Abstract
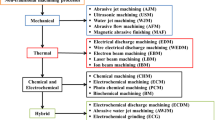
Thorough literature review of various modern machining processes is presented in this paper. The main focus is kept on the optimization aspects of various parameters of the modern machining processes and hence only such research works are included in this work in which the use of advanced optimization techniques were involved. The review period considered is from the year 2006 to 2012. Various modern machining processes considered in this work are electric discharge machining, abrasive jet machining, ultrasonic machining, electrochemical machining, laser beam machining, micro-machining, nano-finishing and various hybrid and modified versions of these processes. The review work on such a large scale was not attempted earlier by considering many processes at a time, and hence, this review work may become the ready information at one place and it may be very useful to the subsequent researchers to decide their direction of research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar S, Singh R, Singh TP, Sethi BL (2009) Surface modification by electrical discharge machining: a review. J Mater Process Technol 209:3675–3687
Parikh PJ, Lam SS (2009) Parameter estimation for abrasive water jet machining process using neural networks. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40:497–502
Singh R, Khamba JS (2006) Ultrasonic machining of titanium and its alloys: a review. J Mater Process Technol 173:125–135
Burger M, Koll L, Werner EA, Platz A (2012) Electrochemical machining characteristics and resulting surface quality of the nickel-base single-crystalline material LEK94. J Manuf Process 14:62–70
Dubey AK (2008) A hybrid approach for multi-performance optimization of the electro-chemical honing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-008-1422-8
Dubey AK (2009) Multi-response optimization of electro-chemical honing using utility-based Taguchi approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 41:749–759
Dubey AK (2012) Multi-performance modeling and optimization control strategies for electro-chemical honing: a critical evaluation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-008-1477-6
Dubey AK, Shan HS, Jain NK (2008) Analysis of surface roughness and out-of-roundness in the electro-chemical honing of internal cylinders. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 38:491–500
Lee ES, Shin TH (2011) An evaluation of the machinability of nitinol shape memory alloy by electrochemical polishing. J Mech Sci Technol 25(4):963–969
Lee ES, Won JK, Shin TH, Kim SH (2012) Investigation of machining characteristics for electrochemical micro-deburring of the AZ31 lightweight magnesium alloy. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13(3):339–345
Hung JC, Chang CH, Chiu KC, Lee SJ (2012) Simulation-based fabrication of micro-helical grooves in a hydrodynamic thrust bearing by using ECMM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4062-y
Munda J, Bhattacharyya B (2008) Investigation into electrochemical micromachining (EMM) through response surface methodology based approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 35:821–832
Munda J, Malapati M, Bhattacharyya B (2010) Investigation into the influence of electrochemical micromachining (EMM) parameters on radial overcut through RSM-based approach. Int J Manuf Technol Manage 21:54–66
Malapati M, Bhattacharyya B (2011) Investigation into electrochemical micromachining process during micro-channel generation. Mater Manuf Process 26:1019–1027
Dubey AK, Yadava V (2008) Laser beam machining—a review. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 48:609–628
Almeida IA, Rossi WD, Lima MSF, Berretta JR, Nogueira GEC, Wetter NU, Vieira ND (2006) Optimization of titanium cutting by factorial analysis of the pulsed Nd:YAG laser parameters. J Mater Process Technol 179:105–110
Li CH, Tsai MJ, Yang CD (2007) Study of optimal laser parameters for cutting QFN packages by Taguchi’s matrix method. Opt Laser Technol 39:786–795
Dubey A, Yadava V (2008) Multi-objective optimisation of laser beam cutting process. Opt Laser Technol 40:562–570
Dubey A, Yadava V (2008) Multi-objective optimization of Nd:YAG laser cutting of nickel-based superalloy sheet using orthogonal array with principal component analysis. Opt Lasers Eng 46:124–132
Dubey A, Yadava V (2008) Optimization of kerf quality during pulsed laser cutting of aluminium alloy sheet. J Mater Process Technol 204:412–418
Tsai MJ, Li CH, Chen CC (2008) Optimal laser-cutting parameters for QFN packages by utilizing artificial neural networks and genetic algorithm. J Mater Process Technol 208:270–283
Caydas U, Hascalik A (2008) Use of the grey relational analysis to determine optimum laser cutting parameters with multi-performance characteristics. Opt Laser Technol 40:987–994
Rao R, Yadava V (2009) Multi-objective optimization of Nd:YAG laser cutting of thin superalloy sheet using grey relational analysis with entropy measurement. Opt Laser Technol 41:922–930
