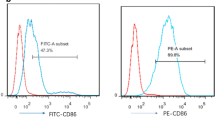
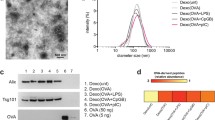
Abstract
We recently described a novel biotechnological platform for the production of unrestricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) vaccines. It relies on in vivo engineering of exosomes, i.e., nanovesicles constitutively released by all cells, with full-length antigens of choice upon fusion with an exosome-anchoring protein referred to as Nefmut. They are produced upon intramuscular injection of a DNA vector and, when uploaded with a viral tumor antigen, were found to elicit an immune response inhibiting the tumor growth in a model of transplantable tumors. However, for a possible application in cancer immunotherapy, a number of key issues remained unmet. Among these, we investigated: (i) whether the immunogenic stimulus induced by the engineered exosomes can break immune tolerance, and (ii) their effectiveness when applied in human system. As a model of immune tolerance, we considered mice transgenic for the expression of activated rat HER2/neu which spontaneously develop adenocarcinomas in all mammary glands. When these mice were injected with a DNA vector expressing the product of fusion between Nefmut and the extracellular domain of HER2/neu, antigen-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes became readily detectable. This immune response associated with a HER2-directed CTL activity and a significant delay in tumor development. On the other hand, through cross-priming experiments, we demonstrated the effectiveness of the engineered exosomes emerging from transfected human primary muscle cells in inducing antigen-specific CTLs. We propose our CTL vaccine platform as part of new immunotherapy strategies against tumors expressing self-antigens, i.e., products highly expressed in oncologic lesions but tolerated by the immune system.
Key messages
-
We established a novel, exosome-based method to produce unrestricted CTL vaccines.
-
This strategy is effective in breaking the tolerance towards tumor self-antigens.
-
Our method is also useful to elicit antigen-specific CTL immunity in humans.
-
These findings open the way towards the use of this antitumor strategy in clinic.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Bonito P, Chiozzini C, Arenaccio C, Anticoli S, Manfredi F, Olivetta E, Ferrantelli F, Falcone E, Ruggieri A, Federico M (2017) Antitumor HPV E7-specific CTL activity elicited by in vivo engineered exosomes produced through DNA inoculation. Int J Nanomedicine 12:4579–4591
Lattanzi L, Federico M (2012) A strategy of antigen incorporation into exosomes: comparing cross-presentation levels of antigens delivered by engineered exosomes and by lentiviral virus-like particles. Vaccine 30(50):7229–7237
Guescini M, Guidolin D, Vallorani L, Casadei L, Gioacchini AM, Tibollo P, Battistelli M, Falcieri E, Battistin L, Agnati LF, Stocchi V (2010) C2C12 myoblasts release micro-vesicles containing mtDNA and proteins involved in signal transduction. Exp Cell Res 316(12):1977–1984
Romancino DP, Paterniti G, Campos Y, De Luca A, Di Felice V, d'Azzo A, Bongiovanni A (2013) Identification and characterization of the nano-sized vesicles released by muscle cells. FEBS Lett 587(9):1379–1384
Schorey JS, Cheng Y, Singh PP, Smith VL (2015) Exosomes and other extracellular vesicles in host-pathogen interactions. EMBO Rep 16(1):24–43
Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ (2010) Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteome 73(10):1907–1920
Percario ZA, Ali M, Mangino G, Affabris E (2015) Nef, the shuttling molecular adaptor of HIV, influences the cytokine network. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 26(2):159–173
D'Aloja P, Santarcangelo AC, Arold S, Baur A, Federico M (2001) Genetic and functional analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1-inhibiting F12-HiVnef allele. J Gen Virol 82(11):2735–2745
Anticoli S, Falcone E, Ruggieri A, Federico M (2016) Engineered exosomes boost the HCV NS3-specific CD8+ T lymphocyte immunity in humans. Trials Vaccinol 5:105–110
