Abstract
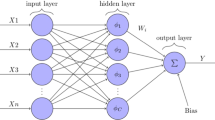
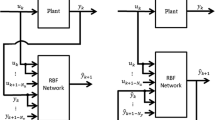
In this research, we propose a novel fractional gradient descent-based learning algorithm (FGD) for the radial basis function neural networks (RBF-NN). The proposed FGD is the convex combination of the conventional, and the modified Riemann–Liouville derivative-based fractional gradient descent methods. The proposed FGD method is analyzed for an optimal solution in a system identification problem, and a closed form Wiener solution of a least square problem is obtained. Using the FGD, the weight update rule for the proposed fractional RBF-NN (FRBF-NN) is derived. The proposed FRBF-NN method is shown to outperform the conventional RBF-NN on four major problems of estimation namely nonlinear system identification, pattern classification, time series prediction and function approximation.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Aftab, M. Moinuddin, M.S. Shaikh, A Novel Kernel for RBF based neural networks. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, (2014)
J. Ahmad, S. Khan, M. Usman, I. Naseem, M. Moinuddin, Fclms: Fractional complex lms algorithm for complex system identification, in 13th IEEE Colloquium on Signal Processing and its Applications (CSPA 2017). IEEE (2017)
J. Ahmad, M. Usman, S. Khan, I. Naseem, H.J. Syed, Rvp-flms : A robust variable power fractional lms algorithm, in 2016 IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering (ICCSCE). IEEE (2016)
A. Alexandridis, E. Chondrodima, N. Giannopoulos, H. Sarimveis, A fast and efficient method for training categorical radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. PP(99), 1–6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2598722
A. Alexandridis, E. Chondrodima, H. Sarimveis, Cooperative learning for radial basis function networks using particle swarm optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 49, 485–497 (2016)
S.H.A. Ali, K. Fukase, S. Ozawa, A fast online learning algorithm of radial basis function network with locality sensitive hashing. Evol. Syst. 7, 1–14 (2016)
I. Aljarah, H. Faris, S. Mirjalili, N. Al-Madi, Training radial basis function networks using biogeography-based optimizer. Neural Computing and Applications (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2559-2
R. An, W.J. Li, H.G. Han, J.F. Qiao, An improved levenberg-marquardt algorithm with adaptive learning rate for rbf neural network. in 2016 35th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), pp. 3630–3635 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ChiCC.2016.7553917
E. Anderson, The species problem in iris. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 23, 457–509 (1936). https://doi.org/10.2307/2394164, URLhttp://biostor.org/reference/11559
G.S. Babu, S. Suresh, Meta-cognitive rbf network and its projection based learning algorithm for classification problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 13(1), 654–666 (2013)
M. Barakat, D. Lefebvre, M. Khalil, F. Druaux, O. Mustapha, Parameter selection algorithm with self adaptive growing neural network classifier for diagnosis issues. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 4(3), 217–233 (2013)
G.W. Bohannan, Analog fractional order controller in temperature and motor control applications. J. Vib. Control 14(9–10), 1487–1498 (2008)
J. Cervera, A. Baños, Automatic loop shaping in qft using crone structures. J. Vib. Control 14(9–10), 1513–1529 (2008)
S. Chen, C.F. Cowan, P.M. Grant, Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2(2), 302–309 (1991)
W. Chen, Z.J. Fu, C.S. Chen, Recent advances in radial basis function collocation methods. Springer (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39572-7
D.P.F. Cruz, R.D. Maia, L.A. da Silva, L.N. de Castro, Beerbf: a bee-inspired data clustering approach to design rbf neural network classifiers. Neurocomputing 172, 427–437 (2016)
L. Debnath, Recent applications of fractional calculus to science and engineering. Int. J. Math. Math. Sci. 2003(54), 3413–3442 (2003)
V. Elanayar, Y.C. Shin et al., Radial basis function neural network for approximation and estimation of nonlinear stochastic dynamic systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 5(4), 594–603 (1994)
M.J. Er, S. Wu, J. Lu, H.L. Toh, Face recognition with radial basis function (rbf) neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 13(3), 697–710 (2002)
R.B. Feng, C.S. Leung, A. Constantinides, LCA based RBF training algorithm for the concurrent fault situation. Neurocomputing 191, 341–351 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.01.047, URLhttp://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231216001375
