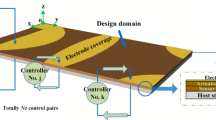
Abstract
This paper investigates topology optimization of the surface electrode coverage on piezoelectric sensor/actuator layers attached to a curved shell structure subjected to stationary random force excitation, with the aim to minimize the random vibration response under active control. In the optimization model, the power spectral density (PSD) of displacement response at the specified point is considered as the objective function. The pseudo-densities describing the surface electrode distribution are assigned as the design variables, and an artificial active damping model with penalization is employed to suppress intermediate density values. The voltage across each actuator is determined by velocity feedback control law. Pseudo excitation method (PEM) is introduced to analyze random vibration response of a piezoelectric curved shell structure with active control. In this context, the adjoint variable method for the sensitivity analysis of displacement PSD with respect to topological design variables is derived. Numerical examples fully demonstrate the validity of the proposed approach.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194(1):363–393
Beckert W, Kreher WS (2003) Modelling piezoelectric modules with interdigitated electrode structures. Comput Mater Sci 26:36–45
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Chacón J, Bellido J, Donoso A (2014) Integration of topology optimized designs into CAD/CAM via an IGES translator. Struct Multidiscip Optim 50(6):1115–1125
Chee CYK, Tong LY, Steven GP (1998) A review on the modelling of piezoelectric sensors and actuators incorporated in intelligent structures. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 9(1):3–19
Deaton JD, Grandhi RV (2014) A survey of structural and multidisciplinary continuum topology optimization: post 2000. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49(1):1–38
Donoso A, Bellido J (2009a) Systematic design of distributed piezoelectric modal sensors/actuators for rectangular plates by optimizing the polarization profile. Struct Multidiscip Optim 38(4):347
Donoso A, Bellido JC (2009b) Tailoring distributed modal sensors for in-plane modal filtering. Smart Mater Struct 18(3):037002
Gonçalves JF, De Leon DM, Perondi EA (2017) Topology optimization of embedded piezoelectric actuators considering control spillover effects. J Sound Vib 388:20–41
Hu J, Zhang X, Kang Z (2018) Layout design of piezoelectric patches in structural linear quadratic regulator optimal control using topology optimization. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 29(10):2277–2294
Huang X, Xie YM (2010) Evolutionary topology optimization of continuum structures: methods and applications. Wiley, New York
Jang Y, Hartarto Tambunan I, Tak H et al (2013) Non-contact printing of high aspect ratio Ag electrodes for polycrystalline silicone solar cell with electrohydrodynamic jet printing. Appl Phys Lett 102(12):123901
Knight RR, Mo C, Clark WW (2011) MEMS interdigitated electrode pattern optimization for a unimorph piezoelectric beam. J Electroceram 26(1-4):14–22
Lin J (1992) A fast CQC algorithm of PSD matrices for random seismic responses. Comput Struct 44(3):683–687
Lin J, Zhang W, Li J (1994) Structural responses to arbitrarily coherent stationary random excitations. Comput Struct 50(5):629–633
Lin J, Zhao Y, Zhang Y (2001) Accurate and highly efficient algorithms for structural stationary/non-stationary random responses. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191(1):103–111
Lin ZQ, Gea HC, Liu ST (2011) Design of piezoelectric energy harvesting devices subjected to broadband random vibrations by applying topology optimization. Acta Mech Sinica 27(5):730–737
Maddisetty H, Frecker M (2002) Dynamic Topology optimization of compliant mechanisms and piezoceramic actuators. J Mech Des 126(6):975–983
Molter A, Fonseca JSO, dos Santos Fernandez L (2016) Simultaneous topology optimization of structure and piezoelectric actuators distribution. Appl Math Model 40(9-10):5576–5588
Nanthakumar S, Lahmer T, Zhuang X et al (2016) Topology optimization of piezoelectric nanostructures. J Mech Phys Solids 94:316–335
Nguyen MD, Nazeer H, Dekkers M et al (2013) Optimized electrode coverage of membrane actuators based on epitaxial PZT thin films. Smart Mater Struct 22(8):085013
Peng FJ, Ng A, Hu YR (2005) Actuator placement optimization and adaptive vibration control of plate smart structures. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 16(3):263–271
Pereira da Silva L, Larbi W, Deü J-F (2015) Topology optimization of shunted piezoelectric elements for structural vibration reduction. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 26(10):1219–1235
Rupp CJ, Evgrafov A, Maute K et al (2009) Design of piezoelectric energy harvesting systems: a topology optimization approach based on multilayer plates and shells. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 20(16):1923–1939
