Abstract
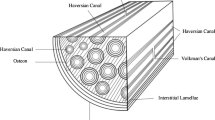
In this paper, a continuum mixture model with evolving mass densities and porosity is proposed to describe the process of bone remodeling in the presence of bio-resorbable materials as driven by externally applied loads. From a mechanical point of view, both bone tissue and biomaterial are modeled as linear elastic media with voids in the sense of Cowin and Nunziato (J Elast 13:125-147, 1983). In the proposed continuum model, the change of volume fraction related to the void volume is directly accounted for by considering porosity as an independent kinematical field. The bio-mechanical coupling is ensured by the introduction of a suitable stimulus which allows for discriminating between resorption (of both bone and biomaterial) and synthesis (of the sole natural bone) depending on the level of externally applied loads. The presence of a ‘lazy zone’ associated with intermediate deformation levels is also considered in which neither resorption nor synthesis occur. Some numerical solutions of the integro-differential equations associated with the proposed model are provided for the two-dimensional case. Ranges of values of the parameters for which different percentages of biomaterial substitution occur are proposed, namely parameters characterizing initial and maximum values of mass densities of bone tissue and of the bio-resorbable material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreaus U., Colloca M., Iacoviello D.: Optimal bone density distributions: Numerical analysis of the osteocyte spatial influence in bone remodeling. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 113(1), 80–91 (2014)
Andreaus, U., Giorgio, I., Lekszycki, T.: A 2-D continuum model of a mixture of bone tissue and bio-resorbable material for simulating mass density redistribution under load slowly variable in time. J. Applied Math and Mech. (ZAMM), pp. 1–23. (2013) doi:10.1002/zamm.201200182
Andreaus U., Colloca M., Iacoviello D.: Modelling of trabecular architecture as result of an optimal control procedure, Chapter II. In: Andreaus, U., Iacoviello, D. Biomedical Imaging and Computational Modeling in Biomechanics, pp. 19--37. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Andreaus U., Colloca M., Iacoviello D.: An optimal control procedure for bone adaptation under mechanical stimulus. Control Eng. Pract. 20, 575–583 (2012)
Andreaus U., Colloca M., Iacoviello D., Pignataro M.: Optimal-tuning pid control of adaptive materials for structural efficiency. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 43, 43–59 (2011)
Andreaus U., Colloca M.: Prediction of micromotion initiation of an implanted femur under physiological loads and constraints using the finite element method. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H, J. Eng. Med. 223, 589–605 (2009)
Andreaus U., Colloca M., Toscano A.: Mechanical behaviour of a prosthesized human femur: a comparative analysis between walking and stair climbing by using the finite element method. Biophys. Bioeng. Lett. 1, 1–15 (2008)
Andreaus U., dell’Isola F., Porfiri M.: Piezoelectric passive distributed controllers for beam flexural vibrations. J. Vib. Control 10, 625–659 (2004)
Armentano I., Dottori M., Fortunati E., Mattioli S., Kenny J.M.: Biodegradable polymer matrix nanocomposites for tissue engineering: A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 95, 2126–2146 (2010)
Beaupré G.S., Orr T.E., Carter D.R.: An approach for time-dependent bone modelling and remodelling-Theoretical development. J. Orthopaed. Res. 8, 651–661 (1990)
Beaupré G.S., Orr T.E., Carter D.R.: An approach for time-dependent bone modelling and remodelling-application: A preliminary remodelling simulation. J. Orthopaed. Res. 8, 662–670 (1990)
Carcaterra, A.: Theoretical modelling and simulations of a neuron-based micro-motor, ENOC 2011. In Proceedings of the 7th European Nonlinear Oscillations Conference, July 24–29, Roma (2011)
