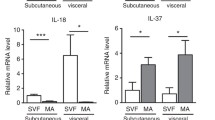
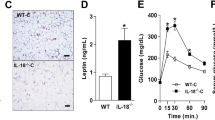
Abstract
IL-33 is a cytokine that belongs to the IL-1 family and is classically associated with type 2-like immune responses. In the adipose tissue, IL-33 is related to the beiging of adipocytes and to the maintenance of adipose tissue-resident immune cells, such as innate lymphoid cells 2, alternatively activated macrophages and regulatory T cells, which contribute to the maintenance of adipose tissue homeostasis. In the obese adipose tissue, the number of these cells is diminished, unlike the expression of IL-33, which is up-regulated. However, despite its increased expression, IL-33 is not able to maintain the homeostasis of the obese adipose tissue. IL-33 treatment, on the other hand, highly improves obesity-related inflammatory and metabolic alterations. The evidence that exogenous IL-33, but not adipose tissue-driven IL-33, regulates the inflammatory process in obesity leaves a gap in the understanding of IL-33 biology. Thus, in this review we discuss the potential mechanisms associated with the impaired action of IL-33 in obesity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurauski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, Gorman DM, Bazan JF, Kastelein RA. IL33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–90.
Hasan A, Al-Ghimlas F, Warsame S, Al-Hubail A, Ahmad R, Bennakhi A, Al-Arouj M, Behbehani K, Dehbi M, Dermime S. IL-33 is negatively associated with the BMI and confers a protective lipid/metabolic profile in non-diabetic but not diabetic subjects. BMC Immunol. 2014;15:1–9.
Ruisong M, Xiaorong H, Gangying H, Chunfeng Y, Changjiang Z, Xuefei L, Yuanhong L, Hong J. The protective role of interleukin-33 in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion is associated with decreased HMGB1 expression and up-regulation of the P38 MAPK signaling pathway. Plos One. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143064.
Momen T, Ahanchian H, Reisi M, Shamsdin SA, Shahsanai A, Keivanfar M. Comparison of interleukin-33 serum levels in asthmatic patients with a control group and relation with the severity of the disease. Int J Prev Med. 2017. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_179_16.
Kageyama Y, Torikai E, Tsujimura K, Kobayashi M. Involvement of IL-33 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: the effect of etanercept on the serum levels of IL-33. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22:89–93.
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Investig. 2007;117:175–84.
Winer S, Chan Y, Paltser G, Truong D, Tsui H, Bahrami J, Dorfman R, Wang Y, Zielenski J, Mastronardi F, Maezawa Y, Drucker D, Engleman E, Winer D, Dosch HM. Normalization of obesity-associated insulin resistance through immunotherapy: CD4+ T cells control glucose homeostasis. Nat Med. 2009;15:921–9.
Miller AM, Asquith DL, Hueber AJ, Anderson LA, Holmes WM, Mckenzie AN, Xu D, Sattar N, Mcinnes IB, Liew FY. IL-33 induces protective effects in adipose tissue inflammation during obesity in mice. Circ Res. 2010;107:650–8.
Brestoff JR, Kim BS, Saenz SA, Stine RR, Monticelli LA, Sonnenberg GF, Thome JJ, Farber DL, Lutfy K, Saele P, Artis D. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells promote beiging of white adipose tissue and limit obesity. Nature. 2015;519:242–6.
Han JM, Wu D, Denroche HC, Yao Y, Verchere CB, Levings MK. IL-33 reverses an obesity-induced deficit in visceral adipose tissue ST2+ T regulatory cells and ameliorates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. J Immunol. 2015;194:4777–83.
Zeyda M, Wernly B, Demyanets S, Kaun C, Hammerle M, Hantusch B, Schranz M, Neuhofer A, Iitariu BK, Keck M, Prager G, Wojta J, Stulnig TM. Severe obesity increases adipose tissue expression of interleukin-33 and its receptor ST2, both predominantly detectable in endothelial cells of human adipose tissue. Int J Obes. 2013;37:658–65.
Baekkevold ES, Roussigné M, Yamanaka T, Johansen FE, Jahnsen FL, Amalric F, Brandtzaeg P, Erard M, Haraldsen G, Girard JP. Molecular characterization of NF-HEV, a nuclear factor preferentially expressed in human high endothelial venules. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:69–79.
Carriere V, Roussel L, Ortega N, Lacorre DA, Americh L, Aguilar L, Bouche G, Girard JP. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. PNAS. 2007;104:282–7.
Moussion C, Ortega N, Girard JP. The IL-1 like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: a novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS One. 2008;3:1–8.