Ryou J, Park K, Kim S (1998) Electrode pattern design of piezoelectric sensors and actuators using genetic algorithms. AIAA J 36(2):227–233
Silva ECN (2003) Topology optimization applied to the design of linear piezoelectric motors. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 14(14):309–322
Svanberg K (2002) A class of globally convergent optimization methods based on conservative convex separable approximations. SIAM J Optim 12(2):555–573
Takezawa A, Kitamura M, Vatanabe SL et al (2014a) Design methodology of piezoelectric energy-harvesting skin using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49(2):281–297
Takezawa A, Makihara K, Kogiso N et al (2014b) Layout optimization methodology of piezoelectric transducers in energy-recycling semi-active vibration control systems. J Sound Vib 333(2):327–344
Wang SY, Tai K, Quek ST (2006) Topology optimization of piezoelectric sensors/actuators for torsional vibration control of composite plates. Smart Mater Struct 15(15):253–269
Wang Y, Luo Z, Zhang X et al (2014) Topological design of compliant smart structures with embedded movable actuators. Smart Mater Struct 23(4):045024
Wein F, Kaltenbacher M, Leugering G et al (2009) Topology optimization of a piezoelectric-mechanical actuator with single- and multiple-frequency excitation. Int J Appl Electromagn Mech 30(3):201–221
Xie YM, Steven GP (1993) A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Comput Struct 49(5):885–896
Xu R, Lei A, Dahl-Petersen C et al (2012) Screen printed PZT/PZT thick film bimorph MEMS cantilever device for vibration energy harvesting. Sensors Actuators A Phys 188:383–388
Xu B, Ding H, Xie YM (2017) Optimal design of material microstructure for maximizing damping dissipation velocity of piezoelectric composite beam. Int J Mech Sci 128:527–540
Yang YW, Jin ZL, Soh CK (2006) Integrated optimization of control system for smart cylindrical shells using modified GA. J Aerosp Eng 19(2):68–79
Yang K, Zhu J, Wu M et al (2018) Integrated optimization of actuators and structural topology of piezoelectric composite structures for static shape control. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 334:440–469
Yoon GH, Choi H, Hur S (2018) Multiphysics topology optimization for piezoelectric acoustic focuser. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 332:600–623
Zhai JJ, Zhao GZ, Shang LY (2016) Integrated design optimization of structure and vibration control with piezoelectric curved shell actuators. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 27(19):2672–2691
Zhai J, Zhao G, Shang L (2017) Integrated design optimization of structural size and control system of piezoelectric curved shells with respect to sound radiation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 56(6):1287–1304
Zhang XP, Kang Z (2014a) Dynamic topology optimization of piezoelectric structures with active control for reducing transient response. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 281(1):200–219
Zhang XP, Kang Z (2014b) Topology optimization of piezoelectric layers in plates with active vibration control. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 25(6):697–712
Zhang XP, Kang Z, Li M (2014) Topology optimization of electrode coverage of piezoelectric thin-walled structures with CGVF control for minimizing sound radiation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 50(5):799–814
Zhang X, Takezawa A, Kang Z (2018) Topology optimization of piezoelectric smart structures for minimum energy consumption under active control. Struct Multidiscip Optim 58(1):185–199
Zheng B, Chang CJ, Gea HC (2009) Topology optimization of energy harvesting devices using piezoelectric materials. Struct Multidiscip Optim 38(1):17–23
Zorić ND, Simonović AM, Mitrović ZS et al (2013) Optimal vibration control of smart composite beams with optimal size and location of piezoelectric sensing and actuation. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 24(4):499–526
Funding
The project of research presented in this paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1508209, 11072049), Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program and Dalian Science Technology Innovation Fund (2018J11CY003), Talents Introduction Research Fund of Shenyang Aerospace University (19YB10, 19YB11). The authors would like to acknowledge these funds support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: YoonYoung Kim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral withregard to jurisdictional claims in published mapsand institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, J., Shang, L. & Zhao, G. Topology optimization of piezoelectric curved shell structures with active control for reducing random vibration. Struct Multidisc Optim 61, 1439–1452 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02423-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02423-3