R.A. Fisher, The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Ann. Eugen. 7(2), 179–188 (1936). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.1936.tb02137.x
L. Fu, M. Zhang, H. Li, Sparse rbf networks with multi-kernels. Neural Process. Lett. 32(3), 235–247 (2010)
L. Glass, M. Mackey, Mackey-Glass equation. Scholarpedia 5(3), 6908 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4249/scholarpedia.6908. Revision #91447
G.J. Gordon, Stable function approximation in dynamic programming, in Machine Learning Proceedings 1995, ed. by A. Prieditis, S. Russell (Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (CA), 1995), pp. 261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-55860-377-6.50040-2. URLhttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781558603776500402
M.A. Halali, V. Azari, M. Arabloo, A.H. Mohammadi, A. Bahadori, Application of a radial basis function neural network to estimate pressure gradient in water–oil pipelines. J. Taiwan Instit. Chem. Eng. 58, 189–202 (2016)
H.G. Han, Y.N. Guo, J.F. Qiao, Self-organization of a recurrent rbf neural network using an information-oriented algorithm. Neurocomputing 225, 80–91 (2017)
H.G. Han, J.F. Qiao, Adaptive computation algorithm for rbf neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 23(2), 342–347 (2012)
S.O. Haykin, Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation (Prentice Hall PTR, Upper Saddle River, 1994)
B. Jafrasteh, N. Fathianpour, A hybrid simultaneous perturbation artificial bee colony and back-propagation algorithm for training a local linear radial basis neural network on ore grade estimation. Neurocomputing 235, 217 (2017)
B. Jafrasteh, N. Fathianpour, A hybrid simultaneous perturbation artificial bee colony and back-propagation algorithm for training a local linear radial basis neural network on ore grade estimation. Neurocomputing 235, 217–227 (2017)
D. Jukic, R. Scitovski, Existence of optimal solution for exponential model by least squares. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 78(2), 317–328 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0427(96)00160-4 URLhttp://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0377042796001604
G. Jumarie, Modified riemann-liouville derivative and fractional taylor series of nondifferentiable functions further results. Comput. Math. Appl. 51(9), 1367–1376 (2006)
G. Jumarie, Table of some basic fractional calculus formulae derived from a modified riemann-liouville derivative for non-differentiable functions. Appl. Math. Lett. 22(3), 378–385 (2009)
G. Jumarie, An approach via fractional analysis to non-linearity induced by coarse-graining in space. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(1), 535–546 (2010)
G. Jumarie, On the derivative chain-rules in fractional calculus via fractional difference and their application to systems modelling. Open Phys. 11(6), 617–633 (2013)
S. Khan, J. Ahmad, I. Naseem, M. Moinuddin, A novel fractional gradient-based learning algorithm for recurrent neural networks. Circuits Syst. Signal Process 37, 1–20 (2017)
S. Khan, N. Ahmed, M.A. Malik, I. Naseem, R. Togneri, M. Bennamoun, FLMF: Fractional least mean fourth algorithm for channel estimation in non-gaussian environment, in 2017 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), pp. 466–470 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTC.2017.8191021
S. Khan, I. Naseem, R. Togneri, M. Bennamoun, A novel adaptive kernel for the rbf neural networks. Circuits Syst. Signal Proces. 36, 1–15 (2016)
S. Khan, I. Naseem, R. Togneri, M. Bennamoun, RAFP-Pred: robust prediction of antifreeze proteins using localized analysis of n-peptide compositions. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinfor. 15(1), 244–250 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2016.2617337
S. Khan, M. Usman, I. Naseem, R. Togneri, M. Bennamoun, A robust variable step size fractional least mean square (rvss-flms) algorithm, in 13th IEEE Colloquium on Signal Processing and its Applications (CSPA 2017). IEEE (2017)
S. Khan, M. Usman, I. Naseem, R. Togneri, M. Bennamoun, VP-FLMS: a novel variable power fractional LMS algorithm, in 2017 Ninth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN) (ICUFN 2017). Milan, Italy (2017)
M. Kleinz, T. Osler, A child’s garden of fractional derivatives. College Math. J. 31, 82 (2000)
B. Krishna, K. Reddy, Active and passive realization of fractance device of order 1/2. Act. Passive Electr. Compon. 2008, 1–5 (2008)
M.F. Lima, J.A.T. Machado, M.M. Crisóstomo, Experimental signal analysis of robot impacts in a fractional calculus perspective. JACIII 11(9), 1079–1085 (2007)
R.P. Lippmann, Pattern classification using neural networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 27(11), 47–50 (1989)
