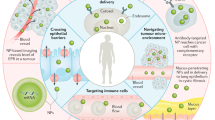
Abstract
Nanoparticles (NPs) comprised of nanoengineered complexes are providing new opportunities for enabling targeted delivery of a range of therapeutics and combinations. A range of functionalities can be included within a nanoparticle complex, including surface chemistry that allows attachment of cell-specific ligands for targeted delivery, surface coatings to increase circulation times for enhanced bioavailability, specific materials on the surface or in the nanoparticle core that enable storage of a therapeutic cargo until the target site is reached, and materials sensitive to local or remote actuation cues that allow controlled delivery of therapeutics to the target cells. However, despite the potential benefits of NPs as smart drug delivery and diagnostic systems, much research is still required to evaluate potential toxicity issues related to the chemical properties of NP materials, as well as their size and shape. The need to validate each NP for safety and efficacy with each therapeutic compound or combination of therapeutics is an enormous challenge, which forces industry to focus mainly on those nanoparticle materials where data on safety and efficacy already exists, i.e., predominantly polymer NPs. However, the enhanced functionality affordable by inclusion of metallic materials as part of nanoengineered particles provides a wealth of new opportunity for innovation and new, more effective, and safer therapeutics for applications such as cancer and cardiovascular diseases, which require selective targeting of the therapeutic to maximize effectiveness while avoiding adverse effects on non-target tissues.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panyam J, Labbhasetwar V (2003) Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:329–347
Faraji AH, Wipf P (2009) Nanoparticles in cellular drug delivery. Bioorg Med Chem 17:2950–2962
Loomis K, McNeeley K, Bellamkonda RV (2011) Nanoparticles with targeting, triggered release, and imaging functionality for cancer applications. Soft Matter 7(3):839–856
Su X, Zhan X, Tang F, Yao JY, Wu J (2011) Magnetic nanoparticles in brain disease diagnosis and targeting drug delivery. Curr Nanosci 7(1):37–46
Khlebtsov N, Dykman L (2011) Biodistribution and toxicity of engineered gold nanoparticles: a review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Chem Soc Rev 40(3):1647–1671
Fitzgerald KT, Holladay CA, McCarthy C, Power KA, Pandit A, Gallagher WM (2011) Standardization of models and methods used to assess nanoparticles in cardiovascular applications. SMALL 7(6):705–717
Petkar KC, Chavhan SS, Agatonovik-Kustrin S, Sawant KK (2011) Nanostructured materials in drug and gene delivery: a review of the state of the art. Cri Rev Ther Drug Carr Sys 28(2):101–164
Das S, Chaudhury A (2011) Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. AAPS Pharmscitech 12(1):62–76
Cheng YY, Zhao LB, Li YW, Xu TW (2011) Design of biocompatible dendrimers for cancer diagnosis and therapy: current status and future perspectives. Chem Soc Rev 40(5):2673–2703
Schroeder A, Levins CG, Cortez C, Langer R, Anderson DG (2010) Lipid-based nanotherapeutics for siRNA delivery. J Intern Med 267(1):9–21
Kaasgaard T, Andresen TL (2010) Liposomal cancer therapy: exploiting tumor characteristics. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7(2):225–243
Slevin M, Badimon L, Grau-Olivares M, Ramis M, Sendra J, Morrison M, Krupinski J (2010) Combining nanotechnology with current biomedical knowledge for the vascular imaging and treatment of atherosclerosis. Mol Biosys 6(3):444–450
Ruenraroengsak P, Cook JM, Florence AT (2010) Nanosystem drug targeting: facing up to complex realities. J Control Release 141(3):265–276
Petros RA, DeSimone JM (2010) Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(8):615–627
Duceppe N, Tabrizian M (2010) Advances in using chitosan-based nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo drug and gene delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7(10):1191–1207
Bharali DJ, Mousa SA (2010) Emerging nanomedicines for early cancer detection and improved treatment: current perspective and future promise. Pharmacol Ther 128(2):324–335