Li CH, Tsai MJ (2009) Multi-objective optimization of laser cutting for flash memory modules with special shapes using grey relational analysis. Opt Laser Technol 41:634–642
Tsai MJ, Li CH (2009) The use of grey relational analysis to determine laser cutting parameters for QFN packages with multiple performance characteristics. Opt Laser Technol 41:914–921
Sharma A, Yadava V, Rao R (2010) Optimization of kerf quality characteristics during Nd:YAG laser cutting of nickel based superalloy sheet for straight and curved cut profiles. Opt Lasers Eng 48:915–925
Syn CZ, Mokhtar M, Feng CJ, Manurung YHP (2011) Approach to prediction of laser cutting quality by employing fuzzy expert system. Expert Syst Appl 38:7558–7568
Adelmann B, Hellmann R (2011) Fast laser cutting optimization algorithm. Phys Procedia 12:591–598
Chen MF, Ho YS, Hsiao WT, Wu TH, Tseng SF, Huang KC (2011) Optimized laser cutting on light guide plates using grey relational analysis. Opt Lasers Eng 49:222–228
Sharma A, Yadava V (2012) Modelling and optimization of cut quality during pulsed Nd:YAG laser cutting of thin Al-alloy sheet for straight profile. Opt Laser Technol 44:159–168
Sharma A, Yadava V (2012) Modelling and optimization of cut quality during pulsed Nd:YAG laser cutting of thin Al-alloy sheet for curved profile. Opt Lasers Eng. doi:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2012.07.012
Pandey A, Dubey A (2012) Simultaneous optimization of multiple quality characteristics in laser cutting of titanium alloy sheet. Opt Laser Technol 44:1858–1865
Pandey A, Dubey A (2012) Taguchi based fuzzy logic optimization of multiple quality characteristics in laser cutting of Duralumin sheet. Opt Lasers Eng 50:328–335
Pandey A, Dubey A (2012) Multiple quality optimization in laser cutting of difficult-to-laser-cut material using grey–fuzzy methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4181-5
Sen M, Shan HS (2006) Optimal selection of machining conditions in the electrojet drilling process using hybrid NN-DF-GA approach. Mater Manuf Process 21:349–356
Yoon HS, Wu R, Lee TM, Ahn SH (2011) Geometric optimization of micro drills using taguchi methods and response surface methodology. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 12(5):871–875
Guu YH, Deng CS, Hou MT, Hsu CH, Tseng KS (2012) Optimization of machining parameters for stress concentration in microdrilling of titanium alloy. Mater Manuf Process 27:207–213
Chen W, Dai P, Chen Y, Chen D, Jiang Z (2012) Parametric optimization of micro drilling using machine vision technique combined with Taguchi method. Adv Mater Res 468(471):2487–2490
Chern GL, Chang YC (2006) Using two-dimensional vibration cutting for micro-milling. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 46:659–666
Cardoso P, Davim JP (2010) Optimization of surface roughness in micromilling. Mater Manuf Process 25:1115–1119
Chiu NH, Weigh GT (2011) Optimization of micro-milling process with genetic algorithm. Adv Mater Res 383–390:7111–7116
Periyanan PR, Natarajan U, Yang SH (2011) A study on the machining parameters optimization of micro-end milling process. Int J Eng Sci Technol 3(6):237–246
Mian AJ, Driver N, Mativenga PT (2011) Identification of factors that dominate size effect in micro-machining. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 51:383–394
Natarajan U, Periyanan PR, Yang SH (2011) Multiple-response optimization for micro-endmilling process using response surface methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 56:177–185
Saedon JB, Soo SL, Aspinwall DK, Barnacle A, Saad NH (2012) Prediction and optimization of tool life in micromilling AISI D2 (∼62 HRC) hardened steel. Procedia Eng 41:1674–1683
Thepsonthi T, Ozel T (2012) Multi-objective process optimization for micro-end milling of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-3980-z
Jain VK (2008) Abrasive-based nano-finishing techniques: an overview. Mach Sci Technol 12:257–294
Jain VK (2009) Magnetic field assisted abrasive based micro-/nano-finishing. J Mater Process Technol 209:6022–6038
Mali HS, Manna A (2009) Current status and application of abrasive flow finishing processes: a review. J Eng Manuf 223(7):809–820
Tavoli MA, Zadeh NN, Khakhali A, Mehran M (2006) Multi-objective optimization of abrasive flow Machining processes using polynomial neural networks and genetic algorithms. Mach Sci Technol 10:491–510
Walia RS, Shan HS, Kumar P (2006) Parametric optimization of centrifugal force-assisted abrasive flow machining (CFAAFM) by the Taguchi method. Mater Manuf Process 21:375–382
Walia RS, Shan HS, Kumar P (2006) Multi-response optimization of CFAAFM process through taguchi method and utility concept. Mater Manuf Process 21:907–914
Singh S, Shan HS, Kumar P (2006) Quality optimization of surface finishing by magnetic field assisted abrasive flow machining through Taguchi technique. Int J Comput Appl Technol 27(1):31–37