Pichery M, Mirey E, Mercier P, Lefrancais E, Dujardin A, Ortega N, Girard JP. Endogenous IL-33 is highly expressed in mouse epithelial barrier tissues, lymphoid organs, brain, embryos, and inflamed tissues: in situ analysis using a novel Il-33-LacZ gene trap reporter strain. J Immunol. 2012;188:3488–95.
Sanada S, Hakuno D, Higgins LJ, Schreiter ER, McKenzie AN, Lee RT. IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J Clin Investig. 2007;117:1538–49.
Miller AM, Xu D, Asquith DL, Denby L, Li Y, Sattar N, Baker AH, McInnes IB, Liew FY. IL-33 reduces the development of atherosclerosis. J Exp Med. 2008;205:339–46.
Smithgall MD, Comeau MR, Yoon BR, Kaufman D, Armitage R, Smith DE. IL-33 amplifies both Th1- and Th2-type responses through its activity on human basophils, allergen-reactive Th2 cells, iNKT and NK cells. Int Immunol. 2008;20:1019–30.
Bao Q, Lv R, Lei M. IL-33 attenuates mortality by promoting IFN-γ production in sepsis. Inflamm Res. 2018;67:531–38.
Zaibi MS, Kępczyńska MA, Harikumar P, Alomar SY, Trayhurn P. IL-33 stimulates expression of the GPR84 (EX33) fatty acid receptor gene and of cytokine and chemokine genes in human adipocytes. Cytokine. 2018;110:189–93.
Chackerian AA, Oldham ER, Murphy EE, Schmitz J, Pflanz S, Kastelein R. A. IL-1 receptor accessory protein and ST2 comprise the IL33 receptor complex. J Immunol. 2007;179:2551–5.
Komai-Koma M, Xu D, Li Y, McKenzie AN, McInnes IB, Liew FY. IL-33 is a chemoattractant for human Th2 cells. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:2779–86.
Vasanthakumar A, Moro K, Xin A, Liao Y, Gloury R, Kawamoto S, Fagarasan S, Mielke LA, Afshar-Sterle S, Masters SL, Nakae S, Saito H, Wentworth JM, Li P, Liao W, Leonard WJ, Smyth GK, Shi W, Nutt SL, Koyasu S, Kallies A. The transcriptional regulators IRF4, BATF and IL-33 orchestrate development and maintenance of adipose tissue-resident regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:276–85.
Kolodin D, Van Panhuys N, Li C, Magnuson AM, Cipolletta D, Miller CM, Wagers A, Germain RN, Benoist C, Mathis D. Antigen- and cytokine-driven accumulation of regulatory t cells in visceral adipose tissue of lean mice. Cell Metab. 2015;21:543–57.
Chen CC, Kobayashi T, Iijima K, Hsu FC, Kita H. IL-33 dysregulates regulatory T cells and impairs established immunologic tolerance in the lungs. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:1351–63.
Yang Z, Grinchuk V, Urban JF Jr, Bohl J, Sun R, Notari L, Yan S, Ramalingam T, Keegan AD, Wynn TA, Shea-Donohue T. Macrophages as IL-25/1L-33 responsive cells play an important role in the induction of type 2 immunity. PLoS One. 2013;8:1–11.
Suzukawa M, Motoyasu I, Koketsu R, Nagase H, Tamura C, Komiya A, Nakae S, Matsushima K, Ohta K, Yamamoto K, Yamaguchi M. An IL-1 cytokine member, IL-33, induces human basophil activation via its ST2 receptor. J Immunol. 2008;181:5981–9.
Ho LH, Ohno T, Oboki K, Kajiwara N, Suto H, Iikura M, Okayama Y, Akira S, Saito H, Galli SJ, Nakae S. IL-33 induces IL-13 production by mouse mast cells independently of IgE-FcepsilonRI signals. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;82:1481–90.
Iikura M, Suto H, Kajiwara N, Oboki K, Ohno T, Okayama Y, Saito H, Galli SJ, Nakae S. IL-33 can promote survival, adhesion and cytokine production in human mast cells. Lab Investig. 2007;87:971–8.
Willebrand R, Voehringer D. IL-33-Induced cytokine secretion and survival of mouse eosinophils is promoted by autocrine GM-CSF. PLoS One. 2016;11:1–14.
Hashiguchi M, Kashiwakura Y, Kojima H, Kobayashi A, Kanno Y, Kobata T. IL-33 activates eosinophils of visceral adipose tissue both directly and via innate lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 2015;45:876–85.