Tran N, Webster TJ (2010) Magnetic nanoparticles: biomedical applications and challenges. J Mater Chem 20(40):8760–8767
Zrazhevskiy P, Sena M, Gao XH (2010) Designing multifunctional quantum dots for bioimaging, detection, and drug delivery. Chem Soc Rev 39(11):4326–4354
Malam Y, Loizidou M, Seifalian AM (2009) Liposomes and nanoparticles: nanosized vehicles for drug delivery in cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30(11):592–599
Puri A, Loomis K, Smith B, Lee JH, Yavlovich A, Heldman E, Blumenthal R (2009) Lipid-based nanoparticles as pharmaceutical drug carriers: from concepts to clinic. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carr Sys 26(6):523–580
Devalapally H, Chakilam A, Amiji M (2007) Role of nanotechnology in pharmaceutical product development. J Pharm Sci 96:2547–2565
Prabaharan M, Grailer JJ, Pilla S, Steeber DA, Gong S (2009) Gold nanoparticles with a monolayer of doxorubicin-conjugated amphiphilic block copolymer for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 30:6065–6075
Choi O, Hu ZQ (2008) Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 42:4583–4588
Bar-Ilan O, Albrecht RM, Fako VE et al (2009) Toxicity assessments of multisized gold and silver nanoparticles in Zebrafish embryos. SMALL 5:1897–1910
Tarantola M, Pietuch A, Schneider D et al (2011) Toxicity of gold-nanoparticles: synergistic effects of shape and surface functionalization on micromotility of epithelial cells Nanotoxicology 5(2):254–268
Jin H, Heller DA, Sharma R et al (2009) Size-dependent cellular uptake and expulsion of single-walled carbon nanotubes: single particle tracking and a generic uptake model for nanoparticles. ACS NANO 3(1):149–158
Chae SR, Badireddy AR, Budarz JF et al (2010) Heterogeneities in fullerene nanoparticle aggregates affecting reactivity, bioactivity, and transport. ACS NANO 4(9):5011–5018
Gillies ER, Frechet JMJ (2005) pH-responsive copolymer assemblies for controlled release of doxorubicin. Bioconj Chem 16:361–368
AillonKL Xie Y, El-Gendy N, BerklandCJ Laird, Forrest M (2009) Effects of nanomaterial physicochemical properties on in vivo toxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:457–466
Alivisatos AP, Johnsson KP, Peng X et al (1996) Organization of ‘nanocrystal molecules’ using DNA. Nature 382:609–611
Chhabra R, Sharma J, Liu Y et al (2010) DNA self-assembly for nanomedicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62(6):617–625
Muller RH, Mader K, Gohla ÈS (2000) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharma Biopharma 50:161–177
van Schooneveld MM, Vucic E, Koole R et al (2008) Improved biocompatibility and pharmacokinetics of silica nanoparticles by means of a lipid coating: a multimodality investigation. Nanoletters 8(8):2517–2525
Stevens PJ, Sekido M, Lee RJ (2004) A folate receptor-targeted lipid nanoparticle formulation for a lipophilic paclitaxel prodrug. Pharm Res 21(12):2153–2157
Liu W, He Z, Liang J, Zhu Y, Xu H, Yang X (2008) Preparation and characterization of novel fluorescent nanocomposite particles: CdSe/ZnS core-shell quantum dots loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 84A:1018
Cormode DP, Chandrasekar R, Delshad A et al (2009) Comparison of synthetic high density lipoprotein (HDL) contrast agents for MR imaging of atherosclerosis. Bioconj Chem 20(5):937–943
Franzen S (2011) A comparison of peptide and folate receptor targeting of cancer cells: from single agent to nanoparticle. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 8(3):281–298
Chen B, Wu W, Wang X (2011) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for tumor-targeted therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 11(2):184–189
Tan ML, Choong PFM, Dass CR (2010) Recent developments in liposomes, microparticles and nanoparticles for protein and peptide drug delivery. Peptides 31(1):184–193
Veiseh O, Gunn JW, Zhang MQ (2010) Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62(3):284–304
Sundar S, Kundu J, Kundu SC (2010) Biopolymeric nanoparticles. Sci Technol Adv Mater 11(1): Art No. 014104 2010
Schartl W (2010) Current directions in core-shell nanoparticle design. Nanoscale 2(6):829–843
Nagpal K, Singh SK, Mishra DN (2010) Chitosan nanoparticles: a promising system in novel drug delivery. Chem Pharm Bull 58(11):1423–1430