Gutierrez C, Schiff R (2011) HER2: biology, detection, and clinical implications. Arch Pathol Lab Med 135(1):55–62
Siegel PM, Muller WJ (1996) Mutations affecting conserved cysteine residues within the extracellular domain of Neu promote receptor dimerization and activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(17):8878–8883
Cavallo F, Offringa R, van der Burg SH, Forni G, Melief CJ (2006) Vaccination for treatment and prevention of cancer in animal models. Adv Immunol 90:175–213
Reilly RT, Gottlieb MB, Ercolini AM, Machiels JP, Kane CE, Okoye FI, Muller WJ, Dixon KH, Jaffee EM (2000) HER-2/neu is a tumor rejection target in tolerized HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Cancer Res 60(13):3569–3576
Rovero S, Amici A, Di Carlo E, Bei R, Nanni P, Quaglino E, Porcedda P, Boggio K, Smorlesi A, Lollini PL, Landuzzi L, Colombo MP, Giovarelli M, Musiani P, Forni G (2000) DNA vaccination against rat her-2/Neu p185 more effectively inhibits carcinogenesis than transplantable carcinomas in transgenic BALB/c mice. J Immunol 165(9):5133–5142
Rolla S, Nicoló C, Malinarich S, Orsini M, Forni G, Cavallo F, Ria F (2006) Distinct and non-overlapping T cell receptor repertoires expanded by DNA vaccination in wild-type and HER-2 transgenic BALB/c mice. J Immunol 177(11):7626–7633
Nanni P, Nicoletti G, De Giovanni C, Landuzzi L, Di Carlo E, Cavallo F, Pupa SM, Rossi I, Colombo MP, Ricci C, Astolfi A, Musiani P, Forni G, Lollini PL (2001) Combined allogeneic tumor cell vaccination and systemic interleukin 12 prevents mammary carcinogenesis in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. J Exp Med 194(9):1195–1205
Halbert CL, Demers GW, Galloway DA (1991) The E7 gene of human papillomavirus type 16 is sufficient for immortalization of human epithelial cells. J Virol 65(1):473–478
Di Bonito P, Grasso F, Mochi S, Petrone L, Fanales-Belasio E, Mei A, Cesolini A, Laconi G, Conrad H, Bernhard H, Dembek CJ, Cosma A, Santini SM, Lapenta C, Donati S, Muratori C, Giorgi C, Federico M (2009) Anti-tumor CD8+ T cell immunity elicited by HIV-1-based virus-like particles incorporating HPV-16 E7 protein. Virology 2009(395):45–55
Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A (2006)) Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol 3. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471143030.cb0322s30
Rieu S, Géminard C, Rabesandratana H, Sainte-Marie J, Vidal M (2000) Exosomes released during reticulocyte maturation bind to fibronectin via integrin alpha4beta1. Eur J Biochem 267(2):583–590
Aricò E, Sestili P, Carpinelli G, Canese R, Cecchetti S, Schiavoni G, D’Urso MT, Belardelli F, Proietti E (2016) Chemo-immunotherapy induces tumor regression in a mouse model of spontaneous mammary carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 7(37):59754–59765
Gritzapis AD, Mahaira LG, Perez SA, Cacoullos NT, Papamichail M, Baxevanis CN (2006) Vaccination with human HER-2/neu (435-443) CTL peptide induces effective antitumor immunity against HER-2/neu-expressing tumor cells in vivo. Cancer Res 66(10):5452–5460
Liang X, Fu TM, Xie X, Emini EA, Shiver JW (2002) Development of HIV-1 Nef vaccine components: immunogenicity study of Nef mutants lacking myristoylation and dileucine motif in mice. Vaccine 20:413–421
Bauer S, Heeg K, Wagner H, Lipford GB (1995) Identification of H-2Kb binding and immunogenic peptides from human papilloma virus tumour antigens E6 and E7. Scand J Immunol 42(3):317–323
Chairoungdua A, Smith DL, Pochard P, Hull M, Caplan MJ (2010) Exosome release of beta-catenin: a novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. J Cell Biol 190(6):1079–1091
Kogure T, Lin WL, Yan IK, Braconi C, Patel T (2011) Intercellular nanovesicle-mediated microRNA transfer: a mechanism of environmental modulation of hepatocellular cancer cell growth. Hepatology 54(4):1237–1248
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Takeshita F, Matsuki Y, Ochiya T (2010) Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J Biol Chem 285(23):17442–17452
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Hagiwara K, Takeshita F, Ochiya T (2012) Competitive interactions of cancer cells and normal cells via secretory microRNAs. J Biol Chem 287(2):1397–1405
