Abstract
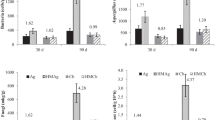
The effects of heavy metals on soil microbial processes were investigated over a period of six weeks. Analytical grade (Sigma) sulphate salts of copper, zinc and nickel were added individually and in combinations to soil samples and incubated in different plastic pots. Samples were taken from the pots forthnightly and the rates of microbial carbon and nitrogen mineralization, microbial biomass carbon and respiration were measured. The results showed the effect of metals on the measured parameters were significant (P<0.05.). By the 6th week postreatment, the rates of carbon accumulated were high in the copper (6.03 %) and copper:Zinc (5.80 %) treatments but low in the nickel and zinc (4.93 % and 5.02 % respectively). The rates of Nitrogen mineralization were 0.41 and 0.44 % in samples treated with copper and copper:zinc compared to 0.22 %–0.24 % obtained at the beginning of the experiments. Soil microbial biomass carbon declined from average value of 183.7–185.6 μg/g before treatment to as low as 100.8 and 124.6 μg/g in samples treated with copper:zinc and copper respectively.The rate of respiration of the soil microbial populations was equally inhibited by the metals. From an average rate of 2.51–2.56 μg of C/g respiration of the soil microbes declined to 0.98, 1.08 and 1.61 μg of C/g in the copper:zinc, copper and zinc treated soils by the end of the experiment. The results suggest additive or synergistic effects of the metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway, B. J., (1995).Soil processes and the behaviour of metals. In: B.J Alloway (Ed.) Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic and Professional, London, Uk. 11–37.
Baath, E., (1989). Effects of heavy metals in soil on microbial processes and populations. Water, Air Soil Pollut., 47(3–4), 335–379.
Baath, E. (1992a). Thymidine incorporation into macromolecules of bacteria extracted from soil by homogenization-centrifugation. Soil Biol. Biochem., 24(11), 1157–1165.
Baath, E., (1992b). Measurement of heavy metal tolerance of soil bacteria using thymidine incorporation into bacteria extracted after homogenization-centrifugation. Soil. Biol. Biochem., 24(11), 1167–1172.
Baath, E.; Arnebrant, K., (1994).Growth rate and response of bacterial communities to pH in limed and ash treated forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem., 26(8), 995–1001.
Baath, E.; Diaz Ravina, M.; Frostegard, A.; Campell, C. D., (1998). Effect of metal rich sludge amendments on the soil microbial community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64(1), 238–245.
Baker. D. E.; Senft, J. P., (1995). Copper. In: B. J. Alloway (Ed.). Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic and Professional, London, UK.179–205.
Bremner, J. M., (1965). Total Nitrogen. In: C.A. Black (Ed.) Methods of Soil analysis. Part 2 Agron. Monogr. 9 A American Society for Agronomy, Madison, WI., 1149–1178.
Brookes, P. C., (1995). The use of microbial parameters in monitoring soil pollution by heavy metals. Biol. Fertile. Soils, 19(4), 269–279.
Chander, K.; Brookes, P. C., (1993). Residual effects of zinc, copper and nickel in sewage sludge on microbial biomass in a sandy loam. Soil. Biol. Biochem., 25(9), 1231–1239.
Chen, X.; Wright, J. V.; Conca, J. L.; Peurrung, L. M., (1997). Evaluation of heavy metal remediation using mineral apatite. Water, Air Soil Pollut., 98(1–2), 57–78.
Chefetz, B.; Hatcher, P. G.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y., (1996). Chemical and biological characterization of organic matter during composting of municipal solid waste. J. Environ. Qual., 25(4), 776–785.
Clarke, K. R., (1999). Nonmetric multivariate analysis in community level ecotoxicology. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 18(2), 118–127.
Diaz Ravina, M.; Baath, E.; Frostegard., A., (1994). Multiple heavy metal tolerance of soil bacterial communities and its measurement by the thymidine incorporation technique. Appl._Environ. Microbiol., 60(7), 2238–2247.
Diaz Ravina, M.; Baath, E., (1996). Development of metal tolerance in soil bacterial communities exposed to experimentally increased metal levels. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 62(8), 2970–2977.
Frostegard, A.; Baath, E., (1996). The use of phospholipids fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils, 22(1–2), 59–65.
Gazso, L. G., (2001). The key microbial processes in the removal of toxic metals and radionuclides from the environment. (a review) Cent. Eur. J of Occup. Environ. Med., 7(3), 178–185.
Illmer, P.; Schinner, F., (1991). Effects of lime and nutrient salts on the microbiological activities of forest soils. Bio. Fertil. Soils, 11(4), 261–266.
Kalembasa, S. J.; Jenkinson, D. S., (1973). A comparative study of titrimetric and gravimenetric methods for the determination of organic carbon in soil. J. Sci. Food and Agric., 24(9), 1085–1090.
Kelly, J. J.; Tate, R. L., (1998). Effects of heavy metal contamination and remediation on soil microbial communities in the vicinity of a zinc smelter. J. Environ. Qual., 27(3), 609–617.
Kosolapov, D. B.; Kuschk, P.; Vainshtein, M. B.; Vatsourina, A.V., Wiebner, A., Kasterner M. and Miler, R.A.,(2004). Microbial processes of heavy metal removal from carbon deficient effluents in constructed wetlands. Engr. Life. Sc., 4(5), 403–411.
Lighthart, B.; Bond, H., (1976). Design and preliminary results from soil/litter microcosms. Int. J. Environ. Stud., 10(1), 51–58.
Marschner, B.; Kalbitz, K., (2003). Control of bioavailability and biodegradation of dissolved organic matter in soils Geoderma., 113(3–4), 211–235.
Pennanem, T.; Frostegard, A.; Fritze, H.; Baath, E., (1996). Phospholipid fattyacid composition and heavy metal tolerance of soil microbial communities along two heavy metal-polluted gradients in coniferous forests. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 62(2), 420–428.
Petersen, S. O.; Klug, M. J., (1994). Effects of sieving, storage and incubation temperature on the phospholipids fattyacid profile of a soil microbial community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 60(7), 2421–2430.
Sani, R. K.; Peyton, B. M.; Jadhyala, M., (2003) Toxicity of lead in aqueous medium to Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20. Environ. Toxicol., 22(2), 252–260.
Utgikar, V. P.; Chaudhary, N.; Koeniger, A.; Tabak, H. H.; Haines, J. R.; Govind, R., (2004). Toxicity of metals and metal mixtures: Analysis of concentration and time dependence for zinc and copper. Water Res., 38(17), 3651–3658.
Utgikar, V. P.; Tabak, H. H.; Haines, J. R.; Govind, R., (2003). Quantification of toxic inhibitory impact of copper and zinc on mixed cultures of sulfate reducing bacteria. Biotech. Bioeng., 82(3), 306–312.
Vance, E. D., Brookes, P. C.; Jenkinson, D. S., (1987). Microbial biomass measurements in forest Soils: The use of the chloroform-fumigation method in strongly acid Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem., 19(6), 697–702.
Zevenhvizen, L. P. T. M.; Dolfing, J.; Eshuis, E. J.; Scholter, I. J., (1979). Inhibitory effects of Cu on bacteria related to the free ion concentration. Microb. Ecol., 5(2), 139–146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nwuche, C.O., Ugoji, E.O. Effects of heavy metal pollution on the soil microbial activity. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 5, 409–414 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326036
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326036