Abstract
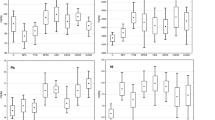
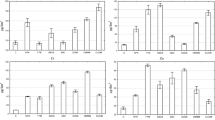
A field study was carried out to evaluate long-term heavy metal accumulation in the top 20 cm of a Tunisian clayey loam soil amended for four consecutive years with municipal solid waste compost at three levels (0, 40 and 80 t/ha/y). Heavy metals uptake and translocation within wheat plants grown on these soils were also investigated. Compared to untreated soils, compost-amended soils showed significant increases in the content of all measured metals: cadmium, chromium, copper, nickel, lead and zinc in the last three years, especially for plots amended with municipal solid waste compost at 80 t/ha/y. Wheat plants grown on compost-amended soils showed a general increase in metal uptake and translocation, especially for chromium and nickel. This heavy metal uptake was about three folds greater in plots amended at 80 t/ha/y as compared to plots amended at 40 t/ha/y. At the end of the experimental period, the diluting effect resulting from enhanced growth rates of wheat plants due to successive compost applications resulted in lower concentrations in the plants (grain part) grown on treated plots. On the other hand, chromium and nickel were less mobile in the aerial part of wheat plants and were accumulated essentially in root tissues. Plant/soil transfer coefficients for compost-amended treatments were higher than threshold range reported in the literature, indicating that there was an important load/transfer of metal ions from soils to wheat plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayari, F.; Chairi, R.; Kossai, R., (2008). Sequential extraction of heavy metals during composting of urban waste. Chin. J. Geochem., 27, 121–125 (6 pages).
Ayten, K., (2004). Effect of organic wastes on the extractability of cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc in soil. Geoderma, 122, 297–303 (8 pages).
Benzarti, S.; Hamdi, H.; Aoyama, A.; Jedidi, N.; Hassen, A.; Dahmane, A., (2007). Assessment of the effect of repetitive municipal solid waste compost application on soil using physico-chemical analyses, solid-phase bioassays and microbial activity characterization. Jpn. J. Environ. Toxicol., 10(1), 19–30 (12 pages).
Castaldi, P.; Santoma, L.; Melis, P., (2005). Heavy metal immobilization by chemical amendments in a polluted soil and influence on white lupin growth. Chemosphere, 60(3), 365–371 (7 pages).
Chukwujindu, M. A. I.; Egun, A. C.; Emuh, F. N.; Isirimah, N. O., (2006). Compost maturity evaluation and its significance to agriculture. Pak. J. Biol. Sci., 9(15), 125–131 (7 pages).
Chukwuji M. A. I.; Nwajei, G. E.; Osakwe, S. A., (2005). Recycling waste in agriculture: Efficacy of composting in ameliorating trace metal availability and soil borne pathogens. Eur. J. Sci. Res., 11(4), 571–577 (7 pages).
Crecchio, C.; Curci, M.; Pizzigallo, M. D. R.; Ricciuti, P.; Ruggiero, P., (2004). Effect of municipal solid waste compost amendments on soil enzymes activities and bacterial genetic diversity. Soil Bio. Biochem., 36(10), 1595–1605 (12 pages).
European Community (1975). Commission Directive No. 442. Off. J. Eur. Commun., 194, 47–49 (3 pages).
European Community (1986). Commission Directive No. 278. Off. J. Eur. Commun., 181, 5–12 (8 pages).
Förstner, U., (1995). Land contamination by metals: global scope and magnitude of problem. Alien, H. E.; Huang, C. P.; Bailey, G. W.; Bowers, A. R. (Eds). Metal speciation and contamination of soil. Lewis, Boca Raton. 1–33.
Gallardo-Lara, F.; Nogales, R., (1987). Effect of the application of town-refuse compost on the soil plant system: A review. Biol. Waste, 19(1), 35–62 (28 pages).
Giusquiani, P. L.; Pagliai, M.; Gigliotti, G.; Businelli, D.; Benetti, A., (1995). Urban waste compost: Effects on physical, chemical and biochemical soil properties. J. Environ. Qual., 24, 175–182 (28 pages).
