035–1046.
Gearing AJ and AG Bruce (1992) Oncostatin M binds the highaffinity leukemia inhibitory factor receptor.New Biol. 4, 61–65.
Gearing AJ, P Beckett, M Christodoulou, M Churchill, J Clements, AH Davidson, AH Drummond, WA Galloway, R Gilbert, JL Gordonet al. (1994) Processing of tumour necrosis factor-alpha precursor by metalloproteinases.Nature 370, 555–557.
Grell M, G Zimmermann, E Grottfried, CM Chen, U Grunwald, DC Huang, YH Wu Lee, H Durkop, H Englemann and P Scheurich (1999) Induction of cell death by tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 2, CD40, and CD30: a role of TNFR1 activation by endogenous membrane-anchored TNF.EMBO J. 18, 3034–3043.
Grinspan JB, MA Marchionni, M Reeves, M Coulaloglou and SS Scherer (1996) Axonal interactions regulate Schwann cell apoptosis in developing peripheral nerve: neuregulin receptors and the role of neuregulins.J. Neurosci. 16, 6107–6118.
Gupta S (2002) A decision between life and death during TNF-α- Induced signaling.J. Clin. Immunol. 22, 185–194.
Hall SM, EJ Redford and KJ Smith (2000) Tumour necrosis factorex has few morphological effects within the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, in contrast to its effects in the peripheral nervous system.J. Neuroimmunol. 106, 130–136.
Hartung HP and BC Kieseier (2000) The role of matrix metalloproteinases in autoimmune damage to the central and peripheral nervous system.J. Neuroimmunol. 107, 140–147.
Herr W, RA Sturm, RG Clerc, LM Corcoran, D Baltimore, PA Sharp, HA Ingraham, MG Rosenfeld, M Finney, G Ruvkun and HR Horvitz (1988) The POU domain, a large conserved region in the mammalianpit-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products.Genes Dev. 2, 1513–1516.
Higuchi H, T Yamashita, H Yoshikawa and M Tohyama (2003) PKA phosphorylates the p75 receptor and regulates its localisation to lipid rafts.EMBO J. 22, 1790–1800.
Hughes PM, GM Wells, JM Clements, AJ Gearing, EJ Redford, M Davies, KJ Smith, RA Hughes, MC Brown and KM Miller (1998) Matrix metalloproteinase expression during experimental autoimmune neuritis.Brain 121, 481–494.
Jessen KR and R Mirsky (1998) Origin and early development of Schwann cells.Microscop. Res. Tech. 41, 393–402.
Keifer R, BC Kieseier, G Stoll and HP Hartung (2001) The role of macrophages in immune-mediated damage to the peripheral nervous system.Prog. Neurobiol. 64, 109–127.
Khursigara G, J Bertin, H Yano, H Moffett, PS DiStefano and MV Chao (2001) A prosurvival function for the p75 receptor death domain mediated via the caspase recruitment domain receptorinteracting protein 2.J. Neurosci. 21, 5854–5863.
Kim HA, SL Pomeroy, W Whoriskey, I Pawlitzky, LI Benowitz, P Sicinski, CD Stiles and TM Roberts (2000) A developmentally regulated switch directs regenerative growth of Schwann cells through cyclin D1.Neuron 26, 405–416.
Kim GM, J Xu, J Xu, SK Song, P Yan, G Ku, XM Xu and CY Hsu (2001a) Tumour necrosis factor receptor deletion reduces nuclear factor-κB activation, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein-2 expression, and functional recovery after traumatic spinal cord injury.J. Neurosci. 21, 6617–6625.
Kim HA, N Ratner, TM Roberts and CD Stiles (2001b) Schwann cell proliferative responses to cAMP and Nf1 are mediated by cyclin D1.J. Neurosci. 21, 1110–1116.
La FleurM, JL Underwood, DA Rappolee and Z Werb (1996) Basement membrane and repair of injury to peripheral nerve, defining a potential role for macrophages, matrix metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1.J. Exp. Med. 184, 2311–2326.
Levi AD, RP Bunge, JA Lofgren, L Meima, F Hefti, K Nikolics and MX Sliwkowski (1995) The influence of heregulins on human Schwann cell proliferation.J. Neurosci. 15, 1329–1340.
Lindenlaub T and C Sommer (2003) Cytokines in sural nerve biopsies from inflammatory and non-inflammatory neuropathies.Acta Neuropathol. 105, 593–602.
Lunn ER, J Scourfield, RJ Keynes and CD Stern (1987) The neural tube origin of ventral root sheath cells in the chick embryo.Development 101, 247–254.