Carcaterra A., Akay A.: Transient energy exchange between a primary structure and a set of oscillators: Return time and apparent damping. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115(2), 683–696 (2004)
Carcaterra A.: An entropy formulation for the analysis of energy flow between mechanical resonators. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 16(5), 905–920 (2002)
Carter D.R., Hayes W.C.: The compressive behaviour of bone as a two-phase porous structure. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 59, 954–962 (1977)
Casanova R., Moukoko D., Pithioux M., Pailler-Mattéi C., Zahouani H., Chabrand P.: Temporal evolution of skeletal regenerated tissue: What can mechanical investigation add to biological?. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 48, 811–819 (2010)
Cazzani A., Ruge P.: Numerical aspects of coupling strongly frequency-dependent soil-foundation models with structural finite elements in the time-domain. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 37, 56–72 (2012)
Cazzani A., Lovadina C.: On some mixed finite element methods for plane membrane problems. Comput. Mech. 20(6), 560–572 (1997)
Cowin S.C., Nunziato J.W.: Linear elastic materials with voids. J. Elast. 13, 125–147 (1983)
Cowin S.C., Goodman M.A.: A variational principle for granular materials. J. Appl. Math. Mech. (ZAMM) 56, 281–286 (1976)
Contrafatto L., Cuomo M.: A globally convergent numerical algorithm for damaging elasto-plasticity based on the Multiplier method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 63(8), 1089–1125 (2005)
Contro R., Poggi C., Cazzani A.: Numerical analysis of fire effects on beam structures. Eng. Comput. (Swansea, Wales) 5(1), 53–58 (1988)
Culla A., Sestieri A., Carcaterra A.: Energy flow uncertainties in vibrating systems: Definition of a statistical confidence factor. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 17(3), 635–663 (2003)
Cuomo, M., Nicolosi, A.: A poroplastic model for hygro-chemo-mechanical damage of concrete. Computational Modelling of Concrete Structures—Proceedings of EURO-C (2006), pp. 533–542
Cuomo M., Contrafatto L.: Stress rate formulation for elastoplastic models with internal variables based on augmented Lagrangian regularisation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 37(29), 3935–3964 (2000)
Cuomo M., Ventura G.: Complementary energy approach to contact problems based on consistent augmented Lagrangian formulation. Math. Comput. Model. 28(4-8), 185–204 (1998)
Currey J.D.: The effect of porosity and mineral content on the Young’s modulus of elasticity of compact bone. J. Biomech. 21, 131–139 (1988)
dell’Isola F., Madeo A., Placidi L.: Linear plane wave propagation and normal transmission and reflection at discontinuity surfaces in second gradient 3D continua. ZAMM Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik 92(1), 52–71 (2011)
dell’Isola F., Madeo A., Seppecher P.: Boundary conditions at fluid-permeable interfaces in porous media: A variational approach. Int. J. Solids Struct. 46(17), 3150–3164 (2009)
dell’Isola F., Batra R.: Saint-Venant’s problem for porous linear elastic materials. J. Elast. 47, 73–81 (1997)
dell’Isola F., Woźniak C.: On continuum modelling the interphase layers in certain two-phase elastic solids. ZAMM Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik 77(7), 519–526 (1997)
dell’Isola F., Woźniak C.: On phase transition layers in certain micro-damaged two-phase solids. Int. J. Fract. 83(2), 175–189 (1997)
dell’Isola F., Rosa L., Woźniak C.: Dynamics of solids with micro periodic nonconnected fluid inclusions. Arch. Appl. Mech. 67(4), 215–228 (1997)
dell’Isola F., Guarascio M., Hutter K.: A variational approach for the deformation of a saturated porous solid. A second gradient theory extending Terzaghi’s effective stress principle. Arch. Appl. Mech. 70, 323–337 (2000)
dell’Isola, F., Hutter, K.:What are the dominant thermomechanical processes in the basal sediment layer of large ice sheets? Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 454(1972), 1169–1195 (1998)