Moro K, Yamada T, Tanabe M, Takeuchi T, Ikawa T, Kawamoto H, Furusawa J, Ohtani M, Fujii H, Koyasu S. Innate production of th2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit(+)Sca-1(+) lymphoid cells. Nature. 2010;463:540–4.
Neill DR, Wong SH, Bellosi A, Flynn RJ, Daly M, Langford TK, Bucks C, Kane CM, Fallon PG, Pannell R, Jolin HE, McKenzie AN. Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature. 2010;464:1367–70.
Price AE, Liang HE, Sullivan BM, Reinhardt RL, Eisley CJ, Erle DJ, Locksley RM. Systemically dispersed innate IL-13-expressing cells in type 2 immunity. PNAS. 2010;107:11489–94.
Pushparaj PN, Tay HK, H’ng SC, Pitman N, Xu D, McKenzie A, Liew FY, Melendez AJ. The cytokine interleukin-33 mediates anaphylactic shock. PNAS. 2009;106:9773–8.
Bonilla WV, Fröhlich A, Senn K, Kallert S, Fernandez M, Johnson S, Kreutzfeldt M, Hegazy AN, Schrick C, Fallon PG, Klemenz R, Nakae S, Adler H, Merkler D, Löhning M, Pinschewer DD. The alarmin interleukin-33 drives protective antiviral CD8+ T cell responses. Science. 2012;335:984–9.
Sesti-Costa R, Silva GK, Proença-Módena JL, Carlos D, Silva ML, Alves-Filho JC, Arruda E, Liew FY, Silva JS. The IL-33/ST2 pathway controls coxsackievirus B5-induced experimental pancreatitis. J Immunol. 2013;191:283–92.
Bourgeois E, Van LP, Samson M, Diem S, Barra A, Roga S, Gombert JM, Schneider E, Dy M, Gourdy P, Girard JP, Herbelin A. The pro-Th2 cytokine IL-33 directly interacts with invariant NKT and NK cells to induce IFN-gamma production. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:1046–55.
Le HT, Tran VG, Kim W, Kim J, Cho HR, Kwon B. IL-33 priming regulates multiple steps of the neutrophil-mediated anti-Candida albicans response by modulating TLR and dectin-1 signals. J Immunol. 2012;189:287–95.
Lan F, Yuan B, Liu T, Luo X, Huang P, Liu Y, Dai L, Yin H. Interleukin-33 facilitates neutrophil recruitment and bacterial clearance in S. aureus-caused peritonitis. Mol Immunol. 2016;72:74–80.
Alves-Filho JC1, Sônego F, Souto FO, Freitas A, Verri WA Jr, Auxiliadora-Martins M, Basile-Filho A, McKenzie AN, Xu D, Cunha FQ, Liew FY. Interleukin-33 attenuates sepsis by enhancing neutrophil influx to the site of infection. Nat Med. 2010;16:708–12.
Zarpelon AC, Rodrigues FC1, Lopes AH, Souza GR, Carvalho TT, Pinto LG1, Xu D, Ferreira SH, Alves-Filho JC, McInnes IB, Ryffel B, Quesniaux VF, Reverchon F, Mortaud S, Menuet A, Liew FY, Cunha FQ, Cunha TM, Verri WA Jr. Spinal cord oligodendrocyte-derived alarmin IL-33 mediates neuropathic pain. FASEB J. 2016;30:54–65.
Cayrol C, Girard JP. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): a nuclear cytokine from the IL-1 family. Immunol Rev. 2018;281:154–68.
Zhao J, Zhang H, Liu SB, Han P, Hu S, Li Q, Wang ZF, Mao-Ying QL, Chen HM, Jiang JW, Wu GC, Mi WL, Wang YQ. Spinal interleukin-33 and its receptor ST2 contribute to bone cancer-induced pain in mice. Neuroscience. 2013;253:172–82.
Aimo A, Migliorini P, Vergaro G, Franzini M, Passino C, Maisel A, Emdin M. The IL-33/ST2 pathway, inflammation and atherosclerosis: trigger and target? Int J Cardiol. 2018;267:188–92.
Ryba-Stanisławowska M, Buksa L, Brandt A, Juhas U, Myśliwiec M. IL-33 improves the suppressive potential of regulatory T cells in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:67–73.
Nascimento DC, Melo PH, Piñeros AR, Ferreira RG, Colón DF, Donate PB, Castanheira FV, Gozzi A, Czaikoski PG, Niedbala W, Borges MC, Zamboni DS, Liew FY, Cunha FQ, Alves-Filho JC. IL-33 contributes to sepsis-induced long-term immunosuppression by expanding the regulatory T cell population. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1–14.
