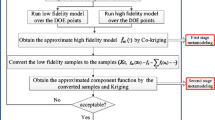
Abstract
Metamodel-based high-dimensional model representation (HDMR) has recently been developed as a promising tool for approximating high-dimensional and computationally expensive problems in engineering design and optimization. However, current stand-alone Cut-HDMRs usually come across the problem of prediction uncertainty while combining an ensemble of metamodels with Cut-HDMR results in an implicit and inefficient process in response approximation. To this end, a novel stand-alone Cut-HDMR is proposed in this article by taking advantage of the explicit polynomial chaos expansion (PCE) and hierarchical Cut-HDMR (named PCE-HDMR). An intelligent dividing rectangles (DIRECT) sampling method is adopted to adaptively refine the model. The novelty of the PCE-HDMR is that the proposed multi-hierarchical algorithm structure by integrating PCE with Cut-HDMR can efficiently and robustly provide simple and explicit approximations for a wide class of high-dimensional problems. An analytical function is first used to illustrate the modeling principles and procedures of the algorithm, and a comprehensive comparison between the proposed PCE-HDMR and other well-established Cut-HDMRs is then made on fourteen representative mathematical functions and five engineering examples with a wide scope of dimensionalities. The results show that the proposed PCE-HDMR has much superior accuracy and robustness in terms of both global and local error metrics while requiring fewer number of samples, and its superiority becomes more significant for polynomial-like functions, higher-dimensional problems, and relatively larger PCE degrees.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baptista R, Stolbunov V, Nair PB (2019) Some greedy algorithms for sparse polynomial chaos expansions. J Comput Phys 387:303–325
Blatman G, Sudret B (2011) Adaptive sparse polynomial chaos expansion based on least angle regression. J Comput Phys 230:2345–2367
Cai XW, Qiu HB, Gao L, Yang P, Shao XY (2016) An enhanced RBF-HDMR integrated with an adaptive sampling method for approximating high dimensional problems in engineering design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53(6):1209–1229
Chen SS, Donoho DL, Saunders MA (1998) Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J Sci Comput 20(1):33–61
Chen LM, Li EY, Wang H (2016) Time-based reflow soldering optimization by using adaptive Kriging-HDMR method. Soldering Surf Mount Technol 28(2):101–113
Chen LM, Wang H, Ye F, Hu W (2019) Comparative study of HDMRs and other popular metamodeling techniques for high dimensional problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 59(1):21–42
Cheng GH, Younis A, Hajikolaei KH, Wang GG (2015) Trust region based mode pursuing sampling method for global optimization of high dimensional design problems. J Mech Des 137(2):021407
Cheng K, Lu ZZ, Ling CY, Zhou ST (2020) Surrogate-assisted global sensitivity analysis: an overview. Struct Multidiscip Optim 61(3):1187–1213
Chowdhury R, Rao BN (2009) Hybrid high dimensional model representation for reliability analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198(5–8):753–765
Clarke SM, Griebsch JH, Simpson TW (2005) Analysis of support vector regression for approximation of complex engineering analyses. J Mech Des 127(6):1077–1087
Donoho DL (2006) Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52(4):1289–1306
Eldar YC, Kutyniok G (2012) Compressed sensing: theory and applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fang HB, Horstemeyer MF (2006) Global response approximation with radial basis functions. Eng Optim 38(4):407–424
Ghanem RG, Spanos PD (1991) Stochastic finite elements: a spectral approach. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Gibbons JD, Chakraborti S (2014) Nonparametric statistical inference: revised and expanded. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Goel T, Haftka RT, Wei S, Queipo NV (2007) Ensemble of surrogates. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(3):199–216