dell’Isola F., Vidoli S.: Continuum modelling of piezoelectromechanical truss beams: An application to vibration damping. Arch. Appl. Mech. 68, 1–19 (1998)
dell’Isola F., Vidoli S.: Damping of bending waves in truss beams by electrical transmission lines with PZT actuators. Arch. Appl. Mech. 68, 626–636 (1998)
dell’Isola F., Rosa L., Woźniak C.: A micro-structured continuum modelling compacting fluid-saturated grounds: The effects of pore-size scale parameter. Acta Mech. 127(1-4), 165–182 (1998)
dell’Isola F., Romano A.: A phenomenological approach to phase transition in classical field theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 25(11-12), 1469–1475 (1987)
dell’Isola F., Romano A.: On the derivation of thermomechanical balance equations for continuous systems with a nonmaterial interface. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 25(11-12), 1459–1468 (1987)
DiCarlo A., Quiligotti S.: Growth and balance. Mech. Res. Commun. 29, 449–456 (2002)
Epstein M., Maugin G.A.: Thermomechanics of volumetric growth in uniform bodies. Int. J. Plast. 16, 951–978 (2000)
Eremeyev V.A., Pietraszkiewicz W.: Thermomechanics of shells undergoing phase transition. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 59(7), 1395–1412 (2011)
Eremeyev V.A., Pietraszkiewicz W.: Phase transitions in thermoelastic and thermoviscoelastic shells. Arch. Mech. 61(1), 41–67 (2009)
Eremeyev V.A., Pietraszkiewicz W.: The nonlinear theory of elastic shells with phase transitions. J. Elast. 74(1), 67–86 (2004)
Eremeev V.A., Freidin A.B., Sharipova L.L.: Nonuniqueness and stability in problems of equilibrium of elastic two-phase bodies. Doklady Phys. 48(7), 359–363 (2003)
Eshelby J.D.: The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion and related problems. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 241, 376–396 (1957)
Federico S.: On the linear elasticity of porous materials. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 52(2), 175–182 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2009.09.006
Garusi E., Tralli A., Cazzani A.: An unsymmetric stress formulation for reissner-mindlin plates: A simple and locking-free rectangular element. Int. J. Comput. Eng. Sci. 5(3), 589–618 (2004)
Ghiba, I.D., Neff, P., Madeo, A., Placidi, L., Rosi, G.: The relaxed linear micromorphic continuum: Existence, uniqueness and continuousdependence in dynamics. arXiv:1308.3762 submitted to Math.Mech. Solids
Giorgio I., Culla A., Del Vescovo D.: Multimode vibration control using several piezoelectric transducers shunted with a multiterminal network. Arch. Appl. Mech. 79, 859–879 (2009)
Goodman M.A., Cowin S.C.: A continuum theory for granular materials. Arch. Ration. Mech. An. 44, 249–266 (1972)
Grillo A., Federico S., Wittum G.: Growth, mass transfer, and remodeling in fiber-reinforced, multi-constituent materials. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 47, 388–401 (2012)
Hillsley M.V., Frangos J.A.: Review: Bone tissue engineering: The role of interstitial fluid flow. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 43(7), 573–581 (1994)
Huiskes R., Weinans H., Grootenboer H.J., Dalstra M., Fudala B., Slooff T.J.: Adaptive bone-remodeling theory applied to prosthetic-design analysis. J. Biomech. 20, 1135–1150 (1987)
Klein-Nulend J., Nijweide P.J., Burger E.H.: Osteocyte and bone structure. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 1, 5–10 (2003)
Koç I.M., Carcaterra A., Xu Z., Akay A.: Energy sinks: Vibration absorption by an optimal set of undamped oscillators. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 118(5), 3031–3042 (2005)
Lekszycki T.: Modelling of bone adaptation based on an optimal response hypothesis. Meccanica 37, 343–354 (2002)
Lekszycki T., dell’Isola F.: A mixture model with evolving mass densities for describing synthesis and resorption phenomena in bones reconstructed with bio-resorbable materials. J. Appl. Math Mech. (ZAMM) 92, 426–444 (2012)
Luongo A., Di Egidio A., Paolone A.: Multiscale analysis of defective multiple-Hopf bifurcations. Comput. Struct. 82(31-32), 2705–2722 (2004)