Jain NK, Jain VK, Jha S (2007) Parametric optimization of advanced fine-finishing processes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34:1191–1213
Reddy MK, Sharma AK, Kumar P (2008) Some aspects of centrifugal force assisted abrasive flow machining of 2014 Al alloy. J Eng Manuf 222(7):773–783
Sankar MR, Mondal S, Ramkumar J, Jain VK (2009) Experimental investigations and modeling of drill bit-guided abrasive flow finishing (DBG-AFF) process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 42:678–688
Pawar PJ, Rao RV, Davim JP (2010) Optimization of abrasive flow machining process parameters using particle swarm optimization and simulated annealing algorithms. Artif Intel Manuf Res 51–64
Mali HS, Manna A (2010) Optimum selection of abrasive flow machining conditions during fine finishing of Al/15 wt% SiC-MMC using Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50(9–12):1013–1024
Taweel TAE (2008) Modelling and analysis of hybrid electrochemical turning magnetic abrasive finishing of 6061 Al/Al2O3 composite. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37:705–714
Yang LD, Lin CT, Chow HM (2009) Optimization in MAF operations using Taguchi parameter design for AISI304 stainless steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 42:595–605
Mulik RS, Pandey PM (2011) Experimental investigations and optimization of ultrasonic assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process. J Eng Manuf 225(8):1347–1362
Jung B, Jang KI, Min BK, Seok J (2009) Parameter optimization for finishing hard materials with magnetorheological fluid using the penalized multi-response Taguchi method. J Eng Manuf 223(8):955–968
Das M, Jain VK, Ghoshdastidar PS (2010) Nano-finishing of stainless-steel tubes using rotational magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing process. Mach Sci Technol 14:365–389
Das M, Jain VK, Ghoshdastidar PS (2011) The out-of-roundness of the internal surfaces of stainless steel tubes finished by the rotational–magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing process. Mater Manuf Process 26:1073–1084
Das M, Jain VK, Ghoshdastidar PS (2012) Nanofinishing of flat workpieces using rotational–magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (R-MRAFF) process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62:405–420
Babu AP, Sundaram S, Shanawaz AM, Sankar SP (2011) Optimization of ELID grinding process of Al/SiC composite through neuro-fuzzy network. Int J Eng Sci Technol 3(5):4043–4050
Babu AP, Sundaram S, Shanawaz AM, Sivaprakash M (2011) Grinding Process on Al-SiC composite material and optimization of surface roughness by ANFIS. Int J Eng Technol 3(4):425–430
Babu AP, Sundaram S, Sivaprakash M, Shanawaz AM (2012) Optimizing the process parameters of ELID grinding using grey relation analysis. Adv Prod Eng Manage 7(2):113–122
Chiang KT, Chang FP (2006) Optimization of the WEDM process of particle-reinforced material with multiple performance characteristics using grey relational analysis. J Mater Process Technol 180:96–101
Keskin Y, Halkaci HS, Kizil M (2006) An experimental study for determination of the effects of machining parameters on surface roughness in electrical discharge machining (EDM). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28:1118–1121
Chang TC, Tsai FC, Ke JH (2006) Data mining and Taguchi method combination applied to the selection of discharge factors and the best interactive factor combination under multiple quality properties. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 31:164–174
Manna A, Bhattacharyya B (2006) Taguchi and Gauss elimination method: a dual response approach for parametric optimization of CNC wire cut EDM of PRAlSiCMMC. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28:67–75
Lin YC, Cheng CH, Su BL, Hwang LR (2006) Machining characteristics and optimization of machining parameters of SKH 57 high-speed steel using electrical-discharge machining based on Taguchi method. Mater Manuf Process 21:922–929
Kansal HK, Singh S, Kumar P (2007) Effect of silicon powder mixed EDM on machining rate of AISI D2 die steel. J Manuf Process 9:13–22
Dhar S, Purohit R, Saini N, Sharma A, Kumar GH (2007) Mathematical modeling of electric discharge machining of cast Al–4Cu–6Si alloy–10 wt.% SiCP composites. J Mater Process Technol 194:24–29
Tzeng YF, Chen FC (2007) Multi-objective optimisation of high-speed electrical discharge machining process using a Taguchi fuzzy-based approach. Mater Des 28:1159–1168
Mahapatra SS, Patnaik A (2007) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process parameters using Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34:911–925
Yan MT, Fang CC (2008) Application of genetic algorithm-based fuzzy logic control in wire transport system of wire-EDM machine. J Mater Process Technol 205:128–137
Tzeng YF (2008) Development of a flexible high-speed EDM technology with geometrical transform optimization. J Mater Process Technol 203:355–364
Salman O, Kayacan MC (2008) Evolutionary programming method for modeling the EDM parameters for roughness. J Mater Process Technol 200:347–355
