Abstract
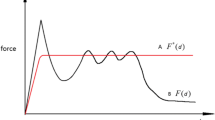
The present work deals with topology optimization for obtaining a desired energy absorption history of a crushed structure. The optimized energy absorbing structures are used to improve the crashworthiness of transportation vehicles. The ground structure consists of rectangular 2D-beam elements with plastic hinges. The elements can undergo large rotations, so the analysis accommodates geometric nonlinearities. A quasi-static nonlinear finite element solution is obtained with an implicit backward Euler algorithm, and the analytical sensitivities are computed by the direct differentiation method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosio, J.A.C.; Pereira. M.S. 1997: Multibody dynamic tools for crashworthiness and impact. In: Ambrosio, J.A.C.; Seabra Pereira, M.F.O.; Pina da Silva, F. (eds.) Crashworthiness of Transportation Systems: Structural Impact and Occupant Protection. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers
Bendsøe, M.P. 1995.: Optimization of Structural Topology, Shape and Material. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag
Bendsøe, M.P.; Guedes, J.M.; Plaxton, S.; Taylor, J.E. 1995: Optimization of structure and material properties for solids composed of softening material. Int. J. Solids Struct. 33, 1799–1813
Bruns, T.; Tortorelli, D.A. 2001: Topology optimization of nonlinear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comp. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190, 3443–3458
Bruns, T.; Tortorelli, D.A. 2003: An element removal and reintroduction strategy for the topology optimization of structures and compliant mechanisms. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 57, 1413–1430
Buhl, T.; Pedersen, C.B.W.; Sigmund, O. 2000: Stiffness design of geometrically non-linear structures using topology optimization. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 19, 93–104
Chen, S. 2001: An approach for impact structure optimization using the robust genetic algorithm. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 37, 431–446
Cho, S.; Choi, K.K. 2000a: Design sensitivity analysis and optimization of non-linear transient dynamics. part i – sizing design. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 48, 351–373
Cho, S.; Choi, K.K. 2000b: Design sensitivity analysis and optimization of non-linear transient dynamics. part ii – configuration design. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 48, 375–399
Diaz, A.R.; Ignatovich, C.L.; Soto, C.A. 2000: Strategies in design for enhanced crashworthiness. In: Rozvany, G.I.N.; Olhoff, N. (eds.) NATO/ISSMO ARW on Topology Optimization of Structures and Composite Continua (held in Budapest, Hungary), Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers
Diaz A.R.; Soto C.A. 1999: Lattice models for crash resistant design and optimization. In: Proc. 3rd WCSMO (New York Univ. Buffalo), pp. 233–235
Ebisugi, T.; Fujita, H.; Watanabe, G. 1998: Study of optimal structure design method for dynamic nonlinear problem. JSAE Rev. 19, 251–255
Esche, S.K.; Kinzel, G.L.; Altan, T. 1997: Issues in convergence improvement for non-linear finite element programs. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 40, 4577–4594
Gebbeken, N. 1998: A refined numerical approach for the ultimate-load analysis of 3-d steel rod structures. Eng. Comput. 15, 312–344
Hajela, P.; Lee, E. 1997: Topological optimization of rotorcraft subfloor structures for crashworthiness considerations. Comput. Struct. 64, 65–76
Heung-Soo, K.; Wierzbicki, T. 2001: Crush behavior of thin-walled prismatic columns under combined bending and compression. Comput. Struct. 79, 1417–1432
Heyman, J. 1975: Overcomplete mechanisms of plastic collapse. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 15, 27–35
Jones, N. 1989: Structural Impact. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Kecman, D. 1997: An engineering approach to crashworthiness of thin-walled beams and joints in vehicle structures. Thin-Walled Struct. 28, 309–320
Kleiber, M.; Antúnez, H.; Hien, T.D.; Kowalczyk, P. 1997: Parameter Sensitivity in Nonlinear Mechanics, Theory and Finite Element Computations. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons
Krenk, S.; Vissing-Jørgensen, C.; Thesbjerg, L. 1999: Efficient collapse techniques for framed structures. Comput. Struct. 72, 481–496
Marklund, P.O.; Nilsson, L. 2001: Optimization of a car body component subjected to side impact. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 21, 383–392
Maute, K.; Schwarz, S.; Ramm, E. 1998: Adaptive topology optimization of elastoplastic structures. Struct. Optim. 15, 81–91
Mayer, R.R.; Kikuchi, N.; Scott, R.A. 1996: Application of topological optimization techniques to structural crashworthiness. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 39, 1383–1403
