Abstract
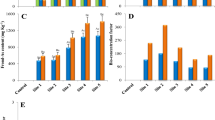
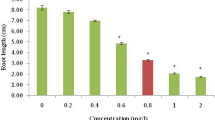
A study was performed for phyto-genotoxic assay of chromium (Cr) and arsenic (As) through Allium cepa. Various concentrations (0, 1, 3, 6 and 12 mg L−1) of Cr and As for 48 and 168 h time points exposed to A. cepa. The phytotoxic effects of metal(loid) were evident through inhibited root length and root protein. Metal(loid) toxicity also lead to genotoxic effects, which included depression of mitotic index and increased frequency of chromosomes aberrations like break, fragments, c-metaphase, multipolar arrangements etc. Genotoxic endpoint as progressive frequency of micronuclei in interphase of root meristem cells in treated plants was also observed. This genotoxic endpoint revealed carcinogenic nature of both aforementioned metal(loid). Along with inhibition in root length and protein content, depression in mitotic index as well as stimulation of various abnormality in mitotic cell division indicated that both metal(loid) are hazardous in nature and causing harmful effect on the environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas G, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Khan MI, Amjad M, Hussain M (2018) Arsenic uptake, toxicity, detoxification, and speciation in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular aspects. Int J Environ Res Pub Health 15(1):59
da Conceição Gomes MA, Hauser-Davis RA (2017) Plant chromium uptake and transport, physiological effects and recent advances in molecular investigations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 140:55–64
Datta JK, Bandhyopadhyay A, Banerjee A, Mondal NK (2011) Phytotoxic effect of chromium on the germination, seedling growth of some wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars under laboratory condition. J Agric Technol 7(2):395–402
Ditika K, Anila M (2013) Assessment of cytotoxic and genotoxic potency of Cr(vi)-doped river water of Nen-shkodra lowland, albania, on Allium cepa L. J Environ Res Dev 7(4):1322–1332
Dube BK, Tewari K, Chatterjee J, Chatterjee C (2003) Excess chromium alters uptake and translocation of certain nutrients in citrullus. Chemosphere 53(9):1147–1153
Dwivedi S, Srivastava S, Mishra S, Kumar A et al (2010) Characterization of native microalgal strains for their chromium bioaccumulation potential: phytoplankton response in polluted habitats. J Hazard Mater 173:95–101
Espinoza-Quiñones FR, Szymanski N, Palácio SM, Módenes AN, Rizzutto MDA, Silva FG, Oliveira AP, Oro ACP, Martin N (2009) Inhibition effect on the Allium cepa L. root growth when using hexavalent chromium-doped river waters. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82(6):767–771
Fiskejo G (1985) The allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas 102:92–112
Gebel TW (2001) Genotoxicity of arsenical compounds. Int J Hyg Environ Health 203:249–262
Glińska S, Bartczak M, Oleksiak S, Wolska A et al (2007) Effects of anthocyanin-rich extract from red cabbage leaves on meristematic cells of Allium cepa L. roots treated with heavy metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 68(3):343–350
Gupta K (2016) Role of Eichhorniacrassipes for evaluation of quality of water polluting Ganga river. Res Environ life Sci 9(10):1266–1269
Gupta K, Gaumat S, Mishra K (2012) Studies on phyto-genotoxic assessment of tannery effluent on Allium cepa. J Environ Biol 33:557–563
Hemachandra CK, Pathiratne A (2015) Assessing toxicity of Co, Cd and Cr levels relevant to discharge limits of industrial effluents into inland surface waters using common onion, Allium cepa bioassay. Bull Environ Contamin Toxicol 94:199–203
JECFA (2010) Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. 73th Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additive. WHO Technical Report Series 960
Kirsch VM, Plas G, Elhajouji A, Lukamowicz M, Gonzalez L, Vande Loock K (2011) The in vitro MN assay in 2011: origin and fate, biological significance, protocols, high throughput methodologies and toxicological relevance. Arch Toxicol 85(8):873–899