Sundaram MM, Pavalarajan GB, Rajurkar KP (2008) A study on process parameters of ultrasonic assisted micro EDM based on Taguchi method. J Mater Eng Perform 17(2):210–215
Markopoulos AP, Manolakos DE, Vaxevanidis NM (2008) Artificial neural network models for the prediction of surface roughness in electrical discharge machining. J Intell Manuf 19:283–292
Chiang KT (2008) Modeling and analysis of the effects of machining parameters on the performance characteristics in the EDM process of Al2O3 + TiC mixed ceramic. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37:523–533
Assarzadeh S, Ghoreishi M (2008) Neural-network-based modeling and optimization of the electro-discharge machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39:488–500
Rao RV, Pawar PJ (2009) Modelling and optimization of process parameters of wire electrical discharge machining. J Eng Manuf 223(11):1431–1440
Kanagarajan D, Karthikeyan R, Palanikumar K, Davim JP (2008) Optimization of electrical discharge machining characteristics of WC/Co composites using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36:1124–1132
Saha P, Singha A, Pal SK, Saha P (2008) Soft computing models based prediction of cutting speed and surface roughness in wire electro-discharge machining of tungsten carbide cobalt composite. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39:74–84
Kung KY, Chiang KT (2008) Modeling and analysis of machinability evaluation in the wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process of aluminium oxide-based ceramic. Mater Manuf Process 23:241–250
Chattopadhyay KD, Verma S, Satsangi PS, Sharma PC (2009) Development of empirical model for different process parameters during rotary electrical discharge machining of copper–steel (EN-8) system. J Mater Process Technol 209:1454–1465
Rao GKM, Rangajanardhaa G, Rao DH, Rao MS (2009) Development of hybrid model and optimization of surface roughness in electric discharge machining using artificial neural networks and genetic algorithm. J Mater Process Technol 209:1512–1520
Saha SK, Choudhury SK (2009) Experimental investigation and empirical modeling of the dry electric discharge machining process. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 49:297–308
Yang SH, Srinivas J, Mohan S, Lee DM, Balaji S (2009) Optimization of electric discharge machining using simulated annealing. J Mater Process Technol 209:4471–4475
Habib SS (2009) Study of the parameters in electrical discharge machining through response surface methodology approach. Appl Math Model 33:4397–4407
Sohani MS, Gaitonde VN, Siddeswarappa B, Deshpande AS (2009) Investigations into the effect of tool shapes with size factor consideration in sink electrical discharge machining (EDM) process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 45:1131–1145
Kung KY, Horng JT, Chiang KT (2009) Material removal rate and electrode wear ratio study on the powder mixed electrical discharge machining of cobalt-bonded tungsten carbide. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40:95–104
Taweel TAE (2009) Multi-response optimization of EDM with Al–Cu–Si–TiC P/M composite electrode. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44:100–113
Patel KM, Pandey PM, Rao PV (2009) Determination of an optimum parametric combination using a surface roughness prediction model for EDM of Al2O3/SiCw/TiC ceramic composite. Mater Manuf Process 24:675–682
Pradhan BB, Bhattacharyya B (2009) Modelling of micro-electrodischarge machining during machining of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V using response surface methodology and artificial neural network algorithm. J Eng Manuf 223(6):683–693
Maji K, Pratihar DK (2010) Forward and reverse mappings of electrical discharge machining process using adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system. Expert Syst Appl 37:8566–8574
Chen HC, Lin JC, Yang YK, Tsai CH (2010) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining for pure tungsten using a neural network integrated simulated annealing approach. Expert Syst Appl 37:7147–7153
Patowari PK, Saha P, Mishra PK (2010) Artificial neural network model in surface modification by EDM using tungsten–copper powder metallurgy sintered electrodes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:627–638
Pradhan MK, Biswas CK (2010) Neuro-fuzzy and neural network-based prediction of various responses in electrical discharge machining of AISI D2 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50:591–610
Patel KM, Pandey PM, Rao PV (2010) Optimisation of process parameters for multi-performance characteristics in EDM of Al2O3 ceramic composite. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47:1137–1147
Kao JY, Tsao CC, Wang SS, Hsu CY (2010) Optimization of the EDM parameters on machining Ti–6Al–4V with multiple quality characteristics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47:395–402
