Abstract
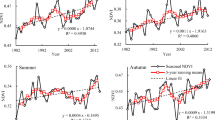
Variations in vegetation activity during the past 18 years in China were investigated using the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) derived from the 3rd generation time series dataset of NOAA-AVHRR from 1982 to 1999. In order to eliminate the effects of non-vegetation factors, we characterized areas with NDVI < 0.1 as “sparsely vegetated areas” and areas with NDVI ≥0.1 as “vegetated areas”. The results showed that increasing NDVI trends were evident, to varying extents, in almost all regions in China in the 18 years, indicating that vegetation activity has been rising in recent years in these regions. Compared to the early 1980s, the vegetated area increased by 3.5% by the late 1990s, while the sparsely vegetated area declined by 18.1% in the same period. The national total mean annual NDVI increased by 7.4% during the study period. Extended growing seasons and increased plant growth rates accounted for the bulk of these increases, while increases in temperature and summer rainfall, and strengthening agricultural activity were also likely important factors. NDVI changes in China exhibited relatively large spatial heterogeneity; the eastern coastal regions experienced declining or indiscernibly rising trends, while agricultural regions and western China experienced marked increases. Such a pattern was due primarily to urbanization, agricultural activity, regional climate characteristics, and different vegetation responses to regional climate changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, P., Shao, G. F., Zhao, G. et al., China’s forest policy for the 21st century, Science, 2000, 288: 2135.
Zang, X. S., Li, B., Shi, P. J., Development and utilization of grassland resources in southern china, Journal of Natural Resources (in Chinese), 1998, 13: 1–7.
Liu, J. Y., Liu, M. L., Zhuang, D. F. et al., Study on spatial pattern of land-use change in China during 1995–2000, Science in China, Ser. D, 2003, 46: 373–384.
Houghton, R. A., Temporal patterns of land-use change and carbon storage in China and tropical Asia, Science in China, Ser. C, 2002, 45(Supp.): 10–17.
Keeling, C. D., Chin, J. F. S., Whorf, T. P., Increased activity of northern vegetation in inferred from atmospheric CO2 measurements, Nature, 1996, 382: 146–149.
Ciais, P., Peylin, P., Bousquet, P., Regional biospheric carbon fluxes as inferred from atmospheric CO2 measurements, Ecol. Appl., 2000, 10: 1574–1589.
Bradley, N. L., Leopold, A. C., Ross, J. et al., Phenological changes reflect climate change in Wisconsin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, 96: 9701–9704.
Menzel, A., Fabian, P., Growing season extended in Europe, Nature, 1999, 397: 659–659.
Fang, J. Y., Chen, A. P., Peng, C. H. et al., Changes in forest biomass carbon storage in China between 1949 and 1998, Science, 2001, 292: 2320–2322.
Pacala, S. W., Hurtt, C. C., Baker, D. et al., Consistent land- and atmosphere-based U.S. carbon sink estimates, Science, 2001, 292: 2316–2320.
Melillo, J. M., McGuire, A. D., Kicklighter, D. W. et al., Global climate change and terrestrial net primary production, Nature, 1993, 363: 234–240.
Schimel, D., Melillo, J., Tian, H. Q. et al., Contribution of increasing CO2 and climate to carbon storage by ecosystems in the United States, Science, 2000, 287: 2004–2006.
Cao, M. K., Prince, S. D., Li, K. R. et al., Response of terrestrial carbon uptake to climate interannual variability in China, Global Change Biol., 2003, 9: 536–546.
Myneni, R. B., Keeling, C. D., Tucker, C. J. et al., Increased plant growth in the northern high latitudes from 1981 to 1991, Nature, 1997, 386: 698–702.
Fang, J. Y., Piao, S. L., Field, C. et al., Increasing net primary production in China from 1982 to 1999, Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2003, 1: 293–297.
Myneni, R. B., Dong, J., Tucker, C. J. et al., A large carbon sink in the woody biomass of Northern forests, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2001, 98: 14784–14789.
Los, S. O., Collatz, G. J., Bounoua, L. et al., Global interannual variations in sea surface temperature and land surface vegetation, air temperature, and precipitation, J. Climate, 2001, 14: 1535–1549.
Tucker, C. J., Slayback, D. A., Pinzon, J. E. et al., Higher northern latitude NDVI and growing season trends from 1982 to 1999, Int. J. Biometeorol., 2001, 45: 184–190.
Zhou, L. M., Tucker, C. J., Kaufmann, R. K. et al., Variations in northern vegetation activity inferred from satellite data of vegetation index during 1981 to 1999, J. Geophys. Res., 2001: 106(D17): 20069–20083.