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Elst LV, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108(6):2064–2110
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26(18):3995–4021
Lu AH, Salabas EL, Schuth F (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalisation, and application. Angewandte Chemie-Int Ed 46(8):1222–1244
Shen L, Laibinis PE, Hatton TA (1999) Bilayer surfactant stabilized magnetic fluids: synthesis and interactions at interfaces. Langmuir 15:447–453
Shen L, Stachowiak A, Fateen SEK, Laibinis PE, Hatton TA (2001) Structure of alkanoic acid stabilized magnetic fluids. A small-angle neutron and light scattering analysis. Langmuir 17(2):288–299
Racuciu M, Creanga DE, Calugaru G (2005) Synthesis and rheological properties of an aqueous ferrofluid. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 7(6):2859–2864
Racuciu M, Creanga DE, Airinei A (2006) Citric-acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles for biological applications. Eur Phy J E 21(2):117–121
Hodenius MAJ, Niendorf T, Krombach GA, Richtering W, Eckert T, Lueken H, Speldrich M, Gunther RW, Baumann M, Soenen SJH, De Cuyper M, Schmitz-Rode T (2008) Synthesis, physicochemical characterization and MR relaxometry of aqueous ferrofluids. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8(5):2399–2409
Prow TW, Rose WA, Wang N, Reece LM, Lvov Y, Leary JF (2005) Biosensor-controlled gene therapy/drug delivery with nanoparticles for nanomedicine. Proc SPIE 5692:199–208
Smitham JB, Evans R, Napper DH (1975) Analytical theories of steric stabilization of colloidal dispersions. J Chem Soc—Faraday Transac I 71(2):285–297
Evans R, Napper DH (1977) Perturbation method for incorporating concentration-dependence of Flory–Huggins parameter in the theory of steric stabilization. J Chem Soc—Faraday Transac I 73:1377–1385
Barnard AS (2010) Modelling of nanoparticles: approaches to morphology and evolution. Rep Prog Phys 73:086502
Lin J, Zhang H, Chen Z, Zheng Y (2010) Penetration of lipid membranes by gold nanoparticles: insights into cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, and their relationship. ACS Nano 284(9):5421–5429
Arbab AS, Wilson LB, Ashari P, Jordan EK, Lewis BK, Frank JA (2005) A model of lysosomal metabolism of dextran coated superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles: implications for cellular magnetic resonance imaging. NMR Biomed 18(6):383–389
Lee HS, Kim EH, Shao HP, Kwak BK (2005) Synthesis of SPIO-chitosan microspheres for MRI-detectable embolotherapy. J Magn Magn Mater 293(1):102–105
Lee HS, Shao HP, Huang YQ, Kwak BK (2005) Synthesis of MRI contrast agent by coating superparamagnetic iron oxide with chitosan. IEEE Transac Magn 41(10):4102–4104
Lee SJ, Jeong JR, Shin SC, Kim JC, Chang YH, Chang YM, Kim JD (2004) Nanoparticles of magnetic ferric oxides encapsulated with poly(d, l latide-co-glycolide) and their applications to magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. J Magn Magn Mater 272(76):2432–2433
Hu FX, Neoh KG, Kang ET (2006) Synthesis and in vitro anti-cancer evaluation of tamoxifen-loaded magnetite/PLLA composite nanoparticles. Biomaterials 27(33):5725–5733
Bulte JWM, de Cuyper M, Despres D, Frank JA (1999) Preparation, relaxometry, and biokinetics of PEGylated magnetoliposomes as MR contrast agent. J Magn Magn Mater 194:204–209
Shultz MD, Calvin S, Fatouros PP, Morrison SA, Carpenter EE (2007) Enhanced ferrite nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. J Magn Magn Mater 311(1):464–468
Martina M-S, Fortin J-P, Ménager C, Clément O, Barratt G, Grabielle-Madelmont C, Gazeau F, Cabuil V, Lesieur S (2005) Generation of superparamagnetic liposomes revealed as highly efficient MRI contrast agents for in vivo imaging. J Am Chem Soc 127:10676–10685
Nitin N, LaConte LEW, Zurkiya O, Hu X, Bao G (2004) Functionalization and peptide-based delivery of magnetic nanoparticles as an intracellular MRI contrast agent. J Biol Inorg Chem 9(6):706–712
Kohler N, Fryxell GE, Zhang MQ (2004) A bifunctional poly(ethylene glycol) silane immobilized on metallic oxide-based nanoparticles for conjugation with cell targeting agents. J Am Chem Soc 126(23):7206–7211
