Abstract
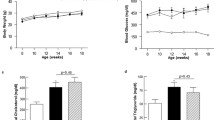
Diabetes mellitus is one of risk factors of cardiovascular diseases including atherosclerosis. Whether and how diabetes promotes the formation of unstable atherosclerotic plaque is not fully understood. Here, we show that streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes reduced collagen synthesis, leading to the formation of unstable atherosclerotic plaque induced by collar placement around carotid in apolipoprotein E knockout (Apoe−/−) mice. These detrimental effects of hyperglycemia on plaque stability were reversed by metformin in vivo without altering the levels of blood glucose and lipids. Mechanistically, we found that high glucose reduced the phosphorylated level of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha (AMPKα) and the transcriptional activity of activator protein 2 alpha (AP-2α), increased the expression of miR-124 expression, and downregulated prolyl-4-hydroxylase alpha 1 (P4Hα1) protein expression and collagen biosynthesis in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Importantly, these in vitro effects produced by high glucose were abolished by AMPKα pharmacological activation or adenovirus-mediated AMPKα overexpression. Further, adenovirus-mediated AMPKα gain of function remitted the process of diabetes-induced plaque destabilization in Apoe−/− mice injected with streptozotocin. Administration of metformin enhanced pAP-2α level, reduced miR-124 expression, and increased P4Hα1 and collagens in carotid atherosclerotic plaque in diabetic Apoe−/− mice. We conclude that streptozotocin-induced toxic diabetes promotes the formation of unstable atherosclerotic plaques based on the vulnerability index in Apoe−/− mice, which is related to the inactivation of AMPKα/AP-2α/miRNA-124/P4Hα1 axis. Clinically, targeting AMPKα/AP-2α/miRNA-124/P4Hα1 signaling should be considered to increase the plaque stability in patients with atherosclerosis.
Key messages
-
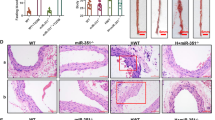
Hyperglycemia reduced collagen synthesis, leading to the formation of unstable atherosclerotic plaque induced by collar placement around carotid in apolipoprotein E knockout mice.
-
Hyperglycemia destabilizes atherosclerotic plaque in vivo through an AMPKα/AP-2α/miRNA-124/P4Hα1-dependent collagen synthesis.
-
Metformin functions as a stabilizer of atherosclerotic plaque to reduce acute coronary accent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nissen SE, Wolski K (2007) Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N Engl J Med 356:2457–2471
Donahoe SM, Stewart GC, McCabe CH, Mohanavelu S, Murphy SA, Cannon CP, Antman EM (2007) Diabetes and mortality following acute coronary syndromes. JAMA 298:765–775
Shah PK (2003) Mechanisms of plaque vulnerability and rupture. J Am Coll Cardiol 41:S15–S22
Libby P (1995) Molecular bases of the acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 91:2844–2850
Myllyharju J (2003) Prolyl 4-hydroxylases, the key enzymes of collagen biosynthesis. Matrix Biol 22:15–24
Rocnik EF, Chan BM, Pickering JG (1998) Evidence for a role of collagen synthesis in arterial smooth muscle cell migration. J Clin Invest 101:1889–1898
Lopez M, Nogueiras R, Tena-Sempere M, Dieguez C (2016) Hypothalamic AMPK: a canonical regulator of whole-body energy balance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 12:421–432
Wang S, Xu J, Song P, Viollet B, Zou MH (2009) In vivo activation of AMP-activated protein kinase attenuates diabetes-enhanced degradation of GTP cyclohydrolase I. Diabetes 58:1893–1901
Ido Y, Carling D, Ruderman N (2002) Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: inhibition by the AMP-activated protein kinase activation. Diabetes 51:159–167
Ouslimani N, Peynet J, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Therond P, Legrand A, Beaudeux JL (2005) Metformin decreases intracellular production of reactive oxygen species in aortic endothelial cells. Metab Clin Exp 54:829–834
Wang S, Zhang M, Liang B, Xu J, Xie Z, Liu C, Viollet B, Yan D, Zou MH (2010) AMPKalpha2 deletion causes aberrant expression and activation of NAD(P)H oxidase and consequent endothelial dysfunction in vivo: role of 26S proteasomes. Circ Res 106:1117–1128
Zang M, Xu S, Maitland-Toolan KA, Zuccollo A, Hou X, Jiang B, Wierzbicki M, Verbeuren TJ, Cohen RA (2006) Polyphenols stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase, lower lipids, and inhibit accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetic LDL receptor-deficient mice. Diabetes 55:2180–2191
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X, Jiang B, Park O, Luo Z, Lefai E, Shyy JY, Gao B, Wierzbicki M, Verbeuren TJ, Shaw RJ, Cohen RA, Zang M (2011) AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab 13:376–388
Park MJ, Kwak HJ, Lee HC, Yoo DH, Park IC, Kim MS, Lee SH, Rhee CH, Hong SI (2007) Nerve growth factor induces endothelial cell invasion and cord formation by promoting matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway and AP-2 transcription factor. J Biol Chem 282:30485–30496
Wang S, Zhang C, Zhang M, Liang B, Zhu H, Lee J, Viollet B, Xia L, Zhang Y, Zou MH (2012) Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha2 by nicotine instigates formation of abdominal aortic aneurysms in mice in vivo. Nat Med 18:902–910
Yang JJ, Li P, Wang F, Liang WJ, Ma H, Chen Y, Ma ZM, Li QZ, Peng QS, Zhang Y, Wang SX (2016) Activation of activator protein 2 alpha by aspirin alleviates atherosclerotic plaque growth and instability in vivo. Oncotarget 7:52729–52739