Zhou, L. M., Kaufmann, R. K., Tian, Y. et al., Relation between interannual variations in satellite measures of vegetation greenness and climate between 1982 and 1999, J. Geophys. Res., 2003, 108(D1), 10.1029/2002JD002510.
Piao, S. L., Fang, J. Y., Zhou, L. M. et al., Interannual variations of monthly and seasonal NDVI in China from 1982 to 1999, J. Geophys. Res., 2003, 108, No. D14, 4401, doi:10.1029/2002JD-002848.
Paruelo, J. M., Epstein, H. E., Lauenroth, W. K. et al., ANPP estimates from NDVI for the central grassland region of United States, Ecology, 1997, 78: 953–958.
Slayback, D., Pinzon, J., Los, S. O. et al., Northern hemisphere photosynthetic trends 1982–1999, Global Change Biol., 2003, 9: 1–15.
Shi, P. J., Gong, P., Li, X. B. et al., Methods and Practice in LUCC Research (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 2000, 67–96.
Shi, P. J., Li, X. B., Zhou, W. G., Detection of vegetation response to climate change in northern china using “3 s” technology, Quaternary Sciences (in Chinese), 2000, 20: 220–228.
Li, K. R., Chen, Y. F., Huang, M. et al., Model studies of the impacts of climate change on land cover and its feedback, Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 2000, 55 (Supplement): 57–63.
Piao, S. L., Fang, J. Y., Dynamic vegetation cover change over the last 18 years in China, Quaternary Sciences (in Chinese), 2000, 21: 294–302.
Xiang Bao, Liu Jiyuan, Relationship of East Asian land cover dynamics and interannual changes of monsoon climate, Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 2002, 57: 39–46.
Gong, D. Y., Shi, P. J., He, X. Z., Spatial features of the coupling between Spring NDVI and temperature over Northern Hemisphere, Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 2002, 57: 505–514.
Holben, B. N., Characteristics of maximum-value composite images for temporal AVHRR data, Int. J. Remote Sens., 1986, 7: 1435–1445.
Piao, S. L., Fang, J. Y., Chen, A. P., Seasonal dynamics of terrestrial net primary production in response to climate change in China, Acta Bot. Sin., 2003, 45: 269–275.
IPCC, Climate Change 2001: Impact, Adaptation, and Vulnerability, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001.
Wang, S. Q., Tian, H. Q., Liu, J. Y. et al., Characterization of changes in land cover and carbon storage in Northeastern China; An analysis based on Landsat TM data, Science in China, Ser. C, 2002, 45(1): 40–47.
Malmström, C. M., Thompson, M. V., Juday, G. P. et al., Interannual variation in global-scale net primary production: Testing model estimates, Global Biogeochem. Cycl. (in Chinese), 1997, 11: 367–392.
China’s Agricultural Yearbook, 1982 to 1999, China’s Agricultural Yearbook 1982 to 1999 (in Chinese), Beijing: Agriculture Press.
Zhang, X. S., Ecological restoration and sustainable agricultural paradigm of Mountain-Oasis-Ecotone-Desert system in the North of the Tianshan Mountains, Acta Botanica Sinica (in Chinese), 2001 43: 1294–1299.
Zhong, D. C., The dynamic changes and trends of modern desert in China, Advance in Earth Sciences (in Chinese), 1999, 14: 230–234.
Wu, W., Study on process of desertification in Mu Us sandy land for last 50 years, China, Journal of Desert Research (in Chinese), 2001, 21: 164–169.
RunnstrÖm, M. C., Is northern China winning the battle against desertification? Satellite remote sensing as a tool to study biomass trends on the Ordos plateau in semiarid China, AMBIO, 2000, 29: 468–476.
Shi, Y. F., Shen, Y. P., Hu, R. J., Preliminary study on signal, impact and foreground of climatic shift from warm-dry to warm-humid in northwest China, Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology (in Chinese), 2002, 24: 219–226.
Shi, Y. F., Shen, Y. P., Li, D. L. et al., Discussion on the present climate change from warm-dry to warm-wet in northwest china, Quaternary Sciences (in Chinese), 2003, 23: 152–164.
Shi, Y. F., Shen, Y. P., Signal, impact and outlook of climatic shift from warm-dry to warm-humid in northwest China, Science & Technology Review, 2003, (2): 54–57.
Qin, D. H. ed., Assessment on Environment of Western China (Synopsis) (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, J., Piao, S., He, J. et al. Increasing terrestrial vegetation activity in China, 1982–1999. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 47, 229–240 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182768
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182768