Abstract
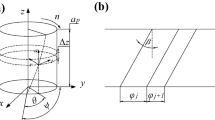
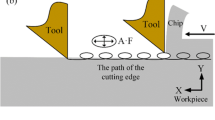
The vibration reduction mechanism of variable pitch end mills was analyzed by the theory of energy balance of the frequency spectrum line. The variable pitch mill can reduce the forced vibration in the cutting process due to the uniform distribution of frequency spectrum line energy and lower peak energy of the cutting force. Aimed at the vibration phenomenon which restricted the efficiency in cutting aero material titanium alloy, high-speed cutting experiments of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V were set with variable and equal pitch mills under dry and down-milling environment. The influences of cutting speeds on cutting forces and tool vibration were analyzed at time domain and frequency domain, respectively, by which the vibration reduction mechanism of variable pitch mill was verified. Due to the misalignment of end mill no. 3, high-level cutting forces and tool vibration were caused by the unequal cutting load on each edge. It is found that severe tool vibration was produced under the cutting speed of 150 m/min because of low-frequency resonance in the cutting process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ezugwu EO, Wang ZM (1997) Titanium alloys and their machinability—a review. J Mater Process Technol 68:262–274
Chen W, Yuan Y (2010) Research development of cutting technology for titanium alloy. Aeronautical Manufactring Technology 15:26–30 (in Chinese)
Sun S, Brandt M, Dargusch MS (2009) Characteristics of cutting forces and chip formation in machining of titanium alloys. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 49:561–568
Basturk S, Senbabaoglu F (2010) Titanium machining with new plasma boronized cutting tools. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 59:101–104
Sun J, Guo YB (2009) Material flow stress and failure in multiscale machining titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 41:651–659
Chen G, Ren CZ, Yang XY, Jin XM, Guo T (2011) Finite element simulation of high-speed machining of titanium alloy (Ti–6Al–4V) based on ductile failure model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 56:1027–1038
Huang PL, Li JF, Sun J, Song LY (2012) Milling force vibration analysis in high-speed-milling titanium alloy using variable pitch angle mill. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 58(1):153–160
Slavicek J (1965) The effect of irregular tooth pitch on stability of milling. Proceedings of the 6th MTDR Conference. Manchester
Shirase (1996) Cutting force and dimensional surface error generation in peripheral milling with variable pitch helical end mills. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 36(5):567–584
Altmtas Y, Engin S, Budak E (1999) Analytical stability prediction and design of variable pitch cutters. J Manuf Sci Eng 121:173–178
Budak E (2003) An analytical design method for milling cutters with nonconstant pitch to increase stability, part I: theory. J Manuf Sci Eng 125:29–34
Budak E (2003) An analytical design method for milling cutters with nonconstant pitch to increase stability, part 2: application. J Manuf Sci Eng 125(35):38
Olgac N, Sipahi R (2007) Dynamics and stability of variable-pitch milling. J Vib Control 13(7):1031–1043
Shirase K, Altintas Y (1996) Cutting force and dimensional surface error generation in peripheral milling with variable pitch helical end mills. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 36(5):567–584
Ning Y, Rahman M, Wong YS (2000) Monitoring of chatter in high speed end milling using audio signals method. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International MATADOR Conference, Manchester, England, pp 421–426
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, P., Li, J., Sun, J. et al. Study on vibration reduction mechanism of variable pitch end mill and cutting performance in milling titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67, 1385–1391 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4575-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4575-4