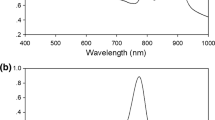
Abstract
A suspended growth photobioreactor was utilized to treat pharmaceutical wastewater by a wild strain purple non-sulfur photosynthetic bacterium isolated from the soil. The strain was named Z08 and identified as Rhodobacter-sphaeroides by 16SrDN. The photobioreactor was illuminated externally with two (40 W) fluorescent compact light sources on both sides. Its operation pH and temperature were between 6.8–7.0 and 20–30 °C, respectively. Optimum growth of the isolate was obtained after enrichment of the pharmaceutical wastewater with 0.5 % ammonium sulfate and 0.1 % yeast extract under microaerobic optimum light (6000 lx) condition at 5d retention. Using these optimum conditions, the maximum dry cell weight and chemical oxygen demand percentage removal were 880 mg/L and 80 %. Chemical analysis of the culture after treatment of the enriched and non-enriched wastewater showed the crude protein content of the biomass to be 54.6 % and 38.0 %, respectively. This study proved that photosynthetic bacteria could transform complex wastewater that contains recalcitrant organic compounds with a resultant recovery of useful products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, (1992). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th Ed. American public Health Association Washington, DC. USA.
Banerjee, S.; Azad, S. A.; Vikineswary, S.; Selvaraj O. S.; Mukherjee, T. K.; (2000). Phototrophic bacteria as fish feed supplements. Asian-Aust. J. Anim. Sci., 13 (7), 991–994 (4 pages). (in-Chinese)
Banu J. R.; Kallappan S.; Yeom I. T.; 2007. Treatment of domestic wastewater using upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (3), 363–370 (8 pages).
Bertling, K.; Hurse, T. J.; Kappler, U.; Bakie, A. D., (2006). Cultivation of photosynthetic bacteria using Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers. UQ ITEE Innovation Expo.
Bitton, G., (2005). Microbiology, 3rd Ed. 55–72, 213-222, 502-518. Wiley-Liss Pub, N.Y.
Cheremisinoff, N. P.; (1996). Biotechnology for Waste and Wastewater Treatment. Noyes Publishers, Westwood, New Jersey, USA. 116.
Choorit, W.; Thanahoset, P.; Thongpradistha, J.; Sasaki, K.; Noparatnaraporn, N.; (2002). Identification and cultivation of photosynthetic bacteria in wastewater from a concentrated latex processing factory. Biotechnol. Lett. 24 (13), 1055–1058 (4 pages).
Cokgor, U. E.; Karahan, O.; Dogruel, S.; Orion, D., (2004). Biological treatability of raw and ozonated penicillin formulated effluent. J. Hazard. Mater., 116 (1–2), 159–166 (8 pages).
Eloi, G; Manuel, O.; Isidre, G.; Montserra, L.; Jordi, B., (1992). Isolation and characterization of a recombination defective-dependent bacteriophage of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Curr. Microbiol., 24 (3), 151–157 (7 pages).
Galley, A. G.; Forster, C. F.; Stafford, D. A, (1977). Treatment of Industrial Effluent. Hodder and Stoughton. London, UK.
Getha, K.; Chong, V. C.; Vikineswary, S., (1998). Potential use of the phototrophic bacteria, Rhodopseudomonas Palustris as an aqua-culture feed. Asian Fish. Sci., 10, 223–232 (10 pages).
Holt, J. G; Krieg, N. R.; Sneath, P. H. A.; Staley, J. T.; Williams, S. T., (1994). Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. 9th. Ed., Baltimore; the Williams Wilkins Co., 787.
Hosseini F.; Malekzadeh F.; Amirmozafari N.; Ghaemi N.; 2007. Biodegradation of anionic surfactant by isolated bacteria from activated sludge. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (1), 127–132 (6 pages).
Howard, G, (1987). The world of microbes. The Benjamin Cummings Publishing, Inc. USA.
Huseyin, T.; Oken, B.; Selale, S. A.; Tolga, H. B.; Ceribas, I. B.; Sarin, F. D.; Filiz, B. D.; Ulku, Y., (2006). Use of fenton oxidation to improve the biodegradability of pharmaceutical wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater., 136 (2), 258–265 (8 pages).
Imhoff, J. F.; Trüper, H. G, (1989). Purple nonsulfur bacteria. In: Staley, J. T. (Ed.), Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins. 3, 9th. Ed., 1904–1910.