Hamdi, H.; Jedidi, N.; Ayari, F.; Yoshida, M.; Ghrabi, A., (2003). Valuation of municipal solid waste compost of Tunis (Tunisia) - Agronomic aspect. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference of the Japan Society of Waste Management Experts, Vol. III, International Session. 62–64.
He, X. T.; Traina, S. J.; Logan, T. J., (1992). Chemical properties of municipal solid waste compost. J. Environ. Qual., 21, 318–329 (12 pages).
Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H., (1992). Trace elements in soils and plants. 2nd. Ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Kloke, A.; Sauerbeck, D. R.; Vetter, H., (1984). The contamination of plants and soils with heavy metals and the transport of metals in terrestrial food chains. Nriagu, J. O. (Ed.). Changing Metal Cycles and Human Health. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Kurihara, K., (1984). Urban and industrial waste as fertilizer material. Swaminathan, M. S. (Ed.). Organic matter and Rice. International Rice Research Institute Philippines.
Lillenberg, M.; Yurchenko, S.; Kipper, K.; Herodes, K.; Pihl, V.; Löhmus, R.; Ivask, M.; Kuu, A.; Kutti, S.; Litvin, S. V.; Nei, L., (2010). Presence of fluoroquinolones and sulfonamides in urban sewage sludge and their degradation as a result of composting. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(2), 307–312 (6 pages).
Madrid, F.; Lopez, R.; Cabrera, F., (2006). Metal accumulation in soil after application of municipal solid waste compost under intensive farming conditions. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 199(3–4), 249–256 (8 pages).
Mahvi, A. H., (2008). Application of agricultural fibers in pollution removal from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(2), 275–285 (11 pages).
Mullin, G. L.; Mitchell, C. C., (1994). Soil amendments: Impact on biotic system. CRC Press Inc., New York.
Nicholson, F. A., Smith, S. R., Alloway, B. J., Carlton-Smith, C., Chambers, B. J., (2003). An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ., 311(1–3), 205–219 (15 pages).
Nouri, J.; Mahvi, A. H.; Babaei, A.; Ahmadpour, E., (2006). Regional pattern distribution of groundwater fluoride in the Shush aquifer of Khuzestan County Iran. Fluoride, 39(4), 321–325 (5 pages).
Nouri, J.; Mahvi, A.H.; Jahed, G.R.; Babaei, A.A. (2008). Regional distribution pattern of groundwater heavy metals resulting from agricultural activities. Environ. Geo. 55(6), 1337–1343 (7 pages).
Nwachukwu, M. A.; Feng, H.; Alinnor, J., (2010). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in soil and their implications within and around mechanic villages. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(2), 347–358 (12 pages).
Paglia, M.; Vittori-Antisari, L., (1993). Influence of waste organic matter on soil micro and macrostructure. Bioresour. Tech., 43(3), 205–213 (8 pages).
Petruzzelli, G.; Lubrano, L.; Guidi, G., (1989). Uptake by corn and chemical extractability of heavy metals from a four year compost treated soil. Plant Soil, 116(1), 23–27 (5 pages).
Williams, D. E.; Vlarnis, J.; Pukite, A. H.; Corey, J. E. (1987). Metal movement in sludge-amended soils: A nine-year study. Soil Sci., 143, 124–131 (8 pages).
Yoshida, M.; Jedidi, N.; Hamdi, H.; Ayari, F.; Hassen, A.; M’hiri, A., (2003). Magnetic susceptibility variation of MSW compost-amended soils: In situ method for monitoring heavy metal contamination. Waste Manage. Res., 21(2), 155–160 (6 pages).
Zaman, A. U., (2010). Comparative study of municipal solid waste treatment technologies using life cycle assessment method. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(2), 225–234 (10 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayari, F., Hamdi, H., Jedidi, N. et al. Heavy metal distribution in soil and plant in municipal solid waste compost amended plots. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 465–472 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326156
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326156