Abstract
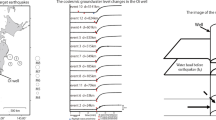
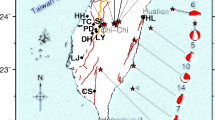
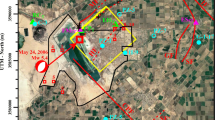
The large scales of co-seismic water level changes in mainland China were observed in response to the tragic 2008 Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake. To better understand the mechanism of these hydrogeological phenomena, groundwater-level data at 17 confined wells, with an epicentral distance of <500 km, were collected. We compare the static strain predicted by dislocation theory with the volumetric strain calculated by the tide effect of the groundwater based on poroelastic theory. The results show that the sign of the co-seismic groundwater level change is consistent with the sign predicted by dislocation theory. Additionally, the magnitude of the strain calculated by the two methods is also concordant in half of the wells. In the rest of the wells, the strains inversed from the groundwater level are one or two orders of magnitude larger than the fault dislocation model. These wells mostly have an epicenter distance larger than 300 km; therefore, the dynamic stress induced by the seismic wave may be responsible for the co-seismic water level changes in these wells. According to these results, we roughly estimate that the effect range of the static stress is approximately 300 km for the Wenchuan earthquake, and the dynamic stresses dominate beyond this epicenter distance. In addition, geological and hydrogeological conditions and other mechanisms may be responsible for these changes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akita, F. and Matsumoto, N. (2004), Hydrological responses induced by the Tokachi-oki earthquake in 2003 at hot spring wells in Hokkaido, Japan, Geophys. Res. Lett., 31(16): L16603.
Beresnev, I. A., and Johnson, P. A. (1994), Elastic-wave stimulation of oil production: a review of methods and results. Geophysics., 59(6), 1000-1017.
Bodvarsson, G. (1970), Confined Fluids as Strain Meters. J Geophy Res., 74, 2711-2718.
Bosl, W. and Nur, A. (2002), Aftershocks and pore fluid diffusion following the 1992 Landers earthquake. J. geophys. Res., 107(B12), 2366.
Che, Y. T., Yu, J. Z., Liu, C. L., Xu, G. M., Zheng, Y. M (2011), Principles on distinguishing interference from seismic precursor of underground water variation and its application. Acta. Seismol. Sinica., 33(6):800-808.
Chen, J. S., Wang, C. Y. (2009), Rising springs along the Silk Road, Geology, 37, 243-246.
Chia, Y., Liu, C., Chuang, P. (2010), Spatial Distribution of Groundwater-Level Changes Induced by Earthquakes. AGU Fall Meeting 2010.
Doan, M. L., Brodsky, E. E., Prious, R., Signer, C. (2006). Tidal analysis of borehole pressure: a tutorial. University of California, Santa Cruz.
Ge, S. and Stover, S. C. (2000), Hydrodynamic response to strike and dip-slip faulting on a half-space. J. geophys. Res., 105: 25,513-525,524.
Gorokhovich,Y. and Fleeger.G (2007). Pymatuning earthquake in Pennsylvania and Late Minoan crisis on Crete. Water. Sci & Tech: Water Supply. 7(1): 245-251.
Gorokhovich,Y.(2005). Abandonment of Minoan palaces on Crete in relation to the earthquake induced changes in groundwater supply. Journal of Archaeological Science. 32(2): 217-222.
Huang, F. (2008), Response of well in Groundwater Monitoring Network in Chinese mainland to distant large earthquakes. Institute of Geophysics, Beijing, China Earthquake Administration, Ph.D. dissertation.
Huang, F. Q., Chen,Y., Zhang, Y., Ma, L., Lai, G. (2008), Groundwater level changes in the digital monitoring network in Mainland of China induced by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, AGU Fall Meeting 2008.
Igarashi, G., and Wakite, H. (1991), Tidal Responses and Earthquake-Related Changes in the Water Level of Deep Wells, J. geophys. Res. 96, 4269-4278.
Jónsson, S., Segall, P., Pedersen, R., Bjornsoon, G. (2003), Post-earthquake ground movements correlated to pore-pressure transients, Nature, 424(6945),179-183.
King C-Y, Azuma, S., Igarashi, G., Ohno, M., Saito, H., Wakita, H. (1999), Earthquake related water-level changes at 16 closely clustered wells in Tono, central Japan, J Geophys Res., 104, B6, 13,073-13,082.
Lan, S. S., Chi, B. M., Jiang, J. Y. (2011), Comparison of Groundwater-Level Response to Near Earthquake and Distant Earthquake: Taking Wenchuan Earthquake and Sumatra Earthquake for Example, J. Jilin. Univ (Earth Science Edition), 41(1):145-152. (in Chinese).
Lee, T., Chia, Y., Lee, R. (2009), Groundwater Level Changes Associated with the Wenchuan Earthquake of May 12, 2008, AGU Fall Meeting 2009.
Li, Z.W., Liu, S.G., Cheng, H.D., Liu, S., Guo, B., Tian, X.B. (2008), Structural segmentation and zonation and differential deformation across and along the Lomgmen thrust belt, West Sichuan, China. J Chendu. Univ. Tech(Science and technology edition)., 35(4), 440-454. (in Chinese).