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, Rajendran L, Wenzel D, Wieland F, Schwille P, Brügger B, Simons M (2008) Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319(5867):1244–1247
Yuyama K, Sun H, Mitsutake S, Igarashi Y (2012) Sphingolipid-modulated exosome secretion promotes clearance of amyloid-beta by microglia. J Biol Chem 287(14):10977–10989
Nanni P, Landuzzi L, Nicoletti G, De Giovanni C, Rossi I, Croci S, Astolfi A, Iezzi M, Di Carlo E, Musiani P, Forni G, Lollini PL (2004) Immunoprevention of mammary carcinoma in HER-2/neu transgenic mice is IFN-gamma and B cell dependent. J Immunol 173(4):2288–2296
Rolla S, Marchini C, Malinarich S, Quaglino E, Lanzardo S, Montani M, Iezzi M, Angeletti M, Ramadori G, Forni G, Cavallo F, Amici A (2008) Protective immunity against neu-positive carcinomas elicited by electroporation of plasmids encoding decreasing fragments of rat neu extracellular domain. Hum Gene Ther 19(3):229–240
Di Bonito P, Ridolfi B, Columba-Cabezas S, Giovannelli A, Chiozzini C, Manfredi F, Anticoli S, Arenaccio C, Federico M (2015) HPV-E7 delivered by engineered exosomes elicits a protective CD8+ T cell-mediated immune response. Viruses 7(3):1079–1099
Busam KJ, Jungbluth AA (1996) Melan-A, a new melanocytic differentiation marker. Adv Anat Pathol 6:12–18
Rivoltini L, Kawakami Y, Sakaguchi K, Southwood S, Sette A, Robbins PF, Marincola FM, Salgaller ML, Yannelli YR, Appella E, Rosenberg SA (1995) Induction of tumor-reactive CTL from peripheral blood and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes of melanoma patients by in vitro stimulation with an immunodominant peptide of the human melanoma antigen MART-1. J Immunol 154(5):2257–2265
Fry EA, Taneja P, Inoue K (2016) Clinical applications of mouse models for breast cancer engaging HER2/neu. Integr Cancer Sci Ther 3(5):593–603
Quaglino E, Iezzi M, Mastini C, Amici A, Pericle F, Di Carlo E, Pupa SM, De Giovanni C, Spadaro M, Curcio C, Lollini PL, Musiani P, Forni G, Cavallo F (2004) Electroporated DNA vaccine clears away multifocal mammary carcinomas in her-2/neu transgenic mice. Cancer Res 64(8):2858–2864
Quaglino E, Mastini C, Iezzi M, Forni G, Musiani P, Klapper LN, Hardy B, Cavallo F (2005) The adjuvant activity of BAT antibody enables DNA vaccination to inhibit the progression of established autochthonous Her-2/neu carcinomas in BALB/c mice. Vaccine 23(25):3280–3287
Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ (2011) Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science 331(6024):1565–1570
van der Burg SH, Arens R, Ossendorp F, van Hall T, Melief CJ (2016) Vaccines for established cancer: overcoming the challenges posed by immune evasion. Nat Rev Cancer 16(4):219–233
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant of “Ricerca Finalizzata” project RF-2010-2308334 from the Ministry of Health, Italy. We thank Deborah Pajalunga and Marco Crescenzi, ISS, for kindly providing SKMC; Mario Falchi, ISS, for the confocal microscope analysis; Paola Sestili, Anna M. Pacca, and Fiorella Ciaffoni, ISS, for their support in animal housing and experimentation; and Pietro Arciero, ISS, for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal studies have been approved by the ISS ethics committee. The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data. All studies with animals here described have been approved by the Ethical Committee of the ISS (protocol n. 107/2016-PR) according to Legislative Decree 116/92 which has implemented in Italy the European Directive 86/609/EEC on laboratory animal protection.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(JPEG 937 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anticoli, S., Aricò, E., Arenaccio, C. et al. Engineered exosomes emerging from muscle cells break immune tolerance to HER2 in transgenic mice and induce antigen-specific CTLs upon challenge by human dendritic cells. J Mol Med 96, 211–221 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1617-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1617-2