Abstract
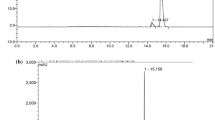
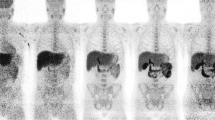
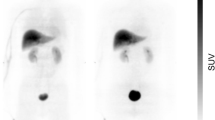
The biodistribution of3H-PK 11195, an antagonist of the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors, was studied in mice. High accumulations of radioactivity in the heart, lung, spleen, kidney and adrenal were observed after intravenous injection of tracer amounts of3H-PK 11195 into the mice. The radioactivity in the heart, lung, spleen, kidney and adrenal was significantly decreased by the coadministration of carrier PK 11195, which indicated that PK 11195 specifically binds to the receptors. No radioactive metabolites were observed in the heart, lung and brain 20 min after intravenous administration of3H-PK 11195. The accumulation of3H-PK 11195 in the lung was not affected by pretreatment with either α-methyl benzylamine or imipramine, suggesting that3H-PK 11195 specifically binds to the receptors. The ratios of radioactivity of the kidney, adrenal and spleen to blood increased as a function of time, whereas that of the lung and heart rapidly reached to a steady state.11C-PK 11195 was synthesized by the N-methylation of desmethyl precursor yielding more than 100 mCi with high specific activity (more than 1.4 Ci/μmol). The labeling and purification procedure was completed within 23 min after the end of bombardment (EOB). The11C-PK 11195 solution for injection seems to have a high potential for thein vivo study of the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in the living human by means of positron emission tomography (PET).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samson Y, Hantraye P, Baron JC, et al: Kinetics and displacement of11C-Ro 15-1788, a benzodiazepine antagonist, studied in human brainin vivo by positron emission tomography.Eur J Pharmacol 110: 247–251, 1985
Persson A, Ehrin E, Eriksson L, et al: Imaging of11C-labelled Ro 15-1788 binding to benzodiazepine receptors in the human brain by positron emission tomography.J Psychiat Res 19: 609–622, 1985
Shinotoh H, Yamasaki T, Inoue O, et al: A study of benzodiazepine receptor in human brain using11C-Ro 15-1788 and positron emission tomography.Kaku Igaku 22: 1789–1797, 1985
Shinotoh H, Yamasaki T, Inoue O, et al: Visualization of specific binding sites of benzodiazepine in human brain.J Nucl Med 27: 1593–1599, 1986
Frost JJ, Wagner HN, Dannals RF, et al: Imaging of benzodiazepine receptors in man with11C-suriclone by positron emission tomography.Eur J Pharmacol 122: 381–383, 1986
Braestrup C, Squires RF: Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity3H-diazepam binding.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 3805–3809, 1977
Le Fur G, Vaucher N, Perrier ML, et al: Differentiation between two ligands for peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites,3H-Ro 5-4864 and3H-PK 11195, by thermodynamic studies.Life Sci 33: 449–457, 1983
Le Fur G, Perrier ML, Vaucher N, et al: Peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites: effect of PK 11195, 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-methyl-N-(l-methylpropyl)-3-isoquinoline carboxamide. I.in vitro studies.Life Sci 32: 1830–1847, 1983
Le Fur G, Guilloux F, Rufat P, et al: Peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites: effect of PK 11195, 1-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-methyI-N-(l-methylpropyl)-3-isoquinoline carboxamide. II.in vivo studies.Life Sci 32: 1849–1856, 1983
Benavides J, Guilloux F, Rufat P, et al:In vivo labelling in several rat tissues of “peripheral type” benzodiazepine binding sites.Eur J Pharmacol 99: 1–7, 1984
Richards JG, Schoch P, Mohler H, et al: Benzodiazepine receptors resolved.Experientia 42: 121–126, 1986
Dubroeucq MC, Benavides J, Doble A, et al: Stereo-selective inhibition of the binding of3H-PK 11195 to peripheral-type benzodiazepine binding sites by a quinolinepropanamide derivative.Eur J Pharmacol 128: 269–272, 1986
Benavides J, Quateronet D, Imbault F, et al: Labelling of “peripheral-type” benzodiazepine binding sites in the rat brain by using3H-PK 11195, an isoquinoline carboxamide derivative: kinetic studies and autoradiographic localization.J Neurochem 41: 1744–1750, 1983
Benavides J, Savaki HE, Malgouris C, et al: Auto-radiographic localization of peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites in the cat brain with3H-PK 11195.Brain Res Bull 13: 69–77, 1984
Anholt RRH, Murphy KMM, Mack GE, et al: Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in the central nervous system: localization to olfactory nervous.J Neurosci 4: 593–603, 1984
Starosta-Rubinstein S, Ciliax BJ, Penney JB, et al: Imaging of a glioma using peripheral benzodiazepine ligands.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 891–895, 1987
De Souza EB, Anholt RRH, Murphy KMM, et al: Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in endocrine organs: autoradiographic localization in rat pituitary, adrenal and testis.Endocrinology 116: 567–573, 1985