Ai H, Flask C, Weinberg B, Shuai X, Pagel MD, Farrell D, Duerk J, Gao JM (2005) Magnetite-loaded polymeric micelles as ultrasensitive magnetic-resonance probes. Adv Mater 17(16):1949
Li Z, Wei L, Gao MY, Lei H (2005) One-pot reaction to synthesize biocompatible magnetite nanoparticles. Adv Mater 17(8):1001
Sun C, Sze R, Zhang MQ (2006) Folic acid-PEG conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticles for targeted cellular uptake and detection by MRI. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 78A(3):550–557
Xie J, Xu C, Kohler N, Hou Y, Sun S (2007) Controlled PEGylation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles for reduced non-specific uptake by macrophage cells. Adv Mater 19(20):3163
Fan QL, Neoh KG, Kang ET, Shuter B, Wang SC (2007) Solvent-free atom transfer radical polymerization for the preparation of poly(poly(ethyleneglycol) monomethacrylate)-grafted Fe3O4 nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and cellular uptake. Biomaterials 28(36):5426–5436
Wang Y, Ng YW, Chen Y, Shuter B, Yi J, Ding J, Wang SC, Feng SS (2008) Formulation of superparamagnetic iron oxides by nanoparticles of biodegradable polymers for magnetic resonance imaging. Adv Func Mater 18(2):308–318
Hu FQ, Wei L, Zhou Z, Ran YL, Li Z, Gao MY (2006) Preparation of biocompatible magnetite nanocrystals for in vivo magnetic resonance detection of cancer. Adv Mater 18(19):2553
Sun C, Veiseh O, Gunn J, Fang C, Hansen S, Lee D, Sze R, Ellenbogen RG, Olson J, Zhang M (2008) In vivo MRI detection of gliomas by chlorotoxin-conjugated superparamagnetic nanoprobes. Small 4(3):372–379
Dodd CH, Hsu HC, Chu WJ, Yang PG, Zhang HG, Mountz JD, Zinn K, Forder J, Josephson L, Weissleder R, Mountz JM, Mountz JD (2001) Normal T-cell response and in vivo magnetic resonance imaging of T cells loaded with HIV transactivator-peptide-derived superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J Immunol Methods 256(1–2):89–105
Dodd C, Mountz J, Chu WJ, Josephson L, Zhang HG, Weissleder R, Mountz JM, Zinn K, Mountz JD, Hsu HC (2001) In vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of T cells loaded with HIV transactivator (tat) peptide-derived super-paramagnetic nanoparticles. Faseb J 15(5):A744–A744
Hsu HC, Dodd C, Chu WJ, Yang PA, Josephson L, Sun SH, Zhang HG, Weissleder R, Mountz JD (2001) Normal response of T cells loaded with HIV transactivator (tat) peptide-derived super-paramagnetic nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Faseb J 15(4):A330–A330
Asongkla N, Bey E, Ren JM, Ai H, Khemtong C, Guthi JS, Chin SF, Sherry AD, Boothman DA, Gao JM (2006) Multifunctional polymeric micelles as cancer-targeted, MRI-ultrasensitive drug delivery systems. Nano Lett 6(11):2427–2430
von zur Muhlen C, von Elverfeldt D, Bassler N, Neudorfer I, Steitz B, Petri-Fink A, Hofmann H, Bode CPK (2007) Superparamagnetic iron oxide binding and uptake as imaged by magnetic resonance is mediated by the integrin receptor Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18): implications on imaging of atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis 193(1):102–111
Martina MS, FortinJP Menager C, Clement O, Barratt G, Grabielle-Madelmont C, Gazeau F, Cabuil V, Lesieur S (2005) Generation of superparamagnetic liposomes revealed as highly efficient MRI contrast agents for in vivo imaging. J Am Chem Soc 127(30):10676–10685
Larsen BA, Haag MA, Serkova NJ, Shroyer KR, Stoldt CR (2008) Controlled aggregation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the development of molecular magnetic resonance imaging probes. Nanotechnology 19(26): 265102. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/19/26/265102
Meincke M, Schlorf T, Kossel E, Jansen O, Glueer CC, Mentlein R (2008) Iron oxide—loaded liposomes for MR imaging. Frontiers Biosci 13:4002–4008
Hultman KL, Raffo AJ, Grzenda AL, Harris PE, Brown TR, O’Brien S (2008) Magnetic resonance imaging of major histocompatibility class II expression in the renal medulla using immunotargeted superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Acs Nano 2(3):477–484
Byrne SJ, Corr SA, Gun’ko YK, Kelly JM, Brougham DF, Ghosh S (2004) Magnetic nanoparticle assemblies on denatured DNA show unusual magnetic relaxivity and potential applications for MRI. Chem Commun 22:2560–2561