Kumar A, Singh RP et al (2014a) Selenium ameliorates arsenic induced oxidative stress through modulation of antioxidant enzymes and thiols in rice. Ecotoxicology 23:1153–1163
Kumar A, Tripathi RD, Singh RP, Dwivedi S, Chakrabarty D, Mallick S et al (2014b) Evaluation of amino acid profile in contrasting arsenic accumulating rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes under arsenic stress grown in hydroponic condition. Biol Plant 58(4):733–742
Kumar A, Dixit G, Singh AP, Srivastava S, Mishra K, Tripathi RD (2016) Selenate mitigates arsenite toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by reducing arsenic uptake and ameliorates amino acid content and thiol metabolism. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:350–359
Leme DM, Marin-Morales MA (2009) Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: a review on its application. Mutat Res Rev 682(1):71–81
Li N, Wang J, Song WY (2016) Arsenic uptake and translocation in plants. Plant Cell Physiol 57(1):4–13
Lowry OH, Rasebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mishra S, Bhargava RN (2016) Toxic and genotoxic effects of hexavalent chromium in environment and its bioremediation strategies. J Environ Sci Health 34:1–32
Nematshahi N, Mehrdad Lahouti M, Ganjeali A (2012) Accumulation of chromium and its effect on growth of (Allium cepa cv. Hybrid). Eur J Exp Biol 2(4):969–974
Panda SK, Choudhory S (2005) Chromium stress in plants. Braz Plant Physiol 17(1):95–102
Santos C, Rodriguez E (2012). Review on some emerging endpoints of chromium (VI) and lead phytotoxicity. In: Mworia JK (ed) Botany, InTech, Rijeka
Schneiderman MH, Dewey WC, Highfield DP (1971) Inhibition of DNA synthesis in synchronized Chinese hamster cells treated in G1 with cycloheximide. Exp Cell Res 67:147–155
Siddiqui S (2015) DNA damage in Cicer plant grown on soil polluted with heavy metal. J King Saud Univ Sci 27(3):217–223
Silveira MA, Datsch DL, Ribeiro et al (2017) Direct and indirect anthropogenic contamination in water sources: evaluation of chromosomal stability and cytotoxicity using the Allium cepa test. Bull Environ Contamin Toxicol 100:1–5
Singh AP, Dixit G, Kumar A, Mishra S, Kumar N, Dixit S, Singh PK, Dwivedi S et al (2017) A protective role for nitric oxide and salicylic acid for arsenite phytotoxicity in rice(Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 115:163–173
Stambulska UY, Bayliak MM, Lushchak VI (2018). Chromium (VI) toxicity in legume plants: modulation effects of rhizobial symbiosis. Bio Med Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8031213
Sudhakar R, Gowda N, Venu G (2001) Mitotic abnormalities induced by silk dyeing industry effluents in the cells of Allium cepa. Cytologia 66:235–239
Van’t Hoff J (1968) The action of IAA and kinetin on the mitotic cycle of proliferative and stationary phase excised root meristem. Exp Cell Res 51:167
World Health Organization (2004). Guidelines for drinking-water quality: recommendations vol 1, WHO, Geneva
Wu L, Yi H, Yi M (2010) Assessment of arsenic toxicity using Allium/Vicia root tip micronucleus assays. J Hazard Mater 176:952–956
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Department of Botany, University of Lucknow, Lucknow for the facilities. Kiran Gupta is thankful to University Grant Commission, New Delhi, India, for the award of the Post-doctoral fellowship for women. Amit Kumar is acknowledging the DSKPDF Cell, Pune, India, and University Grant Commission, New Delhi, India, for the award of the D.S. Kothari Postdoctoral Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, K., Mishra, K., Srivastava, S. et al. Cytotoxic Assessment of Chromium and Arsenic Using Chromosomal Behavior of Root Meristem in Allium cepa L.. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100, 803–808 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2344-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2344-2