Michaleris, P.; Tortorelli, D.A.; Vidal, C.A. 1994: Tangent operators and design sensitivity formulations for transient non-linear coupled problems with applications to elastoplasticity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 37, 2471–2499
Missoum, S.; Gürdal, Z.; Gu, W. 2002: Optimization of nonlinear trusses using a displacement-based approach. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 23, 214–221
Montag, U.; Krätzig, W.B.; Soric, J. 1999: Increasing solution stability for finite-element modeling of elasto-plastic shell response. Adv. Eng. Software 30, 607–619
Olhoff, N. 1989: Multicriterion structural optimization via bound formulation and mathematical programming. Struct. Optim. 1, 11–17
Oran, C. 1973: Tangent stiffness in plane frames. J. Struct. Div., ASCE 99, 973–985
Pedersen, C.B.W. 2001: Topology optimization of 2D-frames for crashworthiness. In: Proc. 4rd WCSMO (held in Dalian, China)
Pedersen, C.B.W. 2002a: On Topology Design of Frame Structures for Crashworthiness. PhD thesis, Dept. Mech. Eng., Solid Mech., Tech. Univ. Denmark
Pedersen, C.B.W. 2002b: Topology optimization of energy absorbing frames. In: Proc. WCCM V – 5th World Congress on Computational Mechanics (held in Vienna, Austria)
Pedersen, C.B.W. 2003a: Topology optimization for crashworthiness of frame structures. Int. J. Crashworthiness 8, 29–39
Pedersen, C.B.W. 2003b: Topology optimization of 2D-frame structures with path dependent response. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 57, 1471–1501
Pedersen, C.B.W.; Buhl, T.; Sigmund, O. 2001: Topology synthesis of large-displacement compliant mechanisms. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 50, 2683–2706
Pereira, M.S.; Ambrosio, J.A.C.; Dias, J.P. 1997: Crashworthiness analysis and design using rigid-flexible multibody dynamics with application to train vehicles. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 40, 655–687
Perez, J.G.; Johnson, E.R.; Boitnott, R.L. 1998: Design and test of semicircular composite frames optimized for crashworthiness. Proc. AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Struct., Struct. Dyn. Mater. Conf. 1, 27–38
Saleeb, A.F.; Wilt, T.E.; Li, W. 1998: An implicit integration scheme for generalized viscoplasticity with dynamic recovery. Comput. Mech. 21, 429–440
Saleeb, A.F.; Wilt, T.E.; Li, W. 2000: Robust integration schemes for generalized viscoplasticity with internal-state variables.Comput. Struct. 74, 601–628
Saxena, A.; Ananthasuresh, G.K. 2001: Topology synthesis of compliant mechanisms for nonlinear force-deflection and curved path specifications. J. Mech. Des. 123, 33–42
Schwarz, S.; Maute, K.; Ramm, E. 2001a: Sensitivity analysis and optimization for non-linear structural response. Eng. Comput. 18, 610–641
Schwarz, S.; Maute, K.; Ramm, E. 2001b: Topology and shape optimization for elastoplastic structural response. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190, 2135–2155
Soric, J.; Montag, U.; Krätzig, W.B. 1997: On the increase of computational algorithm efficiency for elasto-plastic shell analysis. Eng. Comput. 14, 75–97
Soto, C.A. 2001a: Optimal structural topology design for energy absorption: A heuristic approach. In: Proc. ASME Des. Eng. Tech. Conf. (held in Pittsburgh, USA)
Soto, C.A. 2001b: Structural topology optimization: From minimizing compliance to maximizing energy absorption. Int. J. Vehicle Des. 25, 142–163
Stander, N.; Roux, W.; Pattabiraman, S.; Dhulipudi, R. 1999: Response surface approximations for design optimization problems in nonlinear dynamics. ASME, Pressure Vessels and Piping Div. 396, 275–284
Svanberg, K. 1987: The method of moving asymptotes – a new method for structural optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 24, 359–373
Svanberg, K. 1998: The method of moving asymptotes – modelling aspects and solutions schemes. In: Bendsøe, M.P; and Pedersen, P. (eds.) Adv. Topics in Struct. Optim. DCAMM Report No. S 81, Techn. Univ. Denmark
Ueda, Y.; Fujikubo, M. 1992: Plastic node method considering strain-hardening effects. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 94, 317–337
Yamazaki, K.; Han, J. 1998: Maximization of the crushing energy absorption of tubes. Struct. Optim. 16, 37–46
Yang, R.; Akkerman, A.; Anderson, D.F.; Faruque, O.M.; Lei, G. 2000: Robustness optimization for vehicular crash simulations. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2, 8–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedersen, C. Topology optimization design of crushed 2D-frames for desired energy absorption history. Struct Multidisc Optim 25, 368–382 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-003-0282-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-003-0282-y