Ali S, Mohs A, Thomas M, Klare J, Ross R, Schmitz ML, Martin MU. The dual function cytokine IL-33 interacts with the transcription factor NF-κB to dampen NF-κB-stimulated gene transcription. J Immunol. 2011;187:1609–1614.
Lee EJ, So MW, Hong S, Kim YG, Yoo B, Lee CK. Interleukin-33 acts as a transcriptional repressor and extracellular cytokine in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine. 2017;77:35–43.
Gautier V, Cayrol C, Farache D, Roga S, Monsarrat B, Burlet-Schiltz O, Peredo AG, Girard J. Extracellular IL-33 cytokine, but not endogenous nuclear IL-33, regulates protein expression in endothelial cells. Sic Rep. 2016;6:34255.
Cayrol C, Girard JP. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is inactivated after maturation by caspase-1. PNAS. 2009;106:9021–6.
Ali S, Nguyen DQ, Falk W, Martin MU. Caspase 3 inactivates biologically active full length interleukin-33 as a classical cytokine but does not prohibit nuclear translocation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;391:1512–6.
Luthi AU, Cullen SP, McNeela EA, Duriez PJ, Afonina IS, Sheridan C, Brumatti G, Taylor RC, Kersse K, Vandenabeele P, Lavelle EC, Martin SJ. Suppression of interleukin-33 bioactivity through proteolysis by apoptotic caspases. Immunity. 2009;31:84–98.
Talabot-Ayer D, Lamacchia C, Gabay C, Palmer G. Interleukin-33 is biologically active independently of caspase-1 cleavage. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:19420–6.
Ohno T, Oboki K, Kajiwara N, Morii E, Aozasa K, Flavell RA, Okumura K, Saito H, Nakae S. Caspase-1, caspase-8, and calpain are dispensable for IL-33 release by macrophages. J Immunol. 2009;183:7890–7.
Madouri F, Guillou N, Fauconnier L, Marchiol T, Rouxel N, Chenuet P, Ledru A, Aprtoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Chamaillard M, Zheng SG, Trovero F, Quesniaux VFJ, Ryffel B, Togbe D. Caspase-1 activation by NLRP3 inflammasome dampens IL-33 dependent house dust mite-induced allergic lung inflammation. J Mol Cell Biol. 2015;7:351–65.
Zhao W, Hu Z. The enigmatic processing and secretion of interleukin-33. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010;7:260–2.
Lefrançais E, Roga S, Gautier V, Gonzalez-De-Peredo A, Monsarrat B, Girard JP, Cayrol C. IL-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. PNAS. 2012;109:1673–8.
Martin SJ, Henry CM, Cullen SP. A perspective on mammalian caspases as positive and negative regulators of inflammation. Mol Cell. 2012;46:387–97.
Wood IS, Wang B, Trayhurn P. IL-33, a recently identified interleukin-1 gene family member, is expressed in human adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;384:105–9.
Molofsky AB, Nussbaum JC, Liang HE, Van Dyken SJ, Cheng LE, Mohapatra A, Chawla A, Locksley RM. Innate lymphoid type 2 cells sustain visceral adipose tissue eosinophils and alternatively activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 2013;210:535–49.
Lee M, Odegaard JI, Mukundan L, Qiu Y, Molofsky AB, Nussubaum JC, Yun K, Locksley RM, Chawla A. Activated type 2 innate lymphoid cells regulates beige fat biogenesis. Cell. 2015;160:74–87.
Shabalina IG, Petrovic N, de Jong JM, Kalinovich AV, Cannon B, Nedergaard J. UCP1 in brite/beige adipose tissue mitochondria is functionally thermogenic. Cell Rep. 2013;5:1196–203.
Wu J, Boström P, Sparks LM, Ye L, Choi JH, Giang AH, Khandekar M, Virtanen KA, Nuutila P, Schaart G, Huang K, Tu H, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Hoeks J, Enerbäck S, Schrauwen P, Spiegelman BM. Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human. Cell. 2012;150:366–76.
Odegaard JI, Lee MW, Sogawa Y, Bertholet AM, Locksley RM, Weinberg DE, Kirichok Y, Deo RC, Chawla A. Perinatal licensing of thermogenesis by IL-33 and ST2. Cell. 2016;166:841–54.
Stumpo R, Kauer M, Martin S, Kolb H. Alternative activation of macrophage by IL-10. Pathobiology. 1999;67(5–6):245–8.
Nguyen KD, Qiu Y, Cui X, Goh YP, Mwangi J, David T, Mukundan L, Brombacher F, Locksley RM, Chawla A. Alternatively activated macrophages produce catecholamines to sustain adaptive thermogenesis. Nature. 2011;480:104–8.