Majdan M, C Lachance, A Gloster, R Aloyz, C Zeindler, S Bamji, A Bhakar, D Belliveau, J Fawcett, FD Miller and PA Barker (1997) Transgenic mice expressing the intracellular domain of the p75 neurotrophin receptor undergo neuronal apoptosis.J. Neurosci. 17, 6988–6998.
Matsuoka I, M Meyer and H Thoenen (1991) Cell-type-specific regulation of nerve growth factor (NGF) synthesis in non-neuronal cells: comparison of Schwann cells with other cell types.J. Neurosci. 11, 3165–3177.
Meier C, E Parmantier, A Brennan, R Mirsky and KR Jessen (1999) Developing Schwann cells acquire the ability to survive without axons by establishing an autocrine circuit involving insulin-like growth factor, neurotrophin-3, and platelet-derived growth factor-BB.J. Neurosci. 19, 3847–3859.
Michailov GV, MW Sereda, BG Brinkmann, TM Fischer, B Haug, C Birchmeier, L Role, C Lai, MH Schwab and KA Nave (2004) Axonal neuregulin-1 regulates myelin sheath thickness.Science 304, 700–703.
Micheau O and J Tschopp (2003) Induction of TNF receptor Imediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes.Cell 114, 181–190.
Mirsky R and KR Jessen (1996) Schwann cell development, differentiation and myelination.Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 6, 89–96.
Mirsky R and KR Jessen (1999) The neurobiology of Schwann cells.Brain Pathol. 9, 293–311.
Mirsky R and KR Jessen (2001) Embryonic and early postnatal development of Schwann cells, In,Molecular and Cellular Neurobiology Series: Glial Cell Development, 2nd Edition (Jessen KR and WD Richardson, Eds.) (Oxford University Press: New York), pp 1–20.
Mirsky R, KR Jessen, A Brennan, D Parkinson, Z Dong, C Meier, E Parmantier and D Lawson (2002) Schwann cells as regulators of nerve development.J. Physiol. (Paris) 96, 17–24.
Moneo V, M del Valle Guijarro, W Link and A Carnero (2003) Overexpression of cyclin D1 inhibits TNF-induced growth arrest.J. Cell Biochem. 89, 484–499.
Monuki ES, G Weinmaster, R Kuhn and G Lemke (1989) SCIP: a glial POU domain gene regulated by cyclic AMP.Neuron 3, 783–793.
Morrison SJ, SE Perez, Z Qiao, JM Verdi, C Micks, G Weinmaster and DJ Anderson (2000) Transient notch activation initiates an irreversible switch from neurogenesis to gliogenesis by neural crest stem cells.Cell 101, 499–510.
Myers RR, Y Sekiguchi, S Kikuchi, B Scott, S Medicherla, A Protter and WM Campana (2003) Inhibition of p38 MAP kinase activity enhances axonal regeneration.Exp. Neurol. 184, 606–614.
Nagarajan R, J Svaren, N Le, T Araki, M Watson and J Milbrandt (2001) EGR2 mutations in inherited neuropathies dominant-negatively inhibit myelin gene expression.Neuron 30, 355–368.
Nakao J, J Shinoda, Y Nakai, S Murase and K Uyemura (1997) Apoptosis regulates the number of Schwann cells at the premyelinating stage.J. Neurochem. 68, 1853–1862.
Nickols JC, W Valentine, S Kanwal and BD Carter (2003) Activation of the transcription factor NF-κB in Schwann cells is required for peripheral nerve myelin formation.Nat. Neurosci. 6, 161–167.
Parkinson DB, A Bhaskaran, A Droggiti, S Dickinson, M D’Antonio, R Mirsky and KR Jessen (2004)Krox-20 inhibits Jun-NH2-terminal kinase/c-Jun to control Schwann cell proliferation and death.J. Cell. Biol. 164, 385–394.
Perry VH, MC Brown and S Gordon (1987) The macrophage response to central and peripheral nerve injury. A possible role for macrophages in regeneration.J. Exp. Med. 165, 1218–1223.
Perry VH, JW Tsao, S Feam and MC Brown (1995) Radiationinduced reductions in macrophage recruitment have only slight effects on myelin degeneration in sectioned peripheral nerves of mice.Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 271–280.
Petratos S, H Butzkueven, K Shipham, H Cooper, T Bucci, K Reid, E Lopes, B Emery, SS Cheema and TJ Kilpatrick (2003) Schwann cell apoptosis in the postnatal axotomised sciatic nerve is mediated via NGF through the low affinity neurotrophin receptor.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 62, 398–411.