J. Lovoie, T.J. Osler, R. Tremblay, Fractional derivatives and special functions. SIAM Rev. 18(2), 240–268 (1976)
R. Magin, M. Ovadia, Modeling the cardiac tissue electrode interface using fractional calculus. J. Vib. Control 14(9–10), 1431–1442 (2008)
A.W. Moore, C.G. Atkeson, Prioritized sweeping: reinforcement learning with less data and less time. Mach. Learn. 13(1), 103–130 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00993104
K.S. Narendra, K. Parthasarathy, Identification and control of dynamical systems using neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1(1), 4–27 (1990)
I. Naseem, S. Khan, R. Togneri, M. Bennamoun, ECMSRC: a sparse learning approach for the prediction of extracellular matrix proteins. Current Bioinfor. 12(4), 361–368 (2017)
T. Nguyen-Thien, T. Tran-Cong, Approximation of functions and their derivatives: a neural network implementation with applications. Appl. Math. Model. 23(9), 687–704 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0307-904X(99)00006-2, URLhttp://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0307904X99000062
S.K. Oh, W.D. Kim, W. Pedrycz, Design of radial basis function neural network classifier realized with the aid of data preprocessing techniques: design and analysis. Int. J. General Syst. 45, 1–21 (2015)
R. Panda, M. Dash, Fractional generalized splines and signal processing. Signal Proces. 86(9), 2340–2350 (2006)
P.P. Pokharel, J.W. Xu, D. Erdogmus, J.C. Principe, A closed form solution for a nonlinear wiener filter, in 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing Proceedings, vol. 3, pp. III–III (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2006.1660755
Y. Pu, X. Yuan, K. Liao, J. Zhou, N. Zhang, X. Pu, Y. Zeng, A recursive two-circuits series analog fractance circuit for any order fractional calculus, in ICO20: Optical Information Processing, pp. 60,271Y–60,271Y. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2006)
P.D. Reiner, Algorithms for optimal construction and training of radial basis function neural networks. Ph.D. thesis, Auburn University (2015)
J. Sabatier, O.P. Agrawal, J.T. Machado, Advances in fractional calculus (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6042-7
H. Sarimveis, A. Alexandridis, S. Mazarakis, G. Bafas, A new algorithm for developing dynamic radial basis function neural network models based on genetic algorithms. Comput. Chem. Eng. 28(1), 209–217 (2004)
P. Shi, F. Li, L. Wu, C.C. Lim, Neural network-based passive filtering for delayed neutral-type semi-markovian jump systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(9), 2101–2114 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2573853
R. Sikora, Z. Giza, F. Filipowicz, J. Sikora, The bell function approximation of material coefficients distribution in the electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Mag. 36(4), 1023–1026 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/20.877615
L. Sommacal, P. Melchior, A. Oustaloup, J.M. Cabelguen, A.J. Ijspeert, Fractional multi-models of the frog gastrocnemius muscle. J. Vib. Control 14(9–10), 1415–1430 (2008)
A. Tatar, S. Naseri, N. Sirach, M. Lee, A. Bahadori, Prediction of reservoir brine properties using radial basis function (rbf) neural network. Petroleum 1(4), 349–357 (2015)
D. Wettschereck, T. Dietterich, Improving the performance of radial basis function networks by learning center locations. in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 4, pp. 1133–1140. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, Calif, USA (1992)
J. Wu, J. Long, M. Liu, Evolving rbf neural networks for rainfall prediction using hybrid particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm. Neurocomputing 148, 136–142 (2015)
L. Wu, Z. Feng, W.X. Zheng, Exponential stability analysis for delayed neural networks with switching parameters: average dwell time approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 21(9), 1396–1407 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2010.2056383
J. Yoo, S. Sabir, D. Heo, K.H. Kim, A. Wahab, Y. Choi, S.I. Lee, E.Y. Chae, H.H. Kim, Y.M. Bae, et al., Deep learning can reverse photon migration for diffuse optical tomography. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.00912 (2017)
Y.H. Yoon, S. Khan, J. Huh, J.C. Ye, Deep learning in RF Sub-sampled B-mode Ultrasound Imaging. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.06096 (2017)
Acknowledgements
We like to thank anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S., Naseem, I., Malik, M.A. et al. A Fractional Gradient Descent-Based RBF Neural Network. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 5311–5332 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0835-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0835-3