Luongo A., Paolone A., Di Egidio A.: Multiple timescales analysis for 1:2 and 1:3 resonant Hopf bifurcations. Nonlinear Dyn. 34(3-4), 269–291 (2003)
Luongo A., Paolone A.: On the reconstruction problem in the multiple time-scale method. Nonlinear Dyn. 19(2), 133–156 (1999)
Luongo A., Paolone A.: Perturbation methods for bifurcation analysis from multiple nonresonant complex eigenvalues. Nonlinear Dyn. 14(3), 193–210 (1997)
Luongo A.: Perturbation methods for nonlinear autonomous discrete-time dynamical systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 10(4), 317–331 (1996)
Madeo, A., Neff, P.,Ghiba, I.D., Placidi, L., Rosi, G.: Wave propagation in relaxed micromorphic continua: modeling metamaterials with frequency band-gaps.Continuum Mechanics and Thermodynamics. doi:10.1007/s00161-013-0329-2:1-20 (2013)
Madeo A., dell’Isola F., Darve F.: A continuum model for deformable, second gradient porous media partially saturated with compressible fluids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 61(11), 2196–2211 (2013)
Madeo, A., Djeran-Maigre, I., Rosi, G., Silvani, C.: The effect of fluid streams in porous media on acoustic compression wave propagation, transmission, and reflection. Continuum Mech. Therm. 25(2–4), 173–196 (2013)
Madeo A., George D., Lekszycki T., Nierenberger M., Rémond Y.: A second gradient continuum model accounting for some effects of micro-structure on reconstructed bone remodeling. Comptes Rendus Mécanique 340, 575–589 (2012)
Madeo A., Lekszycki T., dell’Isola F.: A continuum model for the bio-mechanical interactions between living tissue and bio-resorbable graft after bone reconstructive surgery. Comptes Rendus Mécanique 339, 625–640 (2011)
Madeo A., dell’Isola F., Ianiro N., Sciarra G.: A variational deduction of second gradient poroelasticity II: An application to the consolidation problem. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 3(4), 607–625 (2008)
Martin R.B.: Porosity and Specific Surface of Bone, CRC Critical reviews in Biomedical Engineering, pp. 179–222. CRC Press, Boca Raton FL (1984)
Maurini C., dell’Isola F., Del Vescovo D.: Comparison of piezoelectronic networks acting as distributed vibration absorbers. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 18, 1243–1271 (2004)
Maurini C., Pouget J., dell’Isola F.: On a model of layered piezoelectric beams including transverse stress effect. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 4473–4502 (2004)
Maurini C., Pouget J., dell’Isola F.: Extension of the Euler-Bernoulli model of piezoelectric laminates to include 3D effects via a mixed approach. Comput. Struct. 84, 1438–1458 (2006)
Neff, P., Ghiba, I.D., Madeo, A., Placidi, L., Rosi, G.: A unifying perspective: The relaxed linear micromorphic continuum. Contin. Mech. and Thermodyn.. doi:10.1007/s00161-013-0322-9 (2013)
Neff P., Forest S.: A geometrically exact micromorphic model for elastic metallic foams accounting for affine microstructure. Modelling, existence of minimizers, identification of moduli and computational results. J. Elast. 87, 239–276 (2007)
Neff P.: The Cosserat couple modulus for continuous solids is zero viz the linearized Cauchy-stress tensor is symmetric. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 86, 892–912 (2006)
Oliveto G., Cuomo M.: Incremental analysis of plane frames with geometric and material nonlinearities. Eng. Struct. 10(1), 2–12 (1988)
Petite H., Viateau V., Bensaïd W., Meunier A., de Pollak C., Bourguignon M., Oudina K., Sedel L., Guillemin G.: Tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 959–963 (2000)
Pietraszkiewicz W., Eremeyev V., Konopińska V.: Extended non-linear relations of elastic shells undergoing phase transitions. ZAMM Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik 87(2), 150–159 (2007)
Placidi L., dell’Isola F., Ianiro N., Sciarra G.: Variational formulation of pre-stressed solid-fluid mixture theory, with an application to wave phenomena. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 27, 582–606 (2008)