Lin, J. and Stein R. S. (2004), Stress triggering in thrust and subduction earthquakes and stress interaction between the southern San Andreas and nearby thrust and strike-slip faults. J. Geophys. Res., 109(B2), B02303
Liu X.Y., Li, J., Zheng, X. J. and Wang, L. (2009), Response of well level to crust body strain caused by Wenchuan Ms 8.0 earthquake. Journal of geodesy and geodynamics, 29(3), 28-33.
Liu, C.L., Wang, G.C., Zhang, W. H., Mei, J. C. (2009), Co-seismic responses of groundwater levels in the Three Gorges well-network to the Wenchuan M S 8.0 earthquake, Earthq. Sci., 22(2),143-148.
Manga, M., and Brodsky, E.E. (2006), Seismic Triggering of Eruptions in the Far Field: Volcanoes and Geysers, Annu. Rev. Earth. Planet. Sci., 34, 263-291.
Manga, M., and Wang, C. Y. (2007), Earthquake hydrology, Treatise on geophysics, 4, 293-320.
Melchior, P. J. (1983), The tides of the planet Earth. New York, Pergamon.
Okada, Y. (1985), Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space, B. Seismol. Soc. Am., 75(4), 1135-1154.
Qiu, G. L., Guan, Z. J., Yang, X.H., Yang, H. (2011), Study on Coseismic Water-Level Changes of the Wenchuan Ms8. 0 Earthquake in Sichuan Area, North. China. Earthq. Sci., 29(2), 40-44.
Quilty, E. G., and Roeloffs, E. A. (1997), Water-Level Changes in Response to the 20 December 1994 Earthquake near Parkfield, California, B. Seismol. Soc. Am., 87, 310-317.
Roeloffs, E. (1996), Poroelastic techniques in the study of earthquake related hydrologic phenomena, Adv. Geophy., 37, 135-195.
Singh, V. (2008), Impact of the Earthquake and Tsunami of December 26, 2004, on the groundwater regime at Neill Island (south Andaman). J. Enviro.Manage. 89(1): 58-62.
Toda, S., Stein, R. S., Dinger, K. B., Bozkurt, S. B. (2005), Forecasting the evolution of seismicity in southern California: animations built on earthquake stress transfer. J. Geophys.Res., 110(B5), B05S16.
Toll, N. J., and Rasmussen, T. C. (2007), Removal of barometric pressure effects and earth tides from observed water levels, Ground water., 45(1), 101-105.
Venedikov, A. P., Arnoso, J., Vieira, R. (2003), VAV: a program for tidal data processing, Comput Geosci, 29(4), 487-502.
Wakita, H. (1975), Water wells as possible indicators of tectonic strain, Science, 189(4202), 553.
Wang, C. M., Che,Y. T., Wan, D. K., Dong, S.Y. (1988), Study of micro-behavior of groundwater, Beijing, Seismological Press. (in chinese).
Wang, C., and Chia, Y. (2008), Mechanism of water level changes during earthquakes: Near field versus intermediate field, Geophys. Res. Lett., 35(12), L12402.
Wang, C., Cheng, L. H., Chin, C.V., Yu, S.B. (2001), Coseismic hydrologic response of an alluvial fan to the 1999 Chi–Chi earthquake, Taiwan, Geology, 29(9), 831.
Wang, C.-Y. and Chia. Y. (2008), Mechanism of water level changes during earthquakes: Near field versus intermediate field, Geophys. Res. Lett., 35: L12402(12405).
Wang, C.-Y., and Manga, M. (2010), Earthquakes and Water, New York, Springer.
Wang, C.-Y., Chia,Y., Wang, P., and Dreger, D. (2009), Role of S waves and Love waves in coseismic permeability enhancement, Geophys. Res. Lett., 36: L09404.
Xu, X. W., Wen, X. Z., Ye, J. Q., Ma, B. Q. et al. (2008), The Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake surface ruptures and its seismogenic structure. Seismol Geol., 30(3), 597-629. (in Chinese).
Yan, R., Chen, Y., Gao, F. w., Huang, F. Q. (2008), Calculating B value of aquifer from volume strain and water level response to seismic waves at Changping seismic station. Acta Seismological Sinica, 30(2), 144-151.
Yang, Z. Z., Deng, Z. H., Liu, C.G. et al. (2008), Co-seismic changes of water level and water temperature caused by Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, Seisomol Geol 30(4), 895-905. (in Chinese).
Zhang, Y., and Huang, F. Q. (2011), Mechanism of Different Coseismic Water-Level Changes in Wells with Similar Epicentral Distances of Intermediate Field, B Seismol Soc Am., 101(4), 1531-1541.
Zhang, Y., Huang, F. Q., Lai, G. (2009), Research on Skempton’s coefficient B based on the observation of groundwater of Changping station, Eartheq. Sci., 22(6), 631-638.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge comments and helpful information from Dr. Shemin Ge, Dr. Brian Mitchell and two anonymous reviewers, which made the quality of manuscript considerably improved. This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (40930637), Special Project of Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration (DF-IGCEA-0608-2-10) and Special Project of Seismological Community (200808079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Z., Wang, G. & Liu, C. Co-Seismic Groundwater Level Changes Induced by the May 12, 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake in the Near Field. Pure Appl. Geophys. 170, 1773–1783 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0606-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0606-1