Gorissen D, Crombecq K, Hendrickx W, Dhaene T (2007) Adaptive distributed metamodeling. High Performance Computing for Computational Science (VECPAR 2006). Lect Notes Comput Sci 4395:579–588
Hajikolaei KH, Wang GG (2014) High dimensional model representation with principal component analysis. J Mech Des 136(1):011003
Huang ZY, Qiu HB, Zhao M, Cai XW, Gao L (2015) An adaptive SVR-HDMR model for approximating high dimensional problems. Eng Comput 32(3):643–667
Hussain MF, Barton RR, Joshi SB (2002) Metamodeling: radial basis functions, versus polynomials. Eur J Oper Res 138(1):142–154
Ishigami T, Homma T (1990) An importance quantification technique in uncertainty analysis for computer models. Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Uncertainty Modeling and Analysis (ISUMA’90), University of Maryland, 398–403. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISUMA.1990.151285
Jin R, Chen W, Simpson TW (2001) Comparative studies of metamodelling techniques under multiple modelling criteria. Struct Multidiscip Optim 23(1):1–13
Johnson ME, Moore LM, Ylvisaker D (1990) Minimax and maximum distance designs. J Stat Plan Infer 26(2):131–148
Jones DR, Perttunen CD, Stuckman BE (1993) Lipschitzian optimization without the Lipschitz constant. J Optim Theory Appl 79(1):157–181
Kenett R, Zacks S (1998) Modern industrial statistics: design and control of quality and reliability. Duxbury Press, Belmont
Lee SH, Chen W (2009) A comparative study of uncertainty propagation methods for black-box-type problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 37(3):239–253
Li EY, Wang H (2016) An alternative adaptive differential evolutionary algorithm assisted by expected improvement criterion and cut-HDMR expansion and its application in time-based sheet forming design. Adv Eng Softw 97:96–107
Li GY, Rosenthal C, Rabitz H (2001) High dimensional model representations. J Phys Chem A 105(33):7765–7777
Li GY, Hu JS, Wang SW, Georgopoulos PG, Schoendorf J, Rabitz H (2006) Radom sampling-high dimensional model representation (RS-HDMR) and orthogonality of its different order component functions. J Phys Chem A 110(7):2474–2485
Li YF, Ng SH, Xie M, Goh TN (2010) A systematic comparison of metamodeling techniques for simulation optimization in decision support systems. Appl Soft Comput 10(4):1257–1273
Li EY, Ye F, Wang H (2017) Alternative Kriging-HDMR optimization method with expected improvement sampling strategy. Eng Comput 34(6):1807–1828
Liu HT, Hervas JR, Ong YS, Cai JF, Wang Y (2018) An adaptive RBF-HDMR modeling approach under limited computational budget. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57(3):1233–1250
Martin JD, Simpson TW (2005) Use of kriging models to approximate deterministic computer models. AIAA J 43(4):853–863
Mukhopadhyay T, Dey TK, Chowdhury R, Chakrabarti A, Adhikari S (2015) Optimum design of FRP bridge deck: an efficient RS-HDMR based approach. Struct Multidiscip Optim 52(3):459–477
Ostergard T, Jensen RL, Maagaard SE (2018) A comparison of six metamodeling techniques applied to building performance simulations. Appl Energy 211:89–103
Parnianifard A, Azfanizam AS, Ariffin MKA, Ismail MIS (2020) Comparative study of metamodeling and sampling design for expensive and semi-expensive simulation models under uncertainty. Simulation 96(1):89–110
Rabitz H, Alis OF (1999) General foundations of high-dimensional model representations. J Math Chem 25(2–3):197–233
Rabitz H, Alis OF, Shorter J, Shim K (1999) Efficient input-output model representations. Comput Phys Commun 117(1–2):11–20
Shan SQ, Wang GG (2010a) Metamodeling for high dimensional simulation-based design problems. J Mech Des 132(5):051009
Shan SQ, Wang GG (2010b) Survey of modeling and optimization strategies to solve high-dimensional design problems with computationally-expensive black-box functions. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(2):219–241
Shan SQ, Wang GG (2011) Turning black-box functions into white functions. J Mech Des 133(3):031003