Putzu GA, D Figarella-Branger, C Bouvier-Labit, A Liprandi, N Bianco and JF Pellissier (2000) Immunohistochemical localisation of cytokines, C5b-9 and ICAM-1 in peripheral nerve of Guillain-Barre syndrome.J. Neurol. Sci. 174, 16–21.
Redford EJ, SM Hall and KJ Smith (1995) Vascular changes and demyelination induced by the intraneural injection of tumour necrosis factor.Brain 118, 869–878.
Redford EJ, KJ Smith, NA Gregson, M Davies, PM Hughes and AJ Gearing (1997) A combined inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase activity and tumour necrosis factor alpha processing attenuates experimental autoimmune neuritis.Brain 120, 1895–1905.
Roberts JM(1999) Evolving ideas about cyclins.Cell 98, 129–132.
Rosenberg GA(2002) Matrix metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation.Glia 39, 279–291.
Rothe M, MG Pan, WJ Henzel, TM Ayres and DV Goeddel (1995) The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins.Cell 83, 1243–1252.
Roux PP and PA Barker (2002) Neurotrophin signaling through the p75 neurotrophin receptor.Prog. Neurobiol. 67, 203–233.
Said G and M Hontebeyrie-Joskowicz (1992) Nerve lesions induced by macrophage activation.Res. Immunol. 143, 589–599.
Sancho S, P Young and U Suter (2001) Regulation of Schwann cell proliferation and apoptosis in PMP22-deficient mice and mouse models of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A.Brain 124, 2177–2187.
Saren P, HG Welgus and PT Kovanen (1996) TNF-α and IL-1β selectively induce expression of 92-kDa gelatinase by human macrophages.J. Immunol. 157, 4159–4165.
Sarih M, B Souvannavong, SC Brown and A Adam (1993) Silica induces apoptosis in macrophages and the release of interleukin1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta.J. Leukocyte Biol. 54, 407–413.
Scherer SS, DY Wang, R Kuhn, G Lemke, L Wrabetz and J Kamholz (1994) Axons regulate Schwann cell expression of the POU transcription factor SCIP.J. Neurosci. 14, 1930–1942.
Scherer SS and JL Salzer (2001) Axon-Schwann cell interactions during peripheral nerve degeneration and regeneration, InGlial Cell Development: Basic Principles and Clinical Relevance (Jessen KR and WD Richardson, Eds.), (Oxford University Press: New York), pp 300–330.
Schulze-Osthoff K, D Ferrari, M Los, S Wesselborg and ME Peter (1998) Apoptosis signaling by death receptors.Eur. J. Biochem. 254, 439–459.
Shamash S, F Reichert and S Rotshenker (2002) The cytokine network of Wallerian degeneration, tumour necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1α, and interleukin-1β.J. Neurosci. 22, 3052–3060.
Sherr CJ (1993) Mammalian GI cyclins.Cell 73, 1059–1065.
Sherr CJ(1996) Cancer cell cycles.Science 274, 1672–1677.
Shubayev VI and RR Myers (2000) Upregulation and interaction of TNFalpha and gelatinases A and B in painful peripheral nerve injury.Brain Res. 855, 83–89.
Siebert H, N Dippel, M Mader, F Weber and W Bruck (2001) Matrix metalloproteinase expression and inhibition after sciatic nerve axotomy.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 60, 85–93.
Skoff AM, RP Lisak, B Bealmear and JA Benjamins (1998) TNF-α and TGF-β act synergistically to kill Schwann cells.J. Neurosci. Res. 53, 747–756.
Soilu-Hanninen M, P Ekert, T Bucci, DE Syroid, PF Bartlett and TJ Kilpatrick (1999) Nerve growth factor signaling through p75 induces apoptosis in Schwann cells via a Bcl2-independent pathway.J. Neurosci. 19, 4828–4838.
Syroid DE, PJ Maycox, M Soilu-Hanninen, S Petratos, T Bucci, P Burrola, S Murray, S Cheema, KF Lee, G Lemke and TJ Kilpatrick (2000) Induction of postnatal Schwann cell death by the low-affinity neurotrophin receptorin vitro and after axotomy.J. Neurosci. 20, 5741–5747.
Taniuchi M, HB Clarke, JB Schweitzer and EMJ Johnson (1988) Expression of nerve growth factor receptors by Schwann cells of axotomised peripheral nerves, ultrastructural location, suppression by axonal contact, and binding properties.J. Neurosci. 8, 664–681.
