Abstract
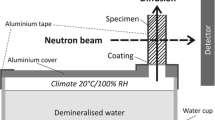
Diffusion processes into multilayered samples of Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] Karst.) exposed to a differentiating climate (dry side/wet side) were determined and quantified by means of neutron imaging (NI). The experiments were carried out at the neutron imaging facility NEUTRA at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) in Villigen (Switzerland).
With NI the influence of different adhesives (polyvinyl acetate (PVAc), urea formaldehyde resin (UF), epoxy resin (EP), one-component polyurethane (1C PUR)) on the diffusion process could be determined by varying the layer number and the thickness of adhesive joints of the samples. Thereby, neutron transmission images were used to measure time dependent water profiles in the diffusion direction. Using Fick’s second law, diffusion coefficients for radial and tangential water transport in spruce wood and in the adhesive joints were calculated depending on moisture content (MC). It was found that the diffusion coefficients of the adhesives (1C PUR, EP at high MC) were up to three orders of magnitude lower than those of spruce wood. PVAc and UF had a smaller barrier effect compared to wood, which in contrast to 1C PUR and EP, clearly depends on the MC.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurden Diffusionsprozesse an mehrlagigen Proben von Fichte (Picea abies [L.] Karst.), welche einem Differenzklima (trocken/feucht) ausgesetzt waren, mittels Neutronenradiographie untersucht und quantifiziert. Die Experimente wurden an der Radiographiestrahllinie NEUTRA am Paul Scherrer Institut (PSI) in Villigen (Schweiz) durchgeführt.
Mittels Neutronenradiographie konnte der Einfluss verschiedener Klebstoffe (Polyvinylacetat (PVAc), Harnstoffharz (UF), Epoxidharz (EP) und Einkomponenten-Polyurethan (1K-PUR)) auf den Diffusionsprozess bestimmt werden, indem die Anzahl und die Dicke der Klebfugen variiert wurden. Dabei wurden Neutronen-Transmissionsbilder verwendet, womit zeitabhängige Profile in Diffusionsrichtung gemessen werden konnten. Anhand des zweiten Fick’schen Gesetzes konnten die Diffusionskoeffizienten für die Klebstoffe sowie für Fichte in radialer und tangentialer Richtung in Abhängigkeit der Feuchte berechnet werden. Dabei wiesen die Klebstoffe (1K-PUR, EP bei hohen Feuchten) bis zu drei Zehnerpotenzen niedrigere Diffusionskoeffizienten als Fichtenholz auf. Bei PVAc und UF war die Sperrwirkung gegenüber dem Holz geringer und es zeigte sich im Gegensatz zu 1K-PUR und EP eine deutliche Abhängigkeit von der Holzfeuchte.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dunky M, Niemz P (2002) Holzwerkstoffe und Leime: Technologie und Einflussfaktoren. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg
Foglia A (2006) Untersuchungen zu ausgewählten Einflussfaktoren auf den Diffusionswiderstand von Holzwerkstoffen. Diploma thesis, ETH Zurich, Institute for Building Materials, Wood Physics, Zurich
Frandsen HL, Damkilde L, Svensson S (2007) A revised multi-Fickian moisture transport model to describe non-Fickian effects in wood. Holzforschung 61(5):563–572
Frühwald A (1973) Ein Beitrag zur Kenntnis des diffusionstechnischen Verhaltens von Furnierplatten und kunstharzbeschichtetem Holz. Dissertation, University of Hamburg, Hamburg
Glaser H (1959) Graphisches Verfahren zur Untersuchung von Diffusionsvorgängen. Kältetechnik 11(10):345–349
Hass P, Wittel FK, Mendoza M, Stampanoni M, Herrmann HJ, Niemz P (2010) Adhesive penetration in beech wood. Part I: Experiments. Wood Sci Technol (in press)
Hassanein R (2006) Correction methods for the quantitative evaluation of thermal neutron tomography. Dissertation, ETH Zurich, Zurich
ISO 12572 (2001) Hygrothermal performance of building materials and products—determination of water vapour transmission properties. Geneva
Kollmann F, Côté WA Jr (1968) Principles of wood science and technology, vol I: Solid wood. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg/New York
Lehmann E, Vontobel P, Scherrer P, Niemz P (2001a) Application of neutron radiography as method in the analysis of wood. Holz Roh- Werkst 59(6):463–471
Lehmann EH, Vontobel P, Wiezel L (2001b) Properties of the radiography facility NEUTRA at SINQ and its potential for Use as European reference facility. Nondestr Test Eval 16:191–202
Liu JY (1989) A new method for separating diffusion coefficient and surface emission coefficient. Wood Fiber Sci 21(2):133–141
Mannes D, Niemz P, Lehmann E (2006) Study on the penetration behaviour of water in corner joints by means of neutron radiography. Wood Res 51(2):1–14
Mannes D, Josic L, Lehmann E, Niemz P (2009a) Neutron attenuation coefficients for non-invasive quantification of wood properties. Holzforschung 63(4):472–478
Mannes D, Sonderegger W, Hering S, Lehmann E, Niemz P (2009b) Non-destructive determination and quantification of diffusion processes in wood by means of neutron imaging. Holzforschung 63(5):589–596
Nelder JA, Mead R (1965) A simplex method for function minimization. Comput J 7(4):308–313
Niemz P, Lehmann E, Vontobel P, Haller P, Hanschke S (2002) Investigations using neutron radiography for evaluations of moisture ingress into corner connections of wood. Holz Roh- Werkst 60(2):118–126
Olek W, Weres J (2007) Effects of the method of identification of the diffusion coefficient on accuracy of modeling bound water transfer in wood. Transp Porous Med 66:135–144
Siau JF (1995) Wood: influence of moisture on physical properties. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Keene
Skaar C (1988) Wood-water relations. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg/New York
Sonderegger W (2010) unpublished results
Stamm AJ (1959a) Bound-water diffusion into wood in the fiber direction. For Prod J 9(1):27–32
Stamm AJ (1959b) Bound-water diffusion into wood in across-the-fiber directions. For Prod J 10(10):524–528
Vanek M, Teischinger A (1989) Diffusionskoeffizienten und Diffusionswiderstandszahlen von verschiedenen Holzarten. Holzforsch Holzverwer 41(1):3–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is dedicated to Gerd Wegener on the occasion of his retirement as professor at the Technische Universität München.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00107-010-0474-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonderegger, W., Hering, S., Mannes, D. et al. Quantitative determination of bound water diffusion in multilayer boards by means of neutron imaging. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 68, 341–350 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-010-0463-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-010-0463-5