Abstract
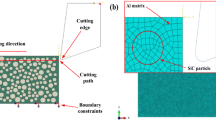
The surface quality of SiC particle-reinforced aluminum matrix (SiCp/Al) composite plays an important role in their practical performance. Therefore, an in-depth understanding of the defect formation mechanism paves the solid foundation for the improvement of machined surface quality, which is the prerequisite for the widespread application of SiCp/Al materials. In this paper, the geometrical analysis of milling process was conducted firstly. Then, two-dimensional meso-scale finite element models composed of hard SiC particles and soft aluminum matrix were established for investigating the milling process of the SiCp/Al composite. Both a randomly distributed circular SiC particles model and a polygon SiC particles model were built respectively with high volume fraction. The simulation result indicated that the rotation, pulling out, big cleavage, micro fracture, and cutting through of the SiC were the main defect formation mechanisms. The simulated machined surface morphology was compared with the profile of a milled surface, and a good correlation was obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y, Ramesh KT, Chin ESC (2007) Plastic deformation and failure in A359 aluminum and an A359–SiCp MMC under quasistatic and high-strain-rate tension. J Compos Mater 41:27–40
Manna A, Bhattacharayya B (2005) Influence of machining parameters on the machinability of particulate reinforced Al/SiC–MMC. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25:850–856
Ozben T, Kilickap E, Cakir O (2008) Investigation of mechanical and machinability properties of SiC particle reinforced Al-MMC. J Mater Process Technol 198:220–225
Wang T, Xie LJ, Wang XB (2013) Surface integrity of high speed milling of Al/SiC/65p aluminum matrix composites. Procedia CIRP 8:475–480
Pramanik A, Zhang LC, Arsecularatne JA (2008) Machining of metal matrix composites: effect of ceramic particles on residual stress, surface roughness and chip formation. Int J Mach Tool Manu 48:1613–1625
Chan KC, Cheung CF, Ramesh MV, Lee WB, To S (2001) A theoretical and experimental investigation of surface generation in diamond turning of an Al6061/SiCp metal matrix composite. Int J Mech Sci 43:2047–2068
El-Gallab M, Sklad M (1997) Machining of Al/SiC particulate metal matrix composites part II: workpiece surface integrity. J Mater Process Technol 83:277–285
Ge YF, Xu JH, Yang H, Luo SB, Fu YC (2008) Workpiece surface quality when ultra-precision turning of SiCpAl composites. J Mater Process Technol 203:166–175
Dandekar CR, Shin YC (2012) Modeling of machining of composite materials: a review. Int J Mach Tool Manu 57:102–121
Monaghan J, Brazil D (1998) Modelling the flow processes of a particle reinforced metal matrix composite during machining. Compos Part A 29:87–99
Monaghan J, Brazil D (1997) Modeling the sub-surface damage associated with the machining of a particle reinforced MMC. Comp Mater Sci 9:99–107
Ramesh MV, Chan KC, Lee WB, Cheung CF (2001) Finite-element analysis of diamond turning of aluminium matrix composites. Compos Sci Technol 61:1449–1456
Zhu Y, Kishawy HA (2005) Influence of alumina particles on the mechanics of machining metal matrix composites. Int J Mach Tool Manu 45:389–398
Pramanik A, Zhang LC, Arsecularatne JA (2007) An FEM investigation into the behavior of metal matrix composites tool–particle interaction during orthogonal cutting. Int J Mach Tool Manu 47:1497–1506
Dandekar CR, Shin YC (2009) Multi-step 3-D finite element modeling of subsurface damage in machining particulate reinforced metal matrix composites. CompPart A 40:1231–1239
Zhou L, Huang ST, Wang D, Yu XL (2011) Finite element and experimental studies of the cutting process of SiCp/Al composites with PCD tools process of SiCp/Al composites with PCD tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 52:619–626
Fathipour M, Zoghipour P, Tarighi J, Yousefi R (2012) Investigation of reinforced Sic particles percentage on machining force of metal matrix composite. Mod Appl 6:9–20
Fathipour M, Hamedi M, Yousefi R (2013) Numerical and experimental analysis of machining of Al (20 vol% SiC) composite by the use of ABAQUS software. Mater Sci & Eng Technol 44:14–20
Hibbitt, Karlsson, Sorensen (2001) BAQUS/Explicit: user’s manual. Hibbitt, Karlsson and Sorensen Incorporated
Kan Y, Liu YK, Zhang SH, Zhang LW, Cheng M, Song HW (2013) Microstructure-based numerical simulation of the tensile behavior of SiC/Al composites. J Mater Eng Perform 23:1069–1076
Bian R, He N, Li L, Zhan ZB, Wu Q, Shi ZY (2013) Precision milling of high volume fraction SiCp/Al composites with monocrystalline diamond end mill. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71:411–419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Xie, L. & Wang, X. Simulation study on defect formation mechanism of the machined surface in milling of high volume fraction SiCp/Al composite. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79, 1185–1194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6876-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6876-x