Tartaglia L, D Pennica and DV Goeddel (1993) Ligand passing: the 75-kDa tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor recruits TNF for signaling by the p55-kDa TNF receptor.J. Biol. Chem. 268, 18542–18548.
Timmerman V, PDe Jonghe, C Ceuterick, EDe Vriendt, A Lofgren, E Nelis, LE Warner, JR Lupski, JJ Martin and CVan Broeckhoven (1999) Novel missense mutation in the early growth response 2 gene associated with Dejerine-Sottas syndrome phenotype.Neurology 52, 1827–1832.
Topilko P, S Schneider-Maunoury, G Levi, ABaron-Van Evercooren, AB Chennoufi, T Seitanidou, C Babinet and P Charnay (1994)Krox-20 controls myelination in the peripheral nervous system.Nature 371, 790–796.
Topilko P, G Levi, G Merlo, S Mantero, C Desmarquet, G Mancardi and P Charnay (1997) Differential regulation of the zinc finger genesKrox-20 andKrox-24 (Egr1) suggests antagonistic roles in Schwann cells.J. Neurosci. Res. 50, 702–712.
Topilko P and D Meijer (2001) Transcription factors that control Schwann cell development and myelination, InGlial Cell Development: Basic Principles and Clinical Relevance (Jessen KR and WD Richardson, Eds.), (Oxford University Press: New York), pp 223–244.
Trinchieri G (1995) Interleukin-12, a proinflammatory cytokine with immunoregulatory functions that bridge innate resistance and antigen-specific adaptive immunity.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 251–276.
Turnley AM and PF Barlett (2000) Cytokines that signal through the Leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor-B complex in the nervous system.J. Neurochem. 74, 1–11.
Wagner R and RR Myers (1996) Schwann cells produce tumour necrosis factor alpha: expression in injured and non-injured nerves.Neuroscience 73, 625–629.
Warner LE, P Mancias, IJ Butler, CM McDonald, L Keppen, KG Koob and JR Lupski (1998) Mutations in the early growth response 2 (EGR2) gene are associated with hereditary myelinopathies.Nat. Genet. 18, 382–384.
Watanabe M, Y Toyama and A Nishiyama (2002) Differentiation of proliferated NG2-positive glial progenitor cells in a remyelinating lesion.J. Neurosci. Res. 69, 826–836.
Weishaupt A, W Bruck, T Hartung, KV Toyka and R Gold (2001) Schwann cell apoptosis in experimental autoimmune neuritis of the Lewis rat and the functional role of tumour necrosis factor-α.Neurosci. Lett. 306, 77–80.
Weiss T, M Grell, K Siekienski, F Muhlenbeck, H Durkop, K Pfizenmaier, P Scheurich and HJ Wajant (1998) TNFR-80-dependent enhancement of TNFR60-induced cell death is mediated by TNFR-associated factor-2 and is specific for TNFR60.J. Immunol. 161, 3136–3142.
Winseck AK, J Caldero, D Ciutat, D Prevette, SA Scott, G Wang, JE Esquerda and RW Oppenheim (2002) In vivo analysis of Schwann cell programmed cell death in the embryonic chick: regulation by axons and glial growth factor.J. Neurosci. 22, 4509–4521.
Yamauchi J, JR Chan and EM Shooter (2003) Neurotrophin 3 activation of TrkC induces Schwann cell migration through the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 14421–14426.
Yamauchi J, JR Chan and EM Shooter (2004) Neurotrophins regulate Schwann cell migration by activating divergent signaling pathways dependent on Rho GTPases.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101(23), 8774–8779. Epub 2004 May 25.
Yang L, K Lindholm, Y Konishi, R Li and S Yong (2002) Target depletion of distinct tumour necrosis factor receptor subtypes reveals hippocampal neuron death and survival through different signal transduction pathways.J. Neurosci. 22, 3025–3032.
Yarden Y and MX Sliwkowski (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network.Nat. Rev. Mole. Cell Biol. 2, 127–137.
Zhang J, X Luo, CJ Xian, Z Liu and X Zhou (2000) Endogenous BDNF is required for myelination and regeneration of injured sciatic nerve in rodents.Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 4171–4180.
Zorick TS, DE Syroid, E Arroyo, SS Scherer and G Lemke (1996) The transcription factors SCIP andKrox-20 mark distinct stages and cell fates in Schwann cell differentiation.Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 8, 129–145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyle, K., Azari, M.F., Profyris, C. et al. Molecular mechanisms in schwann cell survival and death during peripheral nerve development, injury and disease. neurotox res 7, 151–167 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033784
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033784