Wu D, Molofsky AB, Liang HE, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Jouihan HA, Bando JK, Chawla A, Locksley RM. Eosinophils sustain adipose alternatively activated macrophages associated with glucose homeostasis. Science. 2011;332:243–7.
Talukdar S, Oh DY, Bandyopadhyay G, Li D, Xu J, McNelis J, Lu M, Li P, Yan Q, Zhu Y, Ofrecio J, Lin M, Brenner MB, Olefsky JM. Neutrophils mediate insulin resistance in high fat diet fed mice via secreted elastase. Nat Med. 2012;18:1407–12.
Stienstra R, Joosten LAB, Koenen T, Van Tits B, Van Diepen JA, Van Dan Berg SAA, Rensen PCN, Voshol PJ, Fantuzzi G, Hijmans A, Kersten S, Muller M, Van Den Ber WB, Van Rooijen N, Wabitsch M, Kullberg BJ, Van Der Meer JWM, Kanneganti T, Tack CJ, Netea MG. The inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activation controls adipocyte differentiation and insulin sensitivity. Cell Metab. 2010;12:593–605.
Ding X, Luo Y, Zhang X, Zheng H, Yang X, Yang X, Liu M. IL-33-driven ILC2/eosinophil axis in fat is induced by sympathetic tone and suppressed by obesity. J Endocrinol. 2016;231:35–48.
Miller AM, Purves D, McConnachie A, Asquith DL, Batty GD, Burns H, Cavanagh J, Ford I, McLean JS, Packard CJ, Shiels PG, Turner H, Velupillai YN, Deans KA, Welsh P, McInnes IB, Sattar N. Soluble ST2 associates with diabetes but not established cardiovascular risk factors: a new inflammatory pathway of relevance to diabetes? PLoS One. 2012;7:1–7.
Alkhouri N, Gornicka A, Berk MP, Thapaliya S, Dixon LJ, Kashyap S, Schauer PR, Feldstein AE. Adipocyte apoptosis, a link between obesity, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:3428–48.
Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A, Galgani JE, Stadler K, Mynatt RL, Ravussin E, Stephens JM, Dixit VD. The NALP3/NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced autoinflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2011;17:179–88.
Ghayur T, Banerjee S, Hugunin M, Butler D, Herzog L, Carter A, Quintal L, Sekut L, Talanian R, Paskind M, Wong W, Kamen R, Tracey D, Allen H. Caspase-1 processes IFN-gamma-inducing factor and regulates LPS-induced IFN-gamma production. Nature. 1997;386:619–23.
Molofsky AB, Gool FV, Liang H, Van Dyken SJ, Nussbaum JC, Lee J, Bluestone JA, Locksley RM. Interleukin-33 and interferon-g conter-regulate group 2 innate lymphoid cell activation during immune pertubation. Immunity. 2015;34:161–74.
Kumar S, Tzimas MN, Griswold DE, Young PR. Expression of ST2, an interleukin-1 receptor homologue, is induced by proinflammatory stimuli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;235(3):474–8.
Mildner M, Storka A, Lichtenauer M, Mlitz V, Ghannadan M, Hoetzenecker K, Nickl S, Dome B, Tschachler E, Ankersmit HJ. Primary sources and immunological prerequisites for sST2 secretion in humans. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;87(4):769–77.
Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y, Nakayama O, Makishima M, Matsuda M, Shimomura I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Investig. 2004;114:1752–61.
Cohen ES, Scott IC, Majithiya JB, Rapley L, Kemp BP, England E, Rees DG, Overed-Sayer CL, Woods J, Bond NJ, Veyssier CS, Embrey KJ, Sims DA, Sanith MR, Voudsen KA, Strain MD, Chan DTY, Carmen S, Huntington CE, Flavell L, Xu J, Popovic B, Brightling CE, Vaughan TJ, Butler R, Lowe DC, Higazi DR, Corkill DJ, May RD, Sleeman MA, Mustelin T. Oxidation of the alarmin IL-33 regulates ST2-dependent inflammation. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8327.
Acknowledgements
AT credits CNPq (305634/2017-8) for the research productivity fellowship. ERV credits CNPq (208183/2017-5) for the post-doc fellowship.
Funding
Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais/Fapemig (APQ-01420-14) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico/CNPq (447537/2014-8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, M.F.A., Talvani, A. & Rocha-Vieira, E. IL-33 in obesity: where do we go from here?. Inflamm. Res. 68, 185–194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-019-01214-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-019-01214-2