Abstract
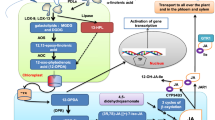
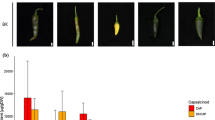
Resveratrol is a phytoalexin produced in various plants like wine, peanut or pine in response to fungal infection or UV irradiation, but it is absent in members of the Brassicaceae. Moreover, resveratrol and its glucoside (piceid) are considered to have beneficial effects on human health, known to reduce heart disease, arteriosclerosis and cancer mortality. Therefore, the introduction of the gene encoding stilbene synthase for resveratrol production in rapeseed is a tempting approach to improve the quality of rapeseed products. The stilbene synthase gene isolated from grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) was cloned under control of the seed-specific napin promotor and introduced into rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by Agrobacterium-mediated co-transformation together with a ds-RNA-interference construct deduced from the sequence of the key enzyme for sinapate ester biosynthesis, UDP-glucose:sinapate glucosyltransferase (BnSGT1), assuming that the suppression of the sinapate ester biosynthesis may increase the resveratrol production in seeds through the increased availability of the precursor 4-coumarate. Resveratrol glucoside (piceid) was produced at levels up to 361 μg/g in the seeds of the primary transformants. This value exceeded by far piceid amounts reported from B. napus expressing VST1 in the wild type sinapine background. There was no significant difference in other important agronomic traits, like oil, protein, fatty acid and glucosinolate content in comparison to the control plants. In the third seed generation, up to 616 μg/g piceid was found in the seeds of a homozygous T3-plant with a single transgene copy integrated. The sinapate ester content in this homozygous T3-plant was reduced from 7.43 to 2.40 mg/g. These results demonstrate how the creation of a novel metabolic sink could divert the synthesis towards the production of piceid rather than sinapate ester, thereby increasing the value of oilseed products.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer M, Libantova J, Moravcikova J, Bekesiova I (1998) Transgenic tobacco plants constitutively expressing acidic chitinase from cucumber. Biologia 52:749–758
Bell JM (1993) Factors affecting the nutritional value of Canola Meal: a review. Can J Anim Sci 73:679–697
Bouchereau A, Hamelin J, Lamour I, Renard M, Larher F (1991) Distribution of sinapine and related compounds in seeds of Brassica and allied Genera. Phytochemistry 30:1873–1881
De Block M, De Brouwer D (1991) Two T- DNA’s cotransformed into Brassica napus by a double Agrobacterium tumefaciens infection are mainly integrated at the same locus. Theor Appl Genet 82:257–263
De Block M, De Brouwer D, Tenning P (1989) Transformation of Brassica napus and Brassica oleracea using Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the expression of the bar and neo Genes in the transgenic Plants. Plant Physiol 91:694–701
Fettig S, Hess D (1998) Expression of a chimeric stilbene synthase gene in transgenic wheat lines. Transgenic Res 8:179–189
Fischer R, Budde I, Hain R (1997) Stilbene synthase gene expression causes changes in flower colour and male sterility in tobacco. Plant J 11:489–498
Hain R, Reif HJ, Krause E, Langebartels R, Kindl H, Vornam B, Wiese W, Schmelzer E, Schreier PH, Stöcker RH, Stenzel K (1993) Disease resistance results from foreign phytoalexin expression in a novel plant. Nature 361:153–156
Hausmann L, Töpfer R (1999) Entwicklung von Plasmid-Vektoren. In: BioEngineering für Rapssorten nach Maß. Vorträge für Pflanzenzüchtung 45:155–173
Hellens RP, Mullineaux P, Klee H (2000) A guide to Agrobacterium binary Ti vectors. Trends Plant Sci 5:446–451
Hipskind JD, Paiva NL (2000) Constitutive accumulation of a resveratrol-glucoside in transgenic alfalfa increases resistance to Phoma medicaginis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:551–562
Hobbs SLA, Warkentin TD, DeLong CMO (1993) Transgene copy number can be positively or negatively associated with transgene expression. Plant Mol Biol 21:17–26
Hüsken A (2004) Untersuchungen zur Sinapinsäureestersuppression und Expression von Resveratrol in transgener Rapssaat (Brassica napus L.). Dissertation Universität Göttingen. http://www.sub.uni-goettingen.de
Jakowitsch J, Papp I, Moscone EA, van der Winden J, Matzke M, Matzke AJ (1999) Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a transgene locus that induces silencing and methylation of homologous promoters in trans. Plant J 17:131–140
Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV, Thomas CF, Beecher CWW, Fong HHS, Farnswoth NR, Kinghorn AD, Metha RG, Moon RC, Pezzuto JM (1997) Cancer chemopreventive activity of piceid, a natural product derived from grapes. Science 275:218–220
Kindl H (1985) Biosynthesis of stilbenes. In: Higuchi T (ed) Biosynthesis and biodegradation of wood components. Academic Press, New York, pp 349–377
Kobayashi S, Ding CK, Nakamura Y, Nakajima I, Matsumoto R (2000) Kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) transformed with a Vitis stilbene synthase gene produce piceid (resveratrol-glucoside). Plant Cell Rep 19:904–910
Komari T, Hiei Y, Saito Y, Murai N, Kumashiro T (1996) Vectors carrying two T-DNA for cotransformation of higher plants mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and segregation of transformants free from selection markers. Plant J 10:165–174