Sobol IM (1993) Sensitivity estimates for nonlinear mathematical models. Math Model Comput Exp 1(4):407–414
Sudret B (2008) Global sensitivity analysis using polynomial chaos expansions. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 93(7):964–979
Szepietowska K, Magnain B, Lubowiecka I, Florentin E (2018) Sensitivity analysis based on non-intrusive regression-based polynomial chaos expansion for surgical mesh modelling. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57(3):1391–1409
Tang L, Wang H, Li GY (2013) Advanced high strength steel springback optimization by projection-based heuristic global search algorithm. Mater Des 43:426–437
Thomas PS, Somers MF, Hoekstra AW, Kroes GJ (2012) Chebyshev high-dimensional model representation (Chebyshev-HDMR) potentials: application to reactive scattering of H2 from Pt(111) and Cu(111) surfaces. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14(24):8628–8643
Tropp JA, Gilbert AC (2007) Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 53(12):4655–4666
Tunga MA (2011) An approximation method to model multivariate interpolation problems: indexing HDMR. Math Comput Model 53(9–10):1970–1982
Tunga MA, Demiralp M (2006) Hybrid high dimensional model representation (HHDMR) on the partitioned data. J Comput Appl Math 185(1):107–132
Van Gelder L, Das P, Janssen H, Roels S (2014) Comparative study of metamodelling techniques in building energy simulation: guidelines for practitioners. Simul Model Pract Theory 49:245–257
Wang H, Tang L, Li GY (2011) Adaptive MLS-HDMR metamodeling techniques for high dimensional problems. Expert Syst Appl 38(11):14117–14126
Wang H, Chen LM, Ye F, Chen L (2017) Global sensitivity analysis for fiber reinforced composite fiber path based on D-MORPH-HDMR algorithm. Struct Multidiscip Optim 56(3):697–712
Xie SJ, Pan BS, Du XP (2017) High dimensional model representation for hybrid reliability analysis with dependent interval variables constrained within ellipsoids. Struct Multidiscip Optim 56(6):1493–1505
Xiu D, Karniadakis GE (2002) The Wiener-Askey polynomial chaos for stochastic differential equations. SIAM J Sci Comput 24(2):619–644
Xu SL, Liu HT, Wang XF, Jiang XM (2014) A robust error-pursuing sequential sampling approach for global metamodeling based on Voronoi diagram and cross validation. J Mech Des 136(7):071009
Yang QW, Xue DY (2015) Comparative study on influencing factors in adaptive metamodeling. Eng Comput 31(3):561–577
Zeng P (2009) Fundamentals of finite element analysis. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Zhang N, Wang P, Dong HC (2019) Research on high-dimensional model representation with various metamodels. Eng Optim 51(8):1336–1351
Zhang J, Yue XX, Qiu JJ, Zhang MY, Wang XM (2021a) A unified ensemble of surrogates with global and local measures for global metamodelling. Eng Optim 53(3):474–495
Zhang J, Yue XX, Qiu JJ, Zhuo LJ, Zhu JG (2021b) Sparse polynomial chaos expansion based on Bregman-iterative greedy coordinate descent for global sensitivity analysis. Mech Syst Signal Process (in press)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11872190, 51805221), Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (Grant No. 2017-KTHY-010), and Research Start-up Foundation for Jinshan Distinguished Professor at Jiangsu University (Grant No. 4111480003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Replication of results
The original codes for the illustrative example in Section 3.4 and fourteen benchmark functions and five engineering examples in Section 4 are available in the supplementary materials, i.e., IllustrativeExample.m, F1.m ~ F15.m, and E1.m ~ E5.m.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Erdem Acar
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(TAR 22516 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, X., Zhang, J., Gong, W. et al. An adaptive PCE-HDMR metamodeling approach for high-dimensional problems. Struct Multidisc Optim 64, 141–162 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-02866-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-02866-7