Benavides J, Malgouris C, Imbault F, et al: Peripheral-type benzodiazepine binding sites in rat adrenals: binding studies with3H-PK 11195 and autoradiographic localization.Arch Int Pharmacodyn 226: 38–49, 1983
Anholt RRH, De Souza EB, Kuhar MJ, et al: Depletion of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors after hypophysectomy in rat adrenal gland and testis.Eur J Pharmacol 110: 41–46, 1985
Anholt RRH, Pedersen PL, De Souza EB, et al: The peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors: localization to the mitochondrial outer membrane.J Biol Chem 261: 576–583, 1986
Mestre M, Carriot T, Belin C, et al: Electrophysiological and pharmacological evidence that peripheral type benzodiazepine receptors are coupled to calcium channels in the heart.Life Sci 36: 391–400, 1985
Mestre M, Carriot T, Neliat G, et al: PK 11195, an antagonist of peripheral type benzodiazepine receptors, modulates BAY K 8644 sensitive but not β- or H2-receptor sensitive voltage operated calcium channels in the guinea pig heart.Life Sci 39: 329–339, 1986
Bolger GT, Weissman BA, Lueddens H, et al: Di-hydropyridine calcium channel antagonist binding in non-mammalian vertebrates: characterization and relationship to “peripheral-type” binding sites for benzodiazepine.Brain Res 368: 351–356, 1986
Basile AS, Lueddens HWM, Skolnick P: Regulation of renal peripheral benzodiazepine receptors by anion transport inhibitors.Life Sci 42: 715–726, 1988
Inoue O, Yamasaki T, Hashimoto K, et al: Evaluation of3H-PK 11195 as a radioligand for thein vivo study of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor.Kaku Igaku 22: 1385–1389, 1985
Suzuki K, Inoue O, Hashimoto K, et al: Computer-controlled large scale production of high specific activity11C-Ro 15-1788 for PET studies of benzodiazepine receptors.Int J Appl Radiat Isot 36: 971–976, 1985
Divertie MB, Owen CA, Barham SS, et al: Accumulation of radionuclide-labelled platelets and fibrinogen in paraquat-damaged rat lungs.Am Rev Respir Dis 125: 574–578, 1982
Rose MS, Lock EA, Smith LL, et al: Paraquat accumulation: tissue and species specifity.Biochem Pharmacol 25: 419–423, 1976
Camsonne R, Crouzel C, Comar D, et al: Synthesis of N-(11C)methyl, N-(methyl-1 propyl), (chloro-2 phenyl)-1-isoquinoline carboxamide-3 (PK 11195): a new ligand for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors.J Label Compounds Radiopharm 21: 985–991, 1984
Benavides J, Quarteronet D, Plouin PF, et al: Characterization of peripheral type benzodiazepine binding sites in human and rat platelets by using3H-PK 11195. Studies in hypertensive patients.Biochem Pharmacol 33: 2467–2472, 1984
Mestre M, Carriot R, Belin C, et al: Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in a guinea pig heart preparation.Life Sci 35: 953–962, 1984
Mestre M, Bouetard G, Uzan A, et al: PK 11195, an antagonist of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors, reduces ventricular arrhythmias during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in the dog.Eur J Pharmacol 112:257–260, 1985
Charbonneau P, Syrota A, Crouzel C, et al: Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in the living heart characterized by positron emission tomography.Circulation 73: 476–483, 1986
Anderson MW, Orton Tc, Pickett RD, et al: Accumulation of amines in the isolated perfused rabbit lung.J Pharmacol Exp Ther 189: 456–466, 1974
Iwasawa Y, Gillis CN: Pharmacological analysis of norepinephrine and 5-hydroxytryptamine removal from the pulmonary circulation: differentiation of uptake sites for each amine.J Pharmacol Exp Ther 188: 386–393, 1974
Fowler JS, Gallagher BM, Macgregor RR, et al: Carbon-11 labelled aliphatic amines in lung uptake and metabolism studies: potential for dynamic measurementsin vivo.J Pharmacol Exp Ther 198: 133–145, 1976
Hashimoto K, Inoue O, Suzuki K, et al: Synthesis and evaluation of11C-cyanoimipramine.Nucl Med Biol 14: 587–592, 1987
Moretti JL, Holman BL, Delmon L, et al: Effect of antidepressant and narcoleptic drugs on N-isopropyl p-iodoamphetamine biodistribution in animals.J Nucl Med 28: 354–359, 1987
Cymerman U, Pazos A, Palacios JM: Evidence for species differences in “peripheral” benzodiazepine receptors: an autoradiographic study.Neurosci Lett 66: 153–158, 1986
Pazos A, Cymerman U, Probst A, et al: “Peripheral” benzodiazepine binding sites in human brain and kidney: autoradiographic studies.Neurosci Lett 66: 147–152, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashimoto, K., Inoue, O., Suzuki, K. et al. Synthesis and evaluation of11C-PK 11195 forin vivo study of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors using position emission tomography. Ann Nucl Med 3, 63–71 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164587
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03164587