Kozlowska H, Naczk M, Shahidi F, Zadernowski R (1990) Phenolic acids and tannins in rapeseed and canola. In: Shahidi, F (ed) Canola and Rapeseed. (Production, Chemistry, Nutrition and Processing Technology). Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp 193–210
Landry LG, Chapple CCS, Last R (1995) Arabidopsis mutants lacking phenolic sunscreens exhibit enhanced ultraviolet-B injury and oxidative damage. Plant Physiol 109:1159–1166
Langcake P (1981) Disease resistance of Vitis spp. and the production of stress metabolites piceid, ε-viniferin, α-viniferin and pterostilben. Physiol Plant Pathol 18:213–226
Langcake P, McCarthy WV (1979) The relationship of piceid production to infection of grapevine leaves by Botrytis cinerea. Vitis 18: 244–253
Langcake P, Pryce RJ (1976) The production of piceid by Vitis vinifera and other members of the Vitaceae as a response to infection or injury. Physiol Plant Pathol 9:77–86
Leckband G, Lörz H (1998) Transformation and expression of a stilbene synthase gene of Vitis vinifera L. in barley and wheat for increased fungal resistance. Theor Appl Genet 96:1001–1012
Liang H, Zheng J, Duan X, Sheng B, Jia S, Wang D, Ouyang J, Li J, Li L, Tian W, Jia X (2000) A transgenic wheat with a stilbene synthase gene resistant to powdery mildew obtained by biolistic method. Chin Sci Bull 45:634–638
Lorenzen M, Racicot V, Strack D, Chapple C (1996) Sinapate ester metabolism in wild type and a sinapoylglucose-accumulating mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 112:1625–1630
Manna SK, Mukhopadhyay A and Aggarwal BB (2000) Piceid suppresses TNF-induced activation of nuclear transcription factors NF-kB, activator protein-1, and apoptosis: potential role of reactive oxygen intermediates and lipid peroxidation. J Immunol 164:6509–6519
McCabe MS, Mohapatra UB, Debnath SC, Power JB, Davey MR (1999) Integration, expression and inheritance of two linked T-DNA marker genes in transgenic lettuce. Mol Breed 5:329–344
Melchior F, Kindl H (1990) Grapevine stilbene synthase cDNA only slightly differing from chalcone synthase cDNA is expressed in Escherichia coli into catalytically active enzyme. FEBS Lett 268: 17–20
Melchior F, Kindl H (1991) Coordinate- and elicitor-dependent expression of stilbene synthase and phenylalanine ammonia lyase genes in Vitis cv. Optima. Arch Biochem Biophys 288:552–557
Milkowski C, Baumert A, Strack D (2000) Cloning and heterologous expression of a rape cDNA encoding UDP-glucose: sinapate glucosyltransferase. Planta 211:883–886
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Naczk M, Aramowicz A, Sullivan A, Shahidi F (1998) Current research developments on polyphenolics of rapeseed/canola: a review. Food Chem 62:489–502
Orsini J, Baumert A, Milkowski C, Weyen J, Leckband G (2003) Agrobacterium-mediated production of Brassica napus transgenic plants with a stilbene synthase gene. In: Proceedings 11th International Rapeseed Congress, Copenhagen, vol 1, BP3.30, p 155
Pace-Asciak CR, Hahn S, Diamanidis EP, Soleas G, Goldberg DM (1995) The red wine phenolics trans-piceid and quercetin block human platelet aggregation and eicosanoid synthesis: implications for protection against coronary heart disease. Clin Chim Acta 235:207–219
Pickford AS, Cogoni C (2003) RNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:871–882
Rupprich N, Kindl H (1978) Stilbene synthase and stilbene carboxylate synthases. I. Enzymatic synthesis of 3,5,4,-trihydroxystilbene from p-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA. Hoppe Seyler’s Z Physiol Chem 359: 165–175
Schoeppner A, Kindl H (1978) Stilbene synthase (Pinosylvine synthase) and its function induction by ultraviolet light. FEBS Lett 108:125–133
Shahidi F, Naczk M (1992) An overview of the phenolics of canola and rapeseed: Chemical, sensory and nutritional significance. J Am Oil Chem Soc 69:917–924
Stark-Lorenzen P, Nelke P, Hänßler G, Mühlbach HP, Thomzik JE (1997) Tranfer of a grapevine stilbene synthase gene to rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 16:668–673
Statistical Graphics Corp. (1997) Statgraphics Plus 3.0, Statistical graphic System by Statistical Graphic Corporation, Rockville
Stein U, Blaich R (1985) Untersuchungen über Stilbenproduktion und Botrytisanfälligkeit bei Vitis-Arten. Vitis 24:75–87
Strack D, Knogge W, Dahlbender B (1983) Enzymatic synthesis of sinapine from 1-O-sinapoylglucose and choline by a cell-free system from developing seeds of red radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Zeitschrift für Naturforschung 38c:21–27
Szankowski I, Briviba K, Fleschhut J, Schönherr J, Jacobsen HJ, Kiesecker H (2003) Transformation of apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) with the stilbene synthase gene from grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) and a PGIP gene from kiwi (Actinidia deliciosa). Plant Cell Rep 22:141–149
Tillmann P (2005) http://www.vdlufa.de/nirs. (Site visited 28 Feb 2005)
Acknowledgements
We thank Rosemarie Clemens and Nicole Ritgen-Homayounfar for technical assistance and José Orsini (Saatenunion Resistenzlabor, Germany) for his helpful hints regarding the transformation protocol. Many thanks also to Petra Jorasch (Universität Hamburg) for providing the binary plasmid pPSty5. This work is part of the research project ’NAPUS 2000—Healthy Food from Transgenic Rape Seeds’, financially supported by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hüsken, A., Baumert, A., Milkowski, C. et al. Resveratrol glucoside (Piceid) synthesis in seeds of transgenic oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 111, 1553–1562 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0085-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0085-1