Ponappa K, Aravindan S, Rao PV, Ramkumar J, Gupta M (2010) The effect of process parameters on machining of magnesium nano alumina composites through EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 46:1035–1042
Kumar A, Maheshwari S, Sharma C, Beri N (2010) A study of multiobjective parametric optimization of silicon abrasive mixed electrical discharge machining of tool steel. Mater Manuf Process 25:1041–1047
Somashekhar KP, Ramachandran N, Mathew J (2010) Optimization of material removal rate in micro-EDM using artificial neural network and genetic algorithms. Mater Manuf Process 25:467–475
Chen YF, Lin YJ, Lin YC, Chen SL, Hsu LR (2010) Optimization of electrodischarge machining parameters on ZrO2 ceramic using the Taguchi method. J Eng Manuf 224(2):195–205
Joshi SN, Pande SS (2011) Intelligent process modeling and optimization of die-sinking electric discharge machining. Appl Soft Comput 11:2743–2755
Prabhu S, Vinayagam BK (2011) AFM surface investigation of Inconel 825 with multi wall carbon nano tube in electrical discharge machining process using Taguchi analysis. Archives Civil Mech Eng 11:149–170
Sanchez HT, Estrems M, Faura F (2011) Development of an inversion model for establishing EDM input parameters to satisfy material removal rate, electrode wear ratio and surface roughness. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 57:189–201
Maji K, Pratihar DK (2011) Modeling of electrical discharge machining process using conventional regression analysis and genetic algorithms. J Mater Eng Perform 20:1121–1127
Kondayya D, Krishna AG (2011) An integrated evolutionary approach for modelling and optimization of wire electrical discharge machining. J Eng Manuf 225(4):549–567
Amini H, Yazdi MRS, Dehghan GH (2011) Optimization of process parameters in wire electrical discharge machining of TiB2 nanocomposite ceramic. J Eng Manuf 225(12):2220–2227
Tzeng CJ, Yang YK, Hsieh MH, Jeng MC (2011) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining of pure tungsten using neural network and response surface methodology. J Eng Manuf 225(6):841–852
Rao RV, Kalyankar VD (2012) Parameter optimization of modern machining processes using teaching–learning-based optimization algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2012.06.007
Singh S (2012) Optimization of machining characteristics in electric discharge machining of 6061Al/Al2O3p/20P composites by grey relational analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-3984-8
Ay M, Caydas U, Hascalik A (2012) Optimization of micro-EDM drilling of Inconel 718 superalloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4385-8
Yang RT, Tzeng CJ, Yang YK, Hsieh MH (2012) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining process parameters for cutting tungsten. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60:135–147
Lingadurai K, Nagasivamuni B, Kamatchi MM, Palavesam J (2012) Selection of wire electrical discharge machining process parameters on stainless steel AISI grade-304 using design of experiments approach. J Inst Eng (India): Ser C 93(2):163–170
Azad MS, Puri AB (2012) Simultaneous optimisation of multiple performance characteristics in micro-EDM drilling of titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61:1231–1239
Mahardika M, Prihandana GS, Endo T, Tsujimoto T, Matsumoto N, Arifvianto B, Mitsui K (2012) The parameters evaluation and optimization of polycrystalline diamond micro-electrodischarge machining assisted by electrode tool vibration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60:985–993
Fonda P, Katahira K, Kobayashi Y, Yamazaki K (2012) WEDM condition parameter optimization for PCD microtool geometry fabrication process and quality improvement. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-3977-7
Somashekhar KP, Mathew J, Ramachandran N (2012) A feasibility approach by simulated annealing on optimization of micro-wire electric discharge machining parameters. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61:1209–1213
Lin YC, Tsao CC, Hsu CY, Hung SK, Wen DC (2012) Evaluation of the characteristics of the microelectrical discharge machining process using response surface methodology based on the central composite design. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-011-3745-0
Paul G, Roy S, Sarkar S, Hanumaiah N, Mitra S (2012) Investigations on influence of process variables on crater dimensions in micro-EDM of γ-titanium aluminide alloy in dry and oil dielectric media. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4235-8
Bharti PS, Maheshwari S, Sharma C (2012) Multi-objective optimization of electric-discharge machining process using controlled elitist NSGA-II. J Mech Sci Technol 26(6):1875–1883
Kumar K, Agarwal S (2012) Multi-objective parametric optimization on machining with wire electric discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-011-3833-1
Bhattacharya A, Batish A, Singh G, Singla VK (2012) Optimal parameter settings for rough and finish machining of die steels in powder-mixed EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61:537–548
