Abstract
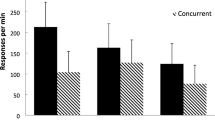
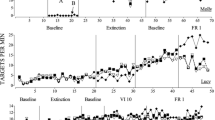
Five suggestible female subjects acquired an operant response conditioned on a variable interval schedule of reinforcement. Each subject was then hypnotized and performed the response during 6-min. alternating baseline and experimental phases in an Abab withdrawal design. Experimental phases were preceded by administration of time-slowing suggestions. Return to baseline condition was accomplished via presentation of a time-normalization suggestion. Four of the subjects demonstrated noticeable decreases in operant response rate during time-slowed phases as compared to the preceding baseline phases. Subjects decreased their response rates despite a perceived response cost in doing so. Subjective reports indicated that all subjects experienced slowed time passage during experimental phases although subjective experiences varied greatly between individuals. An attempt is made to explain the differences between subjects in their overt and covert responses to time-slowing suggestions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BARBER, T. X. 1965. Measuring “hypnotic-like” suggestibility with and without “hypnotic induction.” Psychological Reports, 16, 809–844.
BARBER, T.X. 1972. Suggested (“hypnotic”) behavior: The trance paradigm versus an alternative paradigm. In E. Fromm & R. Shor (Eds.), Hypnosis. Chicago: Aldine.
BARBER, T.X., & CALVERLEY, D. S. 1964. Toward a theory of “hypnotic” behavior: An experimental study of “hypnotic time distortion”. Archives of General Psychiatry, 10, 209–216.
CASEY, G. A. 1966. Hypnotic time distortion and learning. Dissertation Abstracts, 27, 2116–2117.
COOPER, L. F., & ERICKSON, M. H. 1950. Time distortion in hypnosis. The Bulletin Georgetown University Medical Center, 4, 50–68.
COOPER, L.F., & RODGIN D.W. 1952. Time distortion in hypnosis and nonmotor learning. Science, 115, 500–502.
FERSTER, C. B., LEVITT, E. E., ZIMMERMAN, J., & BRADY, J. P. 1961. The measurement of hypnotic effects by operant-reinfor cement techniques. The Psychological Record, 11, 427–430.
HERSEN, M., & BARLOW, D.H. 1976. Single case experimental designs: Strategies for studying behavior change. New York: Pergamon Press.
JOHNSON, R.F.Q. 1976. Hypnotic time distortion and the enhancement of learning: New data pertinent to the Krauss-Katzell-Krauss experiment. The American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis, 19, 98–102.
KAZDIN, A.E. 1976. Statistical analyses for single-case experimental designs. In M. Hersen & D.H. Barlow, Single case experimental designs: Strategies for studying behavior change. New York: Pergamon Press.
KRAUSS, H.H., KATZELL, R., & KRAUSS, B.J. 1974. Effect of hypnotic time distortion upon free-recall learning. Journal of A bnormal Psychology, 83, 140–144.
KROGER, W.S. 1977. Clinical and experimental hypnosis (2nd ed.). Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Company.
KROGER, W.S., & FEZLER, W.D. 1976. Hypnosis and behavior modification: Imagery conditioning. Philadelphia: J. B Lippincott Company.
LINDSLEY, O.R. 1957. Operant behavior during sleep: A measure of depth of sleep. Science, 126, 1290–1291.
SI DMAN, M. 1960. Tactics of scientific research: Evaluating experimental data in psychology. New York: Basic Books, Inc.
WEITZENHOFFER, A. M., & HILGARD, E. R. 1962. Stanford hypnotic susceptibility scale, form C. Palo Alto: Consulting Psychologists Press.
ZIMBARDO, P.G., MASLACH, C., & MARSHALL, G. 1972. Hypnosis and the psychology of cognitive and behavioral control. In E. Fromm & R. Shor, (Eds.), Hypnosis. Chicago: Aldine.
ZIMBARDO, P.G., MARSHALL, G., WHITE, G., & MASLACH, C. 1973. Objective assessment of hypnotically induced time distortion. Science, 181, 282–284.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The author wishes to express his gratitude to Dr. Edward R. Simco, Dr. John M. Flynn, and Dr. Leo J. Reyna for their invaluable assistance throughout the course of this study. A special thanks to Mr. Jerry Adato for his aid as a research assistant.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baer, L. Effect of Time-Slowing Suggestions on Rate of Emission of an Operant Response. Psychol Rec 29, 389–400 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394627
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394627