Philipse AP, Vanbruggen MPB, Pathmamanoharan C (1994) Magnetic silica dispersions—preparation and stability of surface-modified silica particles with a magnetic core. Langmuir 10(1):92–99
Yan F, Xu H, Anker J, Kopelman R, Ross B, Rehemtulla A, Reddy R (2004) Synthesis and characterization of silica-embedded iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 4(1–2):72–76
Liang S, Wang YX, Zhang CF, Liu XQ, Liu ZF, Xu RH, Yin DZ (2006) Synthesis of amino-modified magnetite nanoparticles coated with Hepama-1 and radiolabeled with Re-188 for bio-magnetically targeted radiotherapy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 269(1):3–7
Santra S, Tapec R, Theodoropoulou N, Dobson J, Hebard A, Tan WH (2001) Synthesis and characterization of silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles in microemulsion: the effect of non-ionic surfactants. Langmuir 17(10):2900–2906
Tartaj P, Serna CJ (2002) Microemulsion-assisted synthesis of tuneable superparamagnetic composites. Chem Mater 14(10):4396–4402
Tartaj P, Serna CJ (2003) Synthesis of monodisperse superparamagnetic Fe/silica nanospherical composites. J Am Chem Soc 125(51):15754–15755
Yang HH, Zhang SQ, Chen XL, Zhuang ZX, Xu JG, Wang XR (2004) Magnetite-containing spherical silica nanoparticles for biocatalysis and bioseparations. Anal Chem 76(5):1316–1321
Carpenter EE, Sangregorio C, O’Connor CJ (1999) Effects of shell thickness on blocking temperature of nanocomposites of metal particles with gold shells. IEEE Transac Magn 35(5):3496–3498
Cho SJ, Idrobo JC, Olamit J, Liu K, Browning ND, Kauzlarich SM (2005) Growth mechanisms and oxidation resistance of gold-coated iron nanoparticles. Chem Mater 17(12):3181–3186
Park JI, Cheon J (2001) Synthesis of “solid solution” and “core-shell” type cobalt-platinum magnetic nanoparticles via transmetalation reactions. J Am Chem Soc 123(24):5743–5746
Ban ZH, Barnakov YA, Golub VO, O’Connor CJ (2005) The synthesis of core-shell iron@gold nanoparticles and their characterization. J Mater Chem 15(43):4660–4662
Lyon JL, Fleming DA, Stone MB, Schiffer P, Williams ME (2004) Synthesis of Fe oxide core/Au shell nanoparticles by iterative hydroxylamine seeding. Nano Lett 4(4):719–723
Kim J, Park S, Lee JE, Jin SM, Lee JH, Lee IS, Yang I, Kim JS, Kim SK, Cho MH, Hyeon T (2006) Designed fabrication of multifunctional magnetic gold nanoshells and their application to magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy. Angewandte Chemie-Int Ed 45(46):7754–7758
Hayashi T, Hirono S, Tomita M, Umemura S (1996) Magnetic thin films of cobalt nanocrystals encapsulated in graphite-like carbon. Nature 381(6585):772–774
Nikitenko SI, Koltypin Y, PalchikO Felner I, Xu XN, Gedanken A (2001) Synthesis of highly magnetic, air-stable iron iron carbide nanocrystalline particles by using power ultrasound. Angewandte Chemie-Int Ed 40(23):4447
Davis SS (2004) Coming of age of lipid-based drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56:1241–1242
UlrichAS AS (2002) Biophysical aspects of using liposomes as delivery vehicles. Biosci Rep 22(2):129–150
Wong HL, Bendayan R, Rauth AM, Wu XY (2004) Development of solid lipid nanoparticles containing ionically complexed chemotherapeutic drugs and chemosensitizers. J Pharma Sci 93(8):1993
Brioschi A, Zara GP, Calderoni S, Gasco MR, Mauro A (2008) Cholesterylbutyrate solid lipid nanoparticles as a butyric acid prodrug. Molecules 13:230–254
Almeida AJ, Souto E (2007) Solid lipid nanoparticles as a drug delivery system for peptides and proteins. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:478–490
del Pozo-Rodríguez A, Pujals S, Delgado D, Solinís MA, Gascón AR, Giralt E, Pedraz JL (2009) A proline-rich peptide improves cell transfection of solid lipid nanoparticle-based non-viral vectors. J Control Release 133:52–59
Partlow KC, Lanza GM, Wickline SA (2008) Exploiting lipid raft transport with membrane targeted nanoparticles: a strategy for cytosolic drug delivery. Biomaterials 29:3367–3375
Huang SK, Mayhew E, Gilani S, Lasic D, Martin FJ, Papahadjopoulos D (1992) Pharmacokinetics and therapeutics of sterically stabilized liposomes in mice bearing C-26 colon carcinoma. Cancer Res 52:6774–6781