Puertas I, Luis CJ (2012) Optimization of EDM conditions in the manufacturing process of B4C and WC-Co conductive ceramics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 59:575–582
Shrivastava PK, Dubey AK (2012) Intelligent modeling and multi-objective optimization of electric discharge diamond grinding. Mater Manuf Process. doi:10.1080/10426914.2012.700153
Baraskar SS, Banwait SS, Laroiya SC (2012) Multi-objective optimization of electrical discharge machining process using hybrid method. Mater Manuf Process. doi:10.1080/10426914.2012.700152
Mukherjee R, Chakraborty S (2012) Selection of EDM process parameters using biogeography-based optimization algorithm. Mater Manuf Process 27:954–962
Shahali H, Yazdi MRS, Mohammadi A, Limanian E (2012) Optimization of surface roughness and thickness of white layer in wire electrical discharge machining of DIN 1.4542 stainless steel using micro-genetic algorithm and signal to noise ratio techniques. J Eng Manuf 226(5):803–812
Jain NK, Jain VK, Deb K (2007) Optimization of process parameters of mechanical type advanced machining processes using genetic algorithms. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 47:900–919
Jegaraj JJR, Babu NR (2007) A soft computing approach for controlling the quality of cut with abrasive waterjet cutting system experiencing orifice and focusing tube wear. J Mater Process Technol 185:217–227
Srinivasu DS, Babu NR (2008) A neuro-genetic approach for selection of process parameters in abrasive waterjet cutting considering variation in diameter of focusing nozzle. Appl Soft Comput 8:809–819
Caydas U, Hascalik A (2008) A study on surface roughness in abrasive water jet machining process using artificial neural networks and regression analysis method. J Mater Process Technol 202:574–582
Tsai FC, Yan BH, Kuan CY, Huang FY (2008) A Taguchi and experimental investigation into the optimal processing conditions for the abrasive jet polishing of SKD61 mold steel. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 48:932–945
Rao RV, Pawar PJ, Davim JP (2010) Optimization of process parameters of mechanical type advanced machining processes using a simulated annealing algorithm. Int J Mater Prod Technol 37(1/2):83–101
Zain AM, Haron H, Sharif S (2011) Estimation of the minimum machining performance in the abrasive waterjet machining using integrated ANN-SA. Expert Syst Appl 38:8316–8326
Zain AM, Haronb H, Sharif S (2011) Optimization of process parameters in the abrasive waterjet machining using integrated SA–GA. Appl Soft Comput 11:5350–5359
Zain AM, Haron H, Sharif S (2011) Genetic algorithm and simulated annealing to estimate optimal process parameters of the abrasive water jet machining. Eng Comput 27:251–259
Kok M, Kanca E, Eyercioglu O (2011) Prediction of surface roughness in waterjet machining of particle reinforced MMCs using genetic expression programming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 55:955–968
Ke JH, Tsai FC, Hung JC, Yang TY, Yan BH (2011) Scrap wafer regeneration by precise abrasive jet machining with novel composite abrasive for design of experiments. J Eng Manuf 225(6):881–890
Wenjun G, Jianming W, Gao N (2011) Numerical simulation for abrasive water jet machining based on ALE algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 53:247–253
Kechagias J, Petropoulos G, Vaxevanidis N (2011) Application of Taguchi design for quality characterization of abrasive water jet machining of TRIP sheet steels. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-011-3815-3
Iqbal A, Dar NU, Hussain G (2011) Optimization of abrasive water jet cutting of ductile materials. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed 26(1):88–92
Pawar PJ, Rao RV (2012) Parameter optimization of machining processes using teaching–learning-based optimization algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4524-2
Vundavilli PR, Parappagoudar MB, Kodali SP, Benguluri S (2012) Fuzzy logic-based expert system for prediction of depth of cut in abrasive water jet machining process. Knowl Based Syst 27:456–464
Jadoun RS, Kumar P, Mishra BK, Mehta RCS (2006) Optimization of process parameters for ultrasonic drilling of advanced engineering ceramics using the Taguchi approach. Eng Optim 38(7):771–787
Jadoun RS, Kumar P, Mishra BK, Mehta RCS (2006) Manufacturing process optimization for tool wear rate in ultrasonic drilling of engineering ceramics using the Taguchi method. Int J Mach Mach Mater 1:94–114
Jadoun RS, Kumar P, Mishra BK, Mehta RCS (2007) Optimisation of MRR in ultrasonic drilling (USD) based on Taguchi’s robust design methodology. Int J Mach Mach Mater 1(4):445–462
Jadoun RS, Kumar P, Mishra BK (2009) Taguchi’s optimization of process parameters for production accuracy in ultrasonic drilling of engineering ceramics. Prod Eng Res Devel 3:243–253
Dvivedi A, Kumar P (2007) Surface quality evaluation in ultrasonic drilling through the Taguchi technique. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34:131–140
