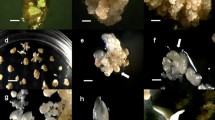
Abstract
Somatic embryogenesis and subsequent plant regeneration were obtained from immature inflorescence segments of two cultivars ofSorghum bicolor L. Moench. Callus was induced on Murashige and Skoog’s medium supplemented with 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2 mg/l) and zeatin (0.1 mg/l). Transfer of calli to Murashige and Skoog medium alone or with reduced level of auxins with or without cytokinins resulted in the production of somatic embryos and plantlets. The combination of a cytokinin with Triiodobenzoic acid promoted the highest number of somatic embryoids. The best response was obtained from inflorescences 10–25 mm in length. Regenerated plants were transferred to field for further evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyes C J and Vasil I K 1984 Plant regeneration by somatic embryogenesis from cultured young inflorescences ofSorghum arundinaceum (Desv) Stampf. var.sudanense (Sudan grass);Plant Sci. Lett. 35 153–157
Brar D S, Rambold S, Gamborg O and Constabel F 1979 Tissue culture of corn andSorghum;Z. Pflanzenphysiol.95 377–388
Brettell R I S, Wernicke W and Thomas E 1980 Embryogenesis from cultured immature inflorescences ofSorghum bicolor;Protoplasma 104 141–148
Chen T H, Lam L and Chen S C 1985 Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from cultured, young inflorescences ofOryza sativa L. (rice);Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 4 51–54
Eapen S and Rao P S 1985 Plant regeneration from immature inflorescence callus cultures of wheat, rye and triticale;Euphytica 34 153–159
Mac Kinnon C, Gunderson G and Nabors M W 1986 Plant regeneration by somatic embryogenesis from callus cultures of sweet sorghum;Plant Cell Rep.5 349–351
Murashige T and Skoog F 1962 A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures;Physiol. Plant. 15 473–497
Smith R H and Bhaskaran S 1986 Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) (L). Moench); inBiotechnology in agriculture and forestry (ed.) Y P S Bajaj (Berlin: Springer Verlag) Vol 2, pp 220–233
Thomas E, King P J and Potrykus I 1977 Shoot and embryo-like structure formation from cultured tissues ofSorghum bicolor;Naturwissen-schaften 64 587
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
George, L., Eapen, S. & Rao, P.S. High frequency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature inflorescence cultures of two Indian cultivars of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 99, 405–410 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03053607
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03053607