Wu X, Deng Y, Wang G, Tao K (2007) Combining siRNAs at two different sites in the EGFR to suppress its expression, induce apoptosis, and enhance 5-fluorouracil sensitivity of colon cancer cells. J Surg Res 138(1):56–63
Schmitt-Sody M, Strieth S, Krasnici S, Sauer B, Schulze B, Teifel M (2003) Neovascular targeting therapy: paclitaxel encapsulated in cationic liposomes improves antitumoral efficacy. Clin Cancer Res 9:2335–2341
Sebastian S, Martin EE, Birgitta S, Brita S, Michael T, Uwe M, Marc D (2004) Neovascular targeting chemotherapy: encapsulation of paclitaxel in cationic liposomes impairs functional tumor microvasculature. Int J Cancer 110:117–124
Furumoto K, Yokoe J-I, Ogawara K-I, Amano S, Takaguchi M, Higaki K, Kai T, Kimura T (2007) Effect of coupling of albumin onto surface of PEG liposome on its in vivo disposition. Int J Pharma 329:110–116
Yokoe J-I, Sakuragi S, Yamatoto K, Teragaki T, Ogowara K-I, Higaki K, Katayama N, Kai T, Sato M, Kimura T (2008) Albumin-conjugated PEG liposome enhances tumor distribution of liposomal doxorubicin in rats. Int J Pharma 353:28–34
Fonseca C, Moreira JN, Ciudad CJ, Pedroso de Lima MC, Simoes S (2005) Targeting of sterically stabilised pH-sensitive liposomes to human T-leukaemia cells. Eur J Pharma Biopharma 59:359–366
Anabousi S, Bakowski U, Schneider M, Huwer H, Lehr C-M, Ehrhardt C (2006) In vitro assessment of transferrin-conjugated liposomes as drug delivery systems for inhalation therapy of lung cancer. Eur J Pharma Sci 29:367–374
Anabousi S, Kleeman E, Bakowski U, Kissel T, Schneider T, Gessler T, Seeger W, Lehr C-M, Ehrhardt C (2006) Effect of PEGylation on the stability of liposomes during nebulisation and in lung surfactant. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 6:3010–3016
Drummond DC, Noble CO, Hayes ME, Park JW, Kirpotin DB (2008) Pharmacokinetics and in vivo drug release rates in liposomal nanocarrier development. J Pharm Sci 97(11):4696–4740
Zhu G, Mock JN, Aljuffali I, Cummings BS, Arnold RD (2011) Secretory phospholipase A2 responsive liposomes. J Pharm Sci. Article first published online: 31 MAR 2011
Andresen TL, Jensen SS, Jørgensen K (2005) Advanced strategies in liposomal cancer therapy: problems and prospects of active and tumor specific drug release. Prog Lipid Res 44(1):68–97
Jensen SS, Andresen TL, Davidsen J, Høyrup P, Shnyder SD, Bibby MC, Gill JH, Jørgensen K (2004) Secretory phospholipase A2 as a tumor-specific trigger for targeted delivery of a novel class of liposomal prodrug anticancer etherlipids. Mol Cancer Ther 3(11):1451–1458
LiS-D Huang L (2006) Targeted delivery of antisense oligodeoxynucleotide and small interference RNA into lung cancer cells. Mol Pharm 3:579–588
Byrne JD, Betancourt T, Brannon-Peppas L (2008) Active targeting schemes for nanoparticle systems in cancer therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1615–1626
Visaria RK, Griffin RJ, Williams BW, Ebbini ES, Paciotti GF, Song CW, Bischo JC (2006) Enhancement of tumor thermal therapy using gold nanoparticle-assisted tumor necrosis factor-A delivery. Mol Cancer Ther 5(4):1014–1020
Farma JM, Puhlmann M, Soriano PA, Cox D, Paciotti GF, Tamarkin L, Alexander HR (2007) Direct evidence for rapid and selective induction of tumor neovascular permeability by tumor necrosis factor and a novel derivative, colloidal gold bound tumor necrosis factor Int. J Cancer 120:2474–2480
Bahtia NS et al. (2009) US Patent Application 2009/0093551
Klostergaard J, Bankson J, Auzenne E, Gibson D, Yuill W, Seeney CE (2007) Magnetic vectoring of magnetically responsive nanoparticles within the murine peritoneum. J Magn Magn Mater 311(1):330–335
Kim J, Lee JE, Lee SH, Yu JH, Lee JH, Park TG, Hyeon T (2008) Designed fabrication of a multifunctional polymer nanomedical platform for simultaneous cancer-targeted imaging and magnetically guided drug delivery. Adv Mater 20(3):478
Jurgons R, Seliger C, Hilpert A, Trahms L, Odenbach S, Alexiou C (2006) Drug loaded magnetic nanoparticles for cancer therapy. J Phys Condens Matter 18(38):S2893–S2902
Hanessian S, Grzyb JA, Cengelli F, Juillerat-Jeanneret L (2008) Synthesis of chemically functionalized superparamagnetic nanoparticles as delivery vectors for chemotherapeutic drugs. Bioorg Med Chem 16(6):2921–2931