Singh R, Khamba JS (2007) Taguchi technique for modeling material removal rate in ultrasonic machining of titanium. Mater Sci Eng A 460–461:365–369
Singh R, Khamba JS (2009) Mathematical modeling of tool wear rate in ultrasonic machining of titanium. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 43:573–580
Kumar V, Khamba JS (2009) Parametric optimization of ultrasonic machining of Co-based super alloy using the Taguchi multi-objective approach. Prod Eng Res Devel 3:417–425
Kumar J, Khamba JS, Mohapatra SK (2009) Investigating and modeling tool-wear rate in the ultrasonic machining of titanium. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 41:1107–1117
Kumar J, Khamba JS (2010) Modeling the material removal rate in ultrasonic machining of titanium using dimensional analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 48:103–119
Singh J, Gill SS (2009) Fuzzy modeling and simulation of ultrasonic drilling of porcelain ceramic with hollow stainless steel tools. Mater Manuf Process 24:468–475
Gill SS, Singh J (2009) Modelling of material removal rate in ultrasonic drilling of alumina ceramic by fuzzy logic. Int J Mechatronics Manuf Syst 2(5/6):552–565
Gill SS, Singh J (2010) An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system modeling for material removal rate in stationary ultrasonic drilling of sillimanite ceramic. Expert Syst Appl 37:5590–5598
Rao RV, Pawar PJ, Davim JP (2010) Parameter optimization of ultrasonic machining process using nontraditional optimization algorithms. Mater Manuf Process 25(10):1120–1130
Liu Y, Zhao Z, Li S, Li Y (2011) Processing parameters’ multi-objective optimization for compound machining with ultrasonic vibration on SiC monocrystal. Procedia Eng 15:777–782
Gauri SK, Chakravorty R, Chakraborty S (2011) Optimization of correlated multiple responses of ultrasonic machining (USM) process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 53:1115–1127
Sarkar BR, Doloi B, Bhattacharyya B (2006) Parametric analysis on electrochemical discharge machining of silicon nitride ceramics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28:873–881
Mediliyegedara TKKR, DeSilva AKM, Harrison DK, McGeough JA, Hepburn D (2006) Designing steps and simulation results of a pulse classification system for the electro chemical discharge machining (ECDM) process – An artificial neural network approach. Adv Soft Comput 34:343–352
Jain NK, Jain VK (2007) Optimization of electro-chemical machining process parameters using genetic algorithms. Mach Sci Technol 11:235–258
Rao RV, Pawar PJ, Shankar R (2008) Multi-objective optimization of electrochemical machining process parameters using a particle swarm optimization algorithm. J Eng Manuf 222(8):949–958
Asokan P, Kumar RR, Jeyapaul R, Santhi M (2008) Development of multi-objective optimization models for electrochemical machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39:55–63
Chak SK, Rao PV (2008) The drilling of Al2O3 using a pulsed DC supply with a rotary abrasive electrode by the electrochemical discharge process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39:633–641
Senthilkumar C, Ganesan G, Karthikeyan R (2009) Study of electrochemical machining characteristics of Al/SiCp composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 43:256–263
Senthilkumar C, Ganesan G, Karthikeyan R (2010) Bi-performance optimization of electrochemical machining characteristics of Al/20%SiCp composites using NSGA-II. J Eng Manuf 224(9):1399–1407
Senthilkumar C, Ganesan G, Karthikeyan R (2011) Parametric optimization of electrochemical machining of Al/15 % SiCp composites using NSGA-II. Trans Non-ferrous Met Soc China 21:2294–2300
Ramarao S, Sravan CRM, Ranga VP, Padmanabhan G (2009) Fuzzy logic-based forward modeling of electro chemical machining process. World Congress on Nature & Biologically Inspired Computing, IEEE 1431–1435
Datta D, Das AK (2010) Tuning process parameters of electrochemical machining using a multi-objective genetic algorithm: A preliminary study. SEAL, LNCS 6457:485–493
Li ZY, Niu ZW (2010) Process parameter optimization and experiment study of aero-engine blade in electrochemical machining. Adv Mater Res 135:418–423
Samanta S, Chakraborty S (2011) Parametric optimization of some non-traditional machining processes using artificial bee colony algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell 24:946–957
Chakradhar D, Venugopal A (2011) Multi-objective optimization of electrochemical machining of EN31 steel by grey relational analysis. Int J Model Optim 1(2):113–117
Rao RV, Kalyankar VD (2011) Parameters optimization of advanced machining processes using TLBO algorithm. Int Conf on Engineering, Project, and Production Management, Singapore 21–31
Panda MC, Yadava V (2012) Intelligent modeling and multiobjective optimization of die sinking electrochemical spark machining process. Mater Manuf Process 27:10–25
