Abstract
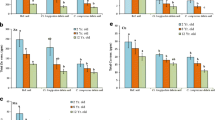
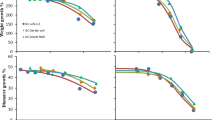
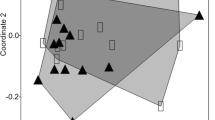
Highly efficient accumulation of trace metals is often reported in ants, but their metal regulation strategies are poorly understood. This study examined the relationships between Zn and Cd total (tot) and water soluble (ws) concentrations in soil and in workers of three ant species collected along a metal-pollution gradient: Formica cunicularia, Lasius flavus and Myrmica rubra. Regression line comparisons showed the body loads of metals to depend strongly on the metal and the species. M. rubra showed the most efficient regulation of Zn, as its average Zn concentration and the regression slope were several times lower than for the other species. Although the species differed in their Cd levels, the slopes of the relationships between Cd concentration in soil and in ants did not differ between species (tot: p = 0.71, ws: p = 0.31). The very weak relationship for Cd found for all species suggests at least some active Cd regulation. These results can be explained in the context of tissue-specific metal accumulation. High Zn accumulation in mandibles and ovarioles may explain its high accumulation in F. cunicularia and L. flavus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craig A, Hare L, Charest PM, Tessier A (1998) Effect of exposure regime on the internal distribution of cadmium in Chironomus staegeri larvae (Insecta Diptera). Aquat Toxicol 41:265–275
Czechowski W, Radchenko A, Czechowska W (2002) The ants (Hymenoptera Formicidae) of Poland. Museum and Institute of Zoology PAS, Warszawa
Eeva T, Sorvari J, Kolvunen V (2004) Effects of heavy metal pollution on red wood ant (Formica s str) populations. Environ Pollut 132:533–539
Grzes IM (2009a) Cadmium regulation by Lasius niger: A contribution to understanding high metal levels in ants. Insect Sci 16:89–92
Grzes IM (2009b) Ant species richness and evenness increase along metal pollution gradient in the Boleslaw zinc smelter. Pedobiologia. doi:101016/jpedobi200903002
Heikens A, Peijnenburg W, Hendriks AJ (2000) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in terrestrial invertebrates. Environ Pollut 113:385–393
Hillerton JE, Vincent JF (1982) The specific location of zinc in insect mandibles. J Exp Biol 101:333–336
Hopkin SP (1989) Ecophysiology of metals in terrestrial invertebrates. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers Ltd, London
Lidqvist L, Block M, Tjälve H (1995) Distribution and excretion of Cd Hg methyl-Hg and Zn in the predatory beetle Pterostichus niger (Coleoptera:Carabidae). Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1195–1201
Migula P, Glowacka E (1996) Heavy metals as stressing factors in the red wood ants (Formica polyctena) from industrially polluted forests. Fresen J Anal Chem 354:653–659
Novgorodova TA (2005) Ant-aphid interactions in multispecies ant communities: Some ecological and ethological aspects. Mar Environ Res 60:339–354
Rabitsch WB (1995) Metal accumulation in arthropods near a lead/zinc smelter in Arnoldstein austria 2. Formicidae. Environ Pollut 90:239–247
Rabitsch WB (1997) Tissue-specific accumulation patterns of Pb Cd Cu Zn Fe and Mn in workers of three ant species (Formicidae Hymenoptera) from a metal-polluted site. Arch Environ Cont Tox 32:172–177
Rainbow PS (2002) Trace metal concentrations in aquatic invertebrates: why and so what? Environ Pollut 120:497–507
Schmidt GH, Ibrahim NMM (1994) Heavy metal content (Hg2+ Cd2+ Pb2+) in various body parts: its impact on cholinesterase activity and binding glycoproteins in the grasshopper Aiolopus thalassinus adults. Ecotox Environ Safe 29:148–164
Silva AFD, Meireles B, Rosa JD, de Oliveira MW, Morini MSD, de Oliveira AF (2006) Evaluation of the level of metals in Camponotus rufipes (Hymenoptera:Formicidae) collected in different environments. Sociobiology 47:293–304
Sohal RS, Lamb RE (1997) Intracellular deposition of metals in the midgut of the adult housefly Musca domestica. J Insect Physiol 23:1349–1354
Stefanowicz AM, Niklińska M, Laskowski R (2008) Metals affect soil bacterial and fungal functional diversity differently. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:591–598
Stone D, Jepson P, Kramarz P, Laskowski R (2001) Time to death response in carabid beetles exposed to multiple stressors along a gradient of heavy metal pollution. Environ Pollut 113:239–244
Teixeira B, Barrento S, Carvalho ML, Nunes ML, Marques A (2008) Macro and trace elements in edible tissues of Carcinus maenas and Necora puber. J Sci Food Agr 88:2451–2459
Warchalowska-Sliwa E, Niklinska M, Gorlich A, Michailova P, Pyza E (2005) Heavy metal accumulation heat shock protein expression and cytogenetic changes in Tetrix tenuicornis (L) (Tetrigidae Orthoptera) from polluted areas. Environ Pollut 133:373–381
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the EU 6th FP grant “ALARM” (No GOCE-CT-2003-506675) and Institute of Environmental Sciences Jagiellonian University (DS 758). The author wishes to thank Renata Śliwińska and Dominika Chmolowska for help in the field work and to Prof. Ryszard Laskowski for helpful comments on a previous version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grześ, I.M. Zinc and Cadmium Regulation Efficiency in Three Ant Species Originating from a Metal Pollution Gradient. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84, 61–65 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9893-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9893-3