Quiligotti S., Maugin G.A., dell’Isola F.: An Eshelbian approach to the nonlinear mechanics of constrained solid-fluid mixtures. Acta Mech. 160, 45–60 (2003)
Ramaswamy Y., Haynes D.R., Berger G., Gildenhaar R., Lucas H.: Bioceramics composition modulate resorption of human osteoclasts. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 16, 1199–1205 (2005)
Reccia E., Cazzani A., Cecchi A.: FEM-DEM Modeling for Out-of-plane loaded masonry panels: A limit analysis approach. Open Civil Eng. J. 6(1), 231–238 (2012)
Rinaldi, A., Placidi, L.: A microscale second gradient approximation of the damage parameter of quasi-brittle heterogeneous lattices. (2013) doi:10.1002/zamm.201300028
Rinaldi A.: A rational model for 2D disordered lattices under uniaxial loading. Int. J. Damage Mech. 18, 233–257 (2009)
Rinaldi A., Lai Y.-C.: Statistical damage theory of 2d lattices: Energetics and physical foundations of damage parameter. Int. J. Plast. 23, 1796–1825 (2007)
Rosi, G., Paccapeli, R., Ollivier, F., Pouget, J.: Optimization of piezoelectric patches positioning for passive sound radiation control of plates. J. Vib. Control 19(5), 658–673 (2013)
Rosi G., Pouget J., dell’Isola F.: Control of sound radiation and transmission by a piezoelectric plate with an optimized resistive electrode. Eur. J. Mech. A-Solids 29, 859–870 (2010)
Rubin C.T., Lanyon L.E.: Osteoregulatory nature of mechanical stimuli: Function as a determinant for adaptive remodeling in bone. J. Orthopaed. Res. 5, 300–310 (1987)
Sanz-Herrera J.A., García-Aznar J.M., Doblaré M.: Micro-macro numerical modelling of bone regeneration in tissue engineering. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 197, 3092–3107 (2008)
Sanz-Herrera J.A., Boccaccini A.R.: Modelling bioactivity and degradation of bioactive glass based tissue engineering scaffolds. Int. J. Solids Struct. 48, 257–268 (2010)
Schilling A.F., Linhart W., Filke S., Gebauer M., Schinke T., Rueger J.M., Amling M.: Resorbability of bone substitute biomaterials by human osteoclasts. Biomaterials 25, 3963–3972 (2004)
Sciarra G., dell’Isola F., Hutter K.: A solid-fluid mixture model allowing for solid dilatation under external pressure. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 13, 287–306 (2001)
Sethuraman S., Nair L.S., El-Amin S., Nguyen M.T., Singh A., Krogman N., Greish Y.E., Allcock H.R., Brown P.W., Laurencin C.T.: Mechanical properties and osteocompatibility of novel biodegradable alanine based polyphosphazenes: Side group effects. Acta Biomater. 6, 1931–1937 (2010)
Tricoteaux A., Rguiti E., Chicot D., Boilet L., Descamps M., Leriche A., Lesage J.: Influence of porosity on the mechanical properties of microporous β-TCP bioceramics by usual and instrumented Vickers microindentation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 1361–1369 (2011)
Yeremeyev V.A., Freidin A.B., Sharipova L.L.: The stability of the equilibrium of two-phase elastic solids. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 71(1), 61–84 (2007)
Yusop, A.H., Bakir, A.A., Shaharom, N.A., Abdul Kadir, M.R., Hermawan, H.: Porous biodegradable metals for hard tissue scaffolds: A review. Int. J. Biomater. (2012), 1–10, Article ID 641430
Zanetta M., Quirici N., Demarosi F., Tanzi M.C., Rimondini L., Farè S.: Ability of polyurethane foams to support cell proliferation and the differentiation of MSCs into osteoblasts. Acta Biomater. 5, 1126–1136 (2009)
Zhou H., Lawrence J.G., Bhaduri S.B.: Fabrication aspects of PLA-CaP/PLGA-CaP composites for orthopedic applications: A review. Acta Biomater. 8, 1999–2016 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreaus, U., Giorgio, I. & Madeo, A. Modeling of the interaction between bone tissue and resorbable biomaterial as linear elastic materials with voids. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 66, 209–237 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-014-0403-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-014-0403-z