Abuzied HH, Awad MA, Senbel HA (2012) Prediction of electrochemical machining process parameters using artificial neural networks. Int J Comput Sci Eng 4:125–132
Mukherjee R, Chakraborty S (2012) Selection of the optimal electrochemical machining process parameters using biogeography-based optimization algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4060-0
Kuar AS, Doloi B, Bhattacharyya B (2006) Modelling and analysis of pulsed Nd:YAG laser machining characteristics during micro-drilling of zirconia (ZrO2). Int J Mach Tool Manuf 46:1301–1310
Chang CW, Kuo CP (2007) Evaluation of surface roughness in laser-assisted machining of aluminium oxide ceramics with Taguchi method. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 47:141–147
Campanelli SL, Ludovico AD, Bonserio C, Cavalluzzi P, Cinquepalmi M (2007) Experimental analysis of the laser milling process parameters. J Mater Process Technol 191:220–223
Dhupal D, Doloi B, Bhattacharyya B (2007) Optimization of process parameters of Nd:YAG laser micro grooving of Al2TiO5 ceramic material by response surface methodology and artificial neural network algorithm. J Eng Manuf 221(8):1341–1350
Dhupal D, Doloi B, Bhattacharyya B (2008) Parametric analysis and optimization of Nd:YAG laser micro-grooving of aluminum titanate (Al2TiO5) ceramics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36:883–893
Dhupal D, Doloi B, Bhattacharyya B (2009) Modeling and optimization on Nd:YAG laser turned micro-grooving of cylindrical ceramic material. Opt Lasers Eng 47:917–925
Dhara SK, Kuar AS, Mitra S (2008) An artificial neural network approach on parametric optimization of laser micro-machining of die-steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39:39–46
Ghoreishi M, Nakhjavani OB (2008) Optimisation of effective factors in geometrical specifications of laser percussion drilled holes. J Mater Process Technol 196:303–310
Samant AN, Paital SR, Dahotre NB (2008) Process optimization in laser surface structuring of alumina. J Mater Process Technol 203:498–504
Karazi SM, Issa A, Brabazon D (2009) Comparison of ANN and DoE for the prediction of laser-machined micro-channel dimensions. Opt Lasers Eng 47:956–964
Ciurana J, Arias G, Ozel T (2009) Neural network modeling and particle swarm optimization (PSO) of process parameters in pulsed laser micromachining of hardened AISI H13 steel. Mater Manuf Process 24:358–368
Biswas R, Kuar AS, Sarkar S, Mitra S (2010) A parametric study of pulsed Nd:YAG laser micro-drilling of gamma-titanium aluminide. Opt Laser Technol 42:23–31
Biswas R, Kuar AS, Biswas SK, Mitra S (2010) Effects of process parameters on hole circularity and taper in pulsed Nd:YAG laser microdrilling of Tin-Al2O3 composites. Mater Manuf Process 25:503–514
Biswas R, Kuar AS, Biswas SK, Mitra S (2010) Artificial neural network modelling of Nd:YAG laser microdrilling on titanium nitride-alumina composite. J Eng Manuf 224(3):473–482
Panda S, Mishra D, Biswal BB (2011) Determination of optimum parameters with multi-performance characteristics in laser drilling—a grey relational analysis approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 54:957–967
Kasman S, Saklakoglu IE (2012) Determination of process parameters in the laser micromilling application using Taguchi method: a case study for AISI H13 tool steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 58:201–209
Ganguly D, Acherjee B, Kuar AS, Mitra S (2012) Hole characteristics optimization in Nd:YAG laser micro-drilling of zirconium oxide by grey relation analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61:1255–1262
Kibria G, Doloi B, Bhattacharyya B (2012) Predictive model and process parameters optimization of Nd:YAG laser micro-turning of ceramics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4161-9
Teixidor D, Ferrer I, Ciurana J, Ozel T (2012) Optimization of process parameters for pulsed laser milling of micro-channels on AISI H13 tool steel. Rob Comput Integr Manuf. doi:10.1016/j.rcim.2012.05.005
Canel T, Kaya AU, Celik B (2012) Parameter optimization of nanosecond laser for microdrilling on PVC by Taguchi method. Opt Laser Technol 44:2347–2353
Ghosal A, Manna A (2012) Response surface method based optimization of ytterbium fiber laser parameter during machining of Al/Al2O3-MMC. Opt Laser Technol. doi:10.1016/j.optlastec.2012.04.030
Padhee S, Pani S, Mahapatra SS (2012) A parametric study on laser drilling of Al/SiCp metal-matrix composite. J Eng Manuf 226(1):76–91
Kuar AS, Acherjee B, Ganguly D, Mitra S (2012) Optimization of Nd:YAG laser parameters for microdrilling of alumina with multiquality characteristics via grey–Taguchi method. Mater Manuf Process 27:329–336
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, R.V., Kalyankar, V.D. Optimization of modern machining processes using advanced optimization techniques: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73, 1159–1188 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5894-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5894-4