Segal E, Satchi-Fainaro R (2009) Design and development of polymer conjugates as anti-angiogenic agents. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:1159–1176
Miller K, Erez R, Segal E, Shabat D, Satchi-Fainaro R (2009) Targeting bone metastases with a bispecific anticancer and antiangiogenic polymer-alendronate-taxane conjugate. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48:2949–2954
Dai H, Jiang X, Tan GC, Chen Y, Torbenson M, Leong KW, Mao HQ (2006) Chitosan-DNA nanoparticles delivered by intrabiliary infusion enhance liver-targeted gene delivery. Int J Nanomed 1(4):507–522
Pradhana P (2010) Targeted temperature sensitive magnetic liposomes for thermo-chemotherapy. J Control Release 142(1):108–121
Spiro SG, Silvestri GA (2005) One hundred years of lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172(5):523–529
Celikoglu F, Celikoglu SI, Goldberg EP (2008) Techniques for intratumoral chemotherapy of lung cancer by bronchoscopic drug delivery. Cancer Ther 6:545–552
Celikoglu F, Celikoglu SI, Goldberg EP (2010) Intratumoural chemotherapy of lung cancer for diagnosis and treatment of draining lymph node metastasis. J Pharm Pharmacol 62(3):287–295
Andresen TL, Jensen SS, Jørgensen K (2005) Advanced strategies in liposomal cancer therapy: problems and prospects of active and tumor specific drug release. Prog Lipid Res 44:68–97
Taylor K, Newton JM (1992) Liposomes for controlled delivery of drugs to the lung. Thorax 47:257–259
Farr SJ, Kellaway IW, Parry-Jones DR, Woolfrey SG (1985) 99 m-Technetium as a marker of liposomal deposition and clearance in the human lung. Int J Pharma 26:303–316
Liu J et al (2008) Solid lipid nanoparticles for pulmonary delivery of insulin. Int J Pharma 356:333–344
Ku T et al (2008) Size dependent interactions of nanoparticles with lung surfactant model systems and the significant impact on surface potential. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8:2971–2978
Kavanagh CA, Rochev YA, Gallagher WM, Dawson KA, Keenan AK (2004) Local drug delivery in restenosis injury: thermoresponsive co-polymers as potential drug delivery systems. Pharmacol Ther 102:1–15
Bennett MJ, O’Sullivan M (2001) Mechanisms of angioplasty and stent restenosis: implications for design of rational therapy. Pharmacol Ther 91:149–166
Burta HM, Hunter WL (2006) Drug-eluting stents: a multidisciplinary success story. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 58(3):350–357
van der Hoeven BL, Pires NM, Warda HM, Oemrawsingh PV, van Vlijmen BJ, Quax PH, Schalij MJ, van der Wall EE, Jukema JW (2005) Drug-eluting stents: results, promises and problems. Int J Cardiol 99(1):9–17
Acharyab G, Park K (2006) Mechanisms of controlled drug release from drug-eluting stents. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 58(3):387–401
Kamath KR, Barrya JJ, Millera KM (2006) The Taxus™ drug-eluting stent: a new paradigm in controlled drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 58(3):412–436
Kuchulakanti PK, Chu WW, Torguson R, Ohlmann P, Rha SW, Clavijo LC et al (2006) Correlates and long-term outcomes of angiographically proven stent thrombosis with sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents. Circulation 113:1108–1113
Sheiban I, Villata G, Bollati M, Sillano D, Lotrionte M, Biondi-Zoccai G (2008) Next-generation drug-eluting stents in coronary artery disease: focus on everolimus-eluting stent (Xience V). Vasc Health Risk Manag 4(1):31–38
Iakovou I, Schmidt T, Bonizzoni E, Ge L, Sangiorgi GM, Stankovic G et al (2005) Incidence, predictors, and outcome of thrombosis after successful implantation of drug-eluting stents. JAMA-J Am Med Assoc 293:2126–2130
Lee SH, Szinai I, Carpenter K, Katsarava R, Jokhadze G, Chu CC et al (2002) In vivo biocompatibility evaluation of stents coated with a new biodegradable elastomeric and functional polymer. Coron Artery Dis 13:237–241
Wickline SA, Neubauer AM, Winter PM, Caruthers SD, Lanza GM (2007) Molecular imaging and therapy of Atherosclerosis with targeted nanoparticles. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:667–680