Kakabadse, G, (1979). Chemistry of effluent treatment. Appl. Sci. Publishers Ltd. Manchester, UK. 25–59.
Kantachote, D.; Salwa, T.; Kamontam, U., (2005). The potential use of anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria for treating latex rubber sheet wastewater. Electron. J. Biotech., 8 (3), 314–323 (10 pages).
Kasomu, I. B. M.; Obst M., (2009). The influence of picocyanobacterial photosynthesis on calcite precipitation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6 (4), 557–562 (6 pages).
Lorrungruang, C.; Martthong, J.; Sasaki, K.; Noparatnaraporn N., (2006). Selection of photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter Sphaeroides 14F for polyhydroxyalkanoate production with two-stage aerobic dark cultivation. J. Biosci.Bioeng., 102 (2), 128–131 (4 pages).
Madigan, M. T.; Jung, D. O.; Woese, C. R.; Achenbach, L. A.; (2000). Rhodoferax antarcticus sp. nov., a moderately psychrophilic purple nonsulfur bacterium isolated from an Antarctic microbial mat. Arch. Microbiol., 173 (4), 269–277 (9 pages).
Martinez-Tabche, L.; Ramirez-Mora, B.; Germán-Fa, C; Galar-Castelán, I.; Madrigal-Ortiz, M.; Ulloa-González, V.; Orozco-Flores, M.; (1997). Toxic effects of sodium dodecylbenzensulfonato, lead, petroleum and their mixtures on the activity of acetylcholinesterase of Moina macrocopa in vitro. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual., 12, (3), 211–215 (5 pages).
Myung, K. K.; Choi, K. M.; Yin, C. R.; Lee, K. Y.; Im, W. T.; Lim, J. H.; Lee, S. T., (2004). Odorous swine wastewater treatment by purple non-sulfur bacteria, Rhodopseupdomonas Pulustris, isolated from eutrophicated ponds. Biotech Lett., 26 (10), 819–822 (4 pages).
Okubo, Y.; Hiroyuki, F.; Akira, H., (2006). Characterization of phototrophic purple non-sulfur Bacteria forming colored microbial mats in a swine wastewater Ditch. Appl. Environ. Microb., 12 (9), 6225–6233 (9 pages).
Prasertsan, P.; Jaturapornpipat, M.; Sirpatana, C., (1997). Utilization and treatment of tuna condensate by photosynthetic bacteria. Pure Appl. Chem., 69 (11), 2438–2445 (8 pages).
Ren, N.; Chen, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Z. P.; Yue, S., (2008). A novel application of TPAD-MBR system to the pilot treatment of chemical synthesis-based pharmaceutical wastewater. Water Res., 42, (13), 3385–3392 (8 pages).
Rodriguez Fuentes, G.; Gold Bouchot, G, (2000). Environmental monitoring using acetyl cholinesterase inhibition in vitro: A case study in two Mexican lagoons. Mar. Environ. Res., 50 (1–5), 357–360 (4 pages).
Sapana, S.; Sujata, B.; Amruta, T.; Kalal, K.; Phalgune, U. D.; Deshpande, N. R., (2008). GC-MS Study of hydrocarbons- A Renewable Biofuel with high calorific value from aerial roots of ficus Benghalensis Linn. Electron. J. Environ., Agri. Food Chem., 7 (14), 2743–2748 (6 pages).
Sasser, M., (1990). Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular Fatty acids. MIDI technical note 101. MIDI, Newark, Del. USA.
Speece, R. E., (1983). Anaerobic biotechnology for industrial Waste treatment. Environ. Sci. Tech., 17 (9), 416–427 (12 pages).
Takeno, K.; Yamaoka, Y.; Sasaki, K., (2005). Treatment of oil- containing sewage wastewater using immobilized photosynthetic bacteria. W. J. of Microb. Biotech., 21 (8–9), 1385–1391 (7 pages).
Tchobanoglous, G.; Franklin, L. B.; Stensel, D. H., (2003). Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse. 4th. Ed. Metcalf and Eddy, Inc. NY. USA.
Yegani, R.; Satoshi, Y.; Kazunori, M.; Tomoshisa, K; Shigeo, K., (2005). Improvement of growth stability of photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter capsulatus. J. Biosci Bioeng., 10 (6), 672–677 (6 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madukasi, E.I., Dai, X., He, C. et al. Potentials of phototrophic bacteria in treating pharmaceutical wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 165–174 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326128
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326128