Ma H, Liang WJ, Shan MR, Wang XQ, Zhou SN, Chen Y, Guo T, Li P, Yu HY, Liu C, Yin YL, Wang YL, Dong B, Pang XY, Wang SX (2017) Pravastatin activates activator protein 2 alpha to augment the angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysms. Oncotarget 8:14294–14305
von der Thusen JH, van Berkel TJ, Biessen EA (2001) Induction of rapid atherogenesis by perivascular carotid collar placement in apolipoprotein E-deficient and low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Circulation 103:1164–1170
Li P, Yin YL, Guo T, Sun XY, Ma H, Zhu ML, Zhao FR, Xu P, Chen Y, Wan GR, Jiang F, Peng QS, Liu C, Liu LY, Wang SX (2016) Inhibition of aberrant microRNA-133a expression in endothelial cells by statin prevents endothelial dysfunction by targeting GTP cyclohydrolase 1 in vivo. Circulation 134:1752–1765
Nagareddy PR, Murphy AJ, Stirzaker RA, Hu Y, Yu S, Miller RG, Ramkhelawon B, Distel E, Westerterp M, Huang LS, Schmidt AM, Orchard TJ, Fisher EA, Tall AR, Goldberg IJ (2013) Hyperglycemia promotes myelopoiesis and impairs the resolution of atherosclerosis. Cell Metab 17:695–708
Kooy A, de Jager J, Lehert P, Bets D, Wulffele MG, Donker AJ, Stehouwer CD (2009) Long-term effects of metformin on metabolism and microvascular and macrovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med 169:616–625
Kivirikko KI, Helaakoski T, Tasanen K, Vuori K, Myllyla R, Parkkonen T, Pihlajaniemi T (1990) Molecular biology of prolyl 4-hydroxylase. Ann N Y Acad Sci 580:132–142
Rhoades MW, Reinhart BJ, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110:513–520
Wang F, Ma H, Liang WJ, Yang JJ, Wang XQ, Shan MR, Chen Y, Jia M, Yin YL, Sun XY, Zhang JN, Peng QS, Chen YG, Liu LY, Li P, Guo T, Wang SX (2017) Lovastatin upregulates microRNA-29b to reduce oxidative stress in rats with multiple cardiovascular risk factors. Oncotarget 8:9021–9034
Chakravarthi BV, Pathi SS, Goswami MT, Cieslik M, Zheng H, Nallasivam S, Arekapudi SR, Jing X, Siddiqui J, Athanikar J, Carskadon SL, Lonigro RJ, Kunju LP, Chinnaiyan AM, Palanisamy N, Varambally S (2014) The miR-124-prolyl hydroxylase P4HA1-MMP1 axis plays a critical role in prostate cancer progression. Oncotarget 5:6654–6669
Parathath S, Grauer L, Huang LS, Sanson M, Distel E, Goldberg IJ, Fisher EA (2011) Diabetes adversely affects macrophages during atherosclerotic plaque regression in mice. Diabetes 60:1759–1769
Sun H, Zhang X, Zhao L, Zhen X, Huang S, Wang S, He H, Liu Z, Xu N, Yang F, Qu Z, Ma Z, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Hu Q (2015) Attenuation of atherosclerotic lesions in diabetic apolipoprotein E-deficient mice using gene silencing of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. J Cell Mol Med 19:836–849
Iwamoto N, Abe-Dohmae S, Ayaori M, Tanaka N, Kusuhara M, Ohsuzu F, Yokoyama S (2007) ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 gene transcription is downregulated by activator protein 2alpha. Doxazosin inhibits activator protein 2alpha and increases high-density lipoprotein biogenesis independent of alpha1-adrenoceptor blockade. Circ Res 101:156–165
Iwamoto N, Abe-Dohmae S, Lu R, Yokoyama S (2008) Involvement of protein kinase D in phosphorylation and increase of DNA binding of activator protein 2 alpha to downregulate ATP-binding cassette transporter A1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:2282–2287
Magnusson SP, Heinemeier KM, Kjaer M (2016) Collagen homeostasis and metabolism. Adv Exp Med Biol 920:11–25
Utsugi T, Yoon JW, Park BJ, Imamura M, Averill N, Kawazu S, Santamaria P (1996) Major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted infiltration and destruction of pancreatic islets by NOD mouse-derived beta-cell cytotoxic CD8+ T-cell clones in vivo. Diabetes 45:1121–1131
Low Wang CC, Hess CN, Hiatt WR, Goldfine AB (2016) Clinical update: cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus: atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and heart failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus—mechanisms, management, and clinical considerations. Circulation 133:2459–2502
Paneni F, Costantino S, Cosentino F (2014) Insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk. Curr Atheroscler Rep 16:419
Shafrir E (1996) Development and consequences of insulin resistance: lessons from animals with hyperinsulinaemia. Diabetes Metab 22:122–131
Nakashima Y, Plump AS, Raines EW, Breslow JL, Ross R (1994) ApoE-deficient mice develop lesions of all phases of atherosclerosis throughout the arterial tree. Arterioscler Thromb 14:133–140
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81770493, 81320108004, 81370411, and 81470591).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.J.L. designed and conducted the experiments and analyzed data. S.N.Z., M.R.S., X.Q.W., M.Z., Y.C., and X.Y.P. partially performed some experiments. Y.Z., T.G., and S.X.W. analyzed the data, wrote the manuscript, and convinced the whole project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 748 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, WJ., Zhou, SN., Shan, MR. et al. AMPKα inactivation destabilizes atherosclerotic plaque in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice through AP-2α/miRNA-124 axis. J Mol Med 96, 403–412 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1627-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1627-8