Abstract
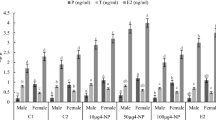
Vitellogenin (Vtg), 17β-estradiol (E2) and testosterone (T) were used as biomarkers of endocrine disruption in mature male nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from three lakes (Rio, Enmedio and Limon) in Chiapas, Mexico. Vitellogenesis induction was found in tilapias from Rio and Limon, moderately high E2 levels in Rio and Limon tilapias, compared with controls (cultured tilapias). Significant correlations between benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) metabolites and hexachlorobenzene (HCB) with Vtg and E2 were found. The results of this study indicate that endocrine disruption exists in tilapias from Rio and Limon lakes, and that exposure to HCB and BaP could be causing these alterations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas E, Beyer J, Goksoyr A (1998) PAH in fish bile detected by fixed wavelength fluorescence. Mar Environ Res 46(1–5):225–228
Ankley G et al (1998) Overview of a workshop on screening methods for detecting potential (anti-) estrogenic/androgenic chemicals in wildlife. Environ Toxicol Chem 17(1):68–87. doi:10.1897/1551–5028(1998)017<0068:OOAWOS>2.3.CO;2
Colborn T, Vom Saal FS, Soto AM (1993) Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ Health Perspect 101(5):378–384. doi:10.2307/3431890
Ezendam J, Staedtler F, Pennings J, Vandebriel RJ, Pieters R, Harleman JH, Vos JG (2004) Toxicogenomics of subchronic hexachlorobenzene exposure in Brown Norway rats. Environ Health Perspect 112(7):782–791
Folmar LC, Denslow ND, Rao V, Chow M, Crain A, Enblom J, Marcino J, Guillete LJ Jr (1996) Vitellogenin induction and reduced serum testosterone concentrations in feral male Carp (Cyprinus carpio) captured near major metropolitan sewage treatment plant. Environ Health Perspect 104:1096–1101. doi:10.2307/3433123
Gold-Bouchot G, Zapata-Pérez O, Rodríguez-Fuentes G, Ceja-Moreno V, del Río-García M, Chan-Cocom E (2006) Biomarkers and pollutants, in four lakes from San Miguel, Chiapas, Mexico. Int J Environ Poll 26(1/2/3):129–141
Jarrell J, Gocmen A, Foster W, Brant R, Chan S, Sevcik M (1998) Evaluation of reproductive outcomes in women inadvertently exposed to hexachlorobenzene in southeastern Turkey in the 1950s. Reprod Toxicol 12:469–476. doi:10.1016/S0890-6238(98)00019-7
Kavlock RJ, Daston GP, DeRosa C, Fenner-Crisp P, Gray LE, Kattari S, Lucier G, Luster M, Mac MJ, Maczka C, Miller R, Moore J, Rolland R, Scoot G, Sheehan DM, Sinks T, Tilson HA (1996) Research needs for risk assessment of health and environmental effects of endocrine disruptors: a report of the U.S. EPA-sponsored workshop. Environ Health Perspect 104(Suppl 4):715–740. doi:10.2307/3432708
Krahn MM, Burrows DG, MacLeod WD Jr, Malins DC (1987) Determination of individual metabolites of aromatic compounds in hydrolyzed bile of english sole (Parophrys vetulus) from polluted sites in Puget Sound, Washington. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 16:511–522. doi:10.1007/BF01055807
Leaños-Castañeda O, Van Der Kraak G, Lister A, Simá-Alvarez R, Gold-Bouchot G (2002) o,p′-DDT induction of vitellogenesis and its inhibition by tamoxifen in nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Mar Environ Res 54:703–707. doi:10.1016/S0141-1136(02)00168-X
Nishihara T, Nishikawa J, Kanayama T, Dakeyama F, Saito K, Imagawa M, Takatori S, Kitagawa Y, Hori S, Utsumi H (2000) Estrogenic activities of 517 chemicals by yeast two-hybrid assay. J Health Sci 46(4):282–298
Rivas A, Granada A, Jiménez M, Olea F, Olea N (2004) Exposición humana a disruptores endocrinos. Ecosistemas 13(3):1–7
Sericano Jl, Atlas EL, Wade TL, Brooks JM (1990) NOAA’s status and trends Mussel watch program: chlorinated pesticides and PCBs in oysters (Crassostrea virginica) and sediments from the Gulf of Mexico, 1986–1987. Mar Environ Res 29:161–203. doi:10.1016/0141-1136(90)90033-K
Tyler CR, Van Aerle R, Hutchinson TH, Maddix S, Trip H (1999) An in vivo testing system for endocrine disruptors in fish early life stages using induction of vitellogenin. Environ Toxicol Chem 18(2):337–347. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1999)018<0337:AIVTSF>2.3.CO;2
Wallace RA, Jared DW (1968) Studies on amphibian yolk. VII. Serum phospho-protein synthesis by vitellogenic females and oestrogen-treated males of Xenopus laevis. Can J Biochem 46:953–959. doi:10.1139/v68-157
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank PEMEX (Producción y Exploración, Refinación, y Petroquímica) for financial support, to Dr. Rene Capurro Filograsso for revising an earlier version, and to Jorge Dominguez Maldonado for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodas-Ortíz, J.P., Ceja-Moreno, V., Chan-Cocom, M.E. et al. Vitellogenin Induction and Increased Plasma 17β-Estradiol Concentrations in Male Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, Exposed to Organochlorine Pollutants and Polycyclic Aromatics Hydrocarbons. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81, 543–547 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9556-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9556-9