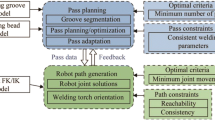
Abstract
In robotic welding, the planning and generation of the motion of the welding torch are crucial in welding complex joints. This paper presents an approach for optimal robot path planning of the centroid pass in welding a Y-joint. Relevant data associated with the welding passes is defined and managed to facilitate robot path planning and generation. With properly selected welding torch inclination angles and welding pass segmentation techniques, a solution space containing a number of robot paths is generated to account for functional redundancy and different welding robot configurations. A solution with minimum joint movement is determined using a beam search algorithm as the optimal robot path for each welding pass segment. A case study of robot path planning of the centroid pass of a scaled-down Y-joint is simulated and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin W, Luo H (2015) Robotic welding. In: Nee AYC (ed) Springer handbook of manufacturing engineering and technology: robotics and automation. Springer-Verlag, London, pp. 2404–2444
Ang MH Jr, Lin W, Lim SY (1999) A walk-through programmed robot for welding in shipyards. Ind Robot: An Int J 26(5):377–388
Chen CL, Hu SS, He DL, Shen JQ (2013) An approach to the path planning of tube–sphere intersection welds with the robot dedicated to J-groove joints. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 29(4):41–48
Shi L, Tian XC (2015) Automation of main pipe-rotating welding scheme for intersecting pipes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 77(5):955–964
Shi L, Tian XC, Zhang CH (2015) Automatic programming for industrial robot to weld intersecting pipes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 81(9):2099–2107
Pires JN, Loureiro A, Bölmsjo G (2006) Welding robots: technology, system issues and application. Springer-Verlag Limited, London
Mavrikios D, Karabatsou V, Fragos D, Chryssolouris G (2006) A prototype virtual reality-based demonstrator for immersive and interactive simulation of welding processes. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 19(3):294–300
Liu ZY, Bu WH, Tan JR (2010) Motion navigation for arc welding robots based on feature mapping in a simulation environment. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 26(2):137–144
Tsai MJ, Lin S-D, Chen M-C (1992) Mathematical model for robotic arc-welding off-line programming system. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 5(4–5):300–309
Yang CD, Ye Z, Chen YX, Zhong JY, Chen SB (2014) Multi-pass path planning for thick plate by DSAW based on vision sensor. Sens Rev 34(4):416–423
Chen SB, Chen XZ, Qiu T, Li JQ (2005) Acquisition of weld seam dimensional position information for arc welding robot based on vision computing. J Intell Robot Syst 43(1):77–97
Chen XZ, Huang YM, Chen SB (2012) Model analysis and experimental technique on computing accuracy of seam spatial position information based on stereo vision for welding robot. Ind Robot: An Int J 39(4):349–356
He YS, Xu YL, Chen YX, Chen HB, Chen SB (2016) Weld seam profile detection and feature point extraction for multi-pass route planning based on visual attention model. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 37(2):251–261
Zhang HJ, Lu HZ, Cai CB, Chen SB (2010) Robot path planning in multi-pass weaving welding for thick plates. In: Tarn TJ, Chen SB, Fang G (eds) Robotic welding, intelligence and automation (LNEE 88). Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 351–359
Xiong J, Zhang GJ, Hu JW, Wu L (2014) Bead geometry prediction for robotic GMAW-based rapid manufacturing through a neural network and a second-order regression analysis. J Intell Manuf 25(1):157–163
Lin H-L (2012) The use of the Taguchi method with grey relational analysis and a neural network to optimize a novel GMA welding process. J Intell Manuf 23(5):1671–1680
Chen HT, Li HC, Gao HM, Wu L (2015) Study on path planning and compensation of off-line programming for thick walled curve welding. China Weld 24(4):69–73
Yan, S.J., Ong, S.K., Nee, A.Y.C. (2016) Optimal pass planning for robotic welding of large-dimension joints with deep grooves, In: Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Digital Enterprise Technology (DET2016)—Intelligent Manufacturing in the Knowledge Economy Era, 29–31 March 2016, Nanjing, China.
Ahmed, S.M., Yuan, J.Q., Wu, Y., Chew, C.M., Pang, C.K. (2015) Collision-free path planning for multi-pass robotic welding, In: Proceedings of 2015 I.E. 20th Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, 8–11 September 2015, Luxembourg.
Huo L, Baron L (2008) The joint-limits and singularity avoidance in robotic welding. Ind Robot: An Int J 35(5):456–464
Huo L, Baron L (2011) The self-adaptation of weights for joint-limits and singularity avoidances of functionally redundant robotic-task. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 27(2):367–376
Ogbemhe J, Mpofu K (2015) Towards achieving a fully intelligent robotic arc welding: a review. Ind Robot: An Int J 42(5):475–484
Yahşi OS, Özgören K (1984) Minimum joint motion optimization of manipulators with extra degrees of freedom. Mech Mach Theory 19(3):325–330
Rampaul H (2002) Pipe welding procedure, 2nd edn. Industrial Press, New York
Hayes MJD, Husty ML, Zsombor-Murray PJ (2002) Singular configurations of wrist-partitioned 6R serial robots: a geometric perspective for users. Trans Can Soc Mech Eng 26(1):41–55
Chong JWS, Ong SK, Nee AYC, Youcef-Youmi K (2009) Robot programming using augmented reality: an interactive method for planning collision-free paths. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 25(3):689–701
Hornung A, Wurm KM, Bennewitz M, Stachniss C, Burgard W (2013) OctoMap: an efficient probabilistic 3D mapping framework based on octrees. Auton Robot 34(3):189–206
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, H., Ong, S. & Nee, A. Robot path planning optimization for welding complex joints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90, 3829–3839 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9684-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9684-z