Abstract
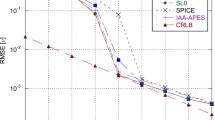
The authors have recently proposed two kinds of gridless sparse methods for direction of arrival estimation in the presence of multiple snapshots that exploit joint sparsity among the snapshots and completely resolve grid mismatches of previous grid-based sparse methods. One is termed as gridless SPICE (GL-SPICE, GLS) that is a gridless version of the covariance-based SPICE method; the other uses deterministic atomic norm optimization which extends the recent super-resolution and continuous compressed sensing framework from the single- to multi-snapshot case. In this paper, we unify these two techniques by interpreting theoretically GLS as atomic norm methods in various scenarios and under different assumptions of noise. The new interpretations of GLS enable us to provide theoretical guarantees of GLS in the case of finite snapshots. Besides, they are applied to show that GLS is robust to source correlations though it was derived under the assumption of uncorrelated sources. Numerical results are also provided to validate our findings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.N. Bhaskar, G. Tang, B. Recht, Atomic norm denoising with applications to line spectral estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(23), 5987–5999 (2013)
E.J. Candès, C. Fernandez-Granda, Towards a mathematical theory of super-resolution. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 67(6), 906–956 (2014)
V. Duval, G. Peyré, Exact support recovery for sparse spikes deconvolution. Found. Comput. Math. 15(5), 1315–1355 (2015)
J. Fang, J. Li, Y. Shen, H. Li, S. Li, Super-resolution compressed sensing: an iterative reweighted algorithm for joint parameter learning and sparse signal recovery. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21(6), 761–765 (2014)
L. Hu, Z. Shi, J. Zhou, Q. Fu, Compressed sensing of complex sinusoids: an approach based on dictionary refinement. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(7), 3809–3822 (2012)
M. Hyder, K. Mahata, Direction-of-arrival estimation using a mixed \(\ell _{2,0}\) norm approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(9), 4646–4655 (2010)
H. Krim, M. Viberg, Two decades of array signal processing research: the parametric approach. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 13(4), 67–94 (1996)
Y. Li, Y. Chi, Off-the-grid line spectrum denoising and estimation with multiple measurement vectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(5), 1257–1269 (2016)
D.A. Linebarger, I.H. Sudborough, I.G. Tollis, Difference bases and sparse sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 39(2), 716–721 (1993)
D. Malioutov, M. Cetin, A. Willsky, A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(8), 3010–3022 (2005)
P. Pal, P. Vaidyanathan, A grid-less approach to underdetermined direction of arrival estimation via low rank matrix denoising. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21(6), 737–741 (2014)
P. Stoica, P. Babu, Sparse estimation of spectral lines: grid selection problems and their solutions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(2), 962–967 (2012)
P. Stoica, P. Babu, J. Li, SPICE: a sparse covariance-based estimation method for array processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(2), 629–638 (2011)
P. Stoica, R.L. Moses, Spectral Analysis of Signals (Pearson/Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, 2005)
P. Stoica, D. Zachariah, J. Li, Weighted SPICE: a unifying approach for hyperparameter-free sparse estimation. Digit. Signal Proc. 33, 1–12 (2014)
Z. Tan, Y.C. Eldar, A. Nehorai, Direction of arrival estimation using co-prime arrays: a super resolution viewpoint. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(21), 5565–5576 (2014)
G. Tang, B.N. Bhaskar, P. Shah, B. Recht, Compressed sensing off the grid. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 59(11), 7465–7490 (2013)
K.-C. Toh, M.J. Todd, R.H. Tütüncü, SDPT3: a MATLAB software package for semidefinite programming, version 1.3. Optim. Methods Softw. 11(1–4), 545–581 (1999)
Z. Yang, L. Xie, On gridless sparse methods for line spectral estimation from complete and incomplete data. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(12), 3139–3153 (2015)
Z. Yang, L. Xie, Enhancing sparsity and resolution via reweighted atomic norm minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(4), 995–1006 (2016)
Z. Yang, L. Xie, Exact joint sparse frequency recovery via optimization methods. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(19), 5145–5157 (2016)
Z. Yang, L. Xie, C. Zhang, Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(1), 38–43 (2013)
Z. Yang, L. Xie, C. Zhang, A discretization-free sparse and parametric approach for linear array signal processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(19), 4959–4973 (2014)
Z. Yang, L. Xie, On gridless sparse methods for multi-snapshot DOA estimation, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (2016), pp. 3236–3240
Y. Zhang, Z. Ye, X. Xu, N. Hu, Off-grid DOA estimation using array covariance matrix and block-sparse Bayesian learning. Sig. Process. 98, 197–201 (2014)
Y.X. Zou, B. Li, C.H. Ritz, Multi-source DOA estimation using an acoustic vector sensor array under a spatial sparse representation framework. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(3), 993–1020 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The research of this project was supported by the Ministry of Education, Republic of Singapore, under Grant AcRF TIER 1 RG78/15, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, under Grant 61603187, and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China, under Grant BK20160845.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Xie, L. On Gridless Sparse Methods for Multi-snapshot Direction of Arrival Estimation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 3370–3384 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0462-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-016-0462-9