Park K, Hong H-Y, Moon HJ, Lee B-H, Kim I-S, Kwon IC, Rhee K (2008) A new atherosclerotic lesion probe based on hydrophobically modified chitosan nanoparticles functionalized by the atherosclerotic plaque targeted peptides. J Control Release 128:217–223
Mulder WJM, Strijkers GJ, Briley-Saboe KC et al (2007) Molecular imaging of macrophages in antherosclerotic plaques using bimodal PEG-micelles. Magn Reson Med 58(6):1164–1170
Broz P, Marsch S, Hunzikel P (2007) Targeting of vulnerable plaque macrophages with polymer-based nanostructures. Trends in Cardiovasc Medic 17(6):190
Peters D et al. (2009) Targeting atherosclerosis by using modular, multifunctional micelles. PNAS 106(24): 9815–9819
Karmali PP et al (2008) Targeting of albumin-embedded paclitaxel nanoparticles to tumors. Nanomedicine 5:73–82
Zweers MLT, Engbers GHM, Grijpma DW, Feijen J (2006) Release of anti-restenosis drugs from poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(dl-lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles. J Control Release 114:317–324
Tong R, Cheng J (2008) Paclitaxel-initiated, controlled polymerization of lactide for the formulation of polymeric nanoparticulate delivery vehicles. Angew Chem 47:4830–4834
Westedt UB-TL, Schaper AK (2002) Deposition of nanoparticles in the arterial vessel by porous balloon catheters: localization by confocal laser scanning microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. AAPS PharmSci 44:1–6
Westedt U, Kalinowski M, Wittmar M, Merdan T, Unger F, Fuchs J, Schaller S, Bakowsky U, Kissel T (2007) Poly(vinyl alcohol)-graft-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for local delivery of paclitaxel for restenosis treatment. J Control Release 119:41–51
Orloff LA, Domb AJ, Teomim D, Fishbein I, Golomb G (1997) Biodegradable implant strategies for inhibition of restenosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 24:3–9
Cohen-Sela E, Rosenweig O, Gao J, Epstein H, Gati I, Reich R, Dananberg HD, Golomb G (2006) Alendronate-loaded nanoparticles deplete monocytes and attenuate restenosis. J Control Release 113:23–30
Brito L, Amiji M (2007) Nanoparticulate carriers for the treatment of coronary restenosis. Int J Nanomed 2:143–161
Zou WCG XIY, Zhang N (2009) New approach for local delivery of rapamycin by bioadhesive PLGA-carbopol nanoparticles. Drug Deliv 16:15–23
Orloff LA, Glenn MG, Domb AJ, Esclamado RA (1995) Prevention of venous thrombosis in microvascular surgery by transmural release of heparin from a polyanhydride polymer. Surgery 117:554–559
Westedt U, Barbu-TudoranL Schaper AK, Kalinowski M, Alfke H, Kissel T (2004) Effects of different application parameters on penetration characteristics and arterial vessel wall integrity after local nanoparticle delivery using a porous balloon catheter. Eur J Pharma Biopharma 58:161–168
McCarthy JR, Perez JM, Bruckner C, Weissleder R (2005) Polymeric nanoparticle preparation that eradicate tumors. Nano Lett 5:2552–2556
Lacroix L-M, Ho D, Sun S (2010) Magnetic nanoparticles as both imaging probes and therapeutic agents. Curr Top Med Chem 10:1184–1197
MaherRC MaierSA, Cohen LF, Koh L, Laromaine A, Dick JAG, Stevens MM (2010) Exploiting SERS hot spots for disease-specific enzyme detection. J Phys Chem C114(16):7231–7235
Khang D, Carpenter J, Chun YW, Pareta R, Webster TJ (2010) Nanotechnology for regenerative medicine. Biomed Microdevices 12(4):575–587
Salgado AJ, Oliveira JM, Pirraco RP, Pereira VH, Fraga JS, Marques AP, Neves NM, Mano JF, Reis RL, Sousa N (2010) Carboxymethylchitosan/poly(amidoamine) dendrimer nanoparticles in central nervous systems-regenerative medicine: effects on neuron/glial cell viability and internalization efficiency. Macromol Biosci 10(10):1130–1140
Acknowledgments
Funding through the Competence Centre for Applied Nanotechnology (CCAN) from Enterprise Ireland and IDA Ireland (Industrial Development Agency) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galvin, P., Thompson, D., Ryan, K.B. et al. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery: case studies for cancer and cardiovascular applications. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